Steering Hydraulic Cylinder for Mast Type Aerial Work Platform
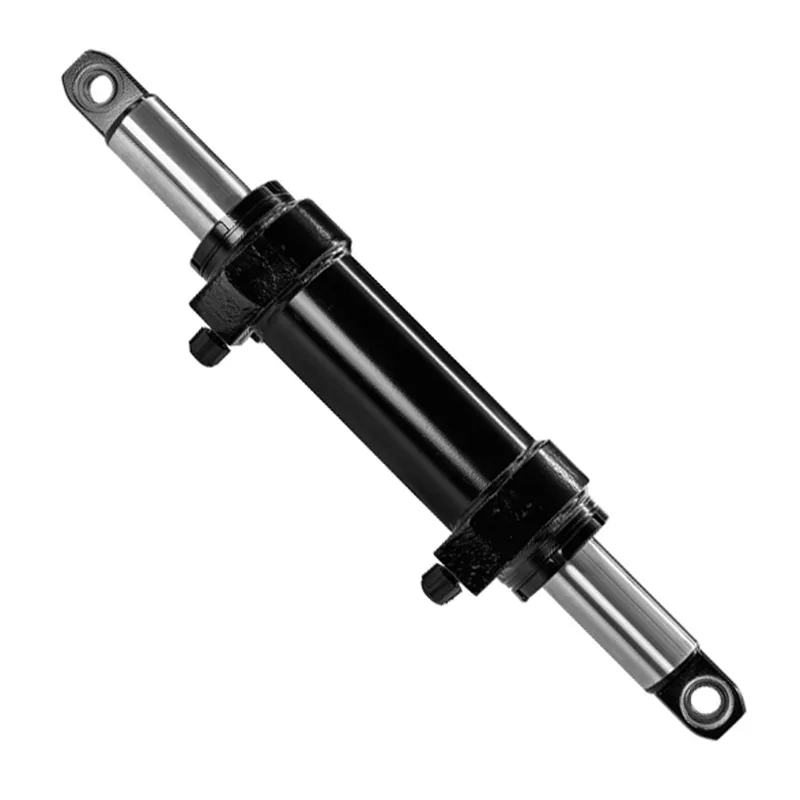
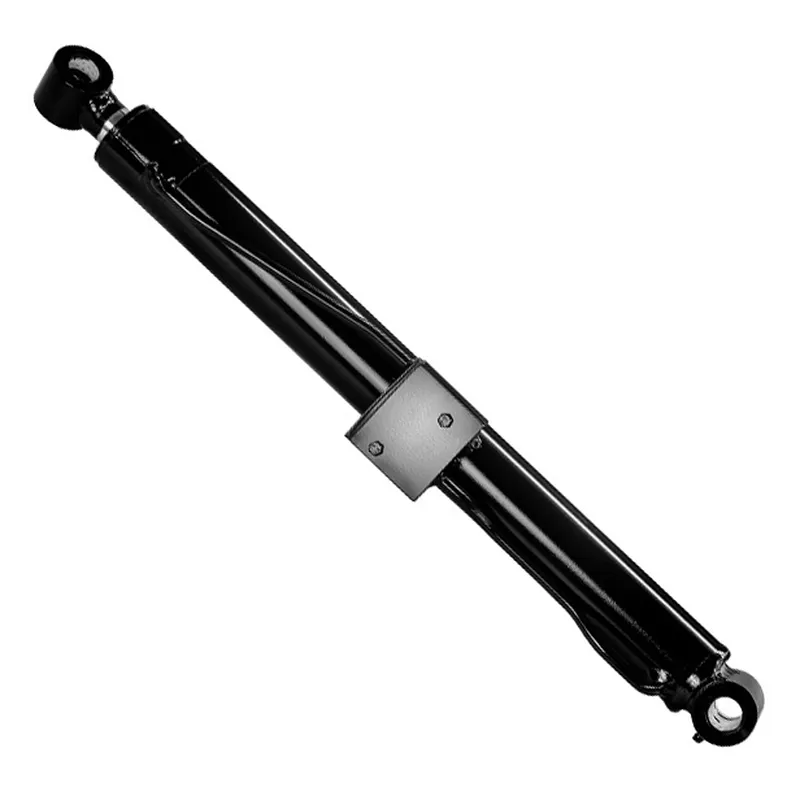
A steering hydraulic cylinder for a mast type aerial work platform (AWP) is a critical component designed to facilitate precise and controlled steering of the platform, ensuring maneuverability in confined or complex work environments. This double-acting hydraulic cylinder converts pressurized hydraulic fluid into linear motion, driving the steering mechanism to position the platform accurately.
A steering hydraulic cylinder for a mast type aerial work platform (AWP) is a critical component designed to facilitate precise and controlled steering of the platform, ensuring maneuverability in confined or complex work environments. This double-acting hydraulic cylinder converts pressurized hydraulic fluid into linear motion, driving the steering mechanism to position the platform accurately.
Typically constructed from durable materials like steel or aluminum, it features a piston, rod, seals, and a cylinder body. The hydraulic steering cylinder’s design ensures smooth, responsive steering, enhancing safety and efficiency during high-altitude operations, such as maintenance or construction tasks, by allowing operators to navigate tight spaces effectively.
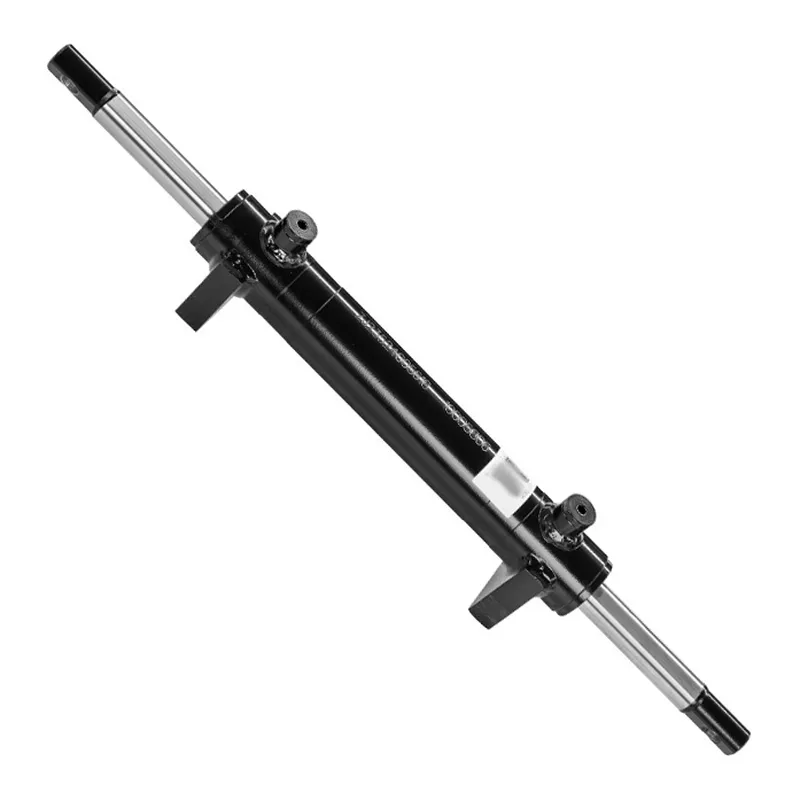

Steering Hydraulic Cylinder Dimensions
 |
|
 |
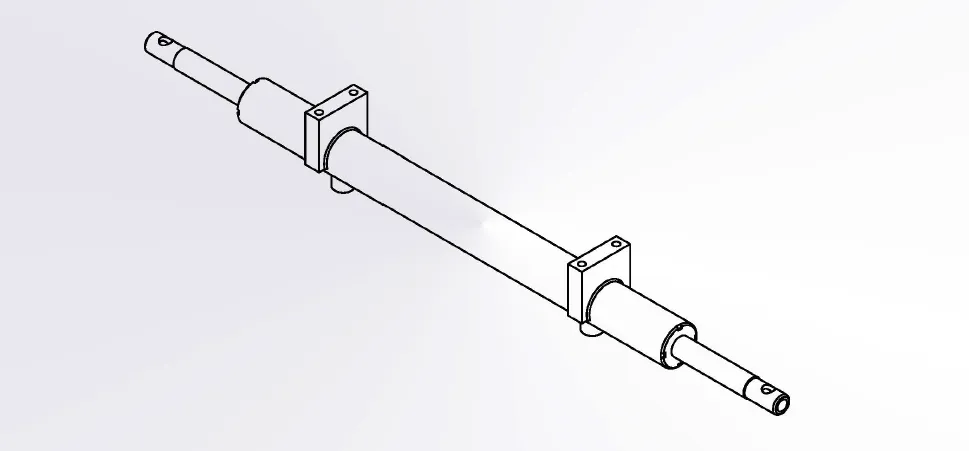 |
| Hydraulic Steering Cylinder | ||||||
| Cylinder model | Specifications | Working pressure | Maximum withstand pressure | Trip | Installation distance | Weight |
| CMNYY11112007 | Φ40xΦ25x100x2 | 10MPa | 15MPa | 100X2 | 645 | 7kg |
| Product Name: | Steering Hydraulic Cylinder |
| Function: | Implement steering axle action and tire steering. |
| Cylinder diameter: | 40mm-50mm |
| Rod diameter: | 20mm-30mm |
| Travel: | 140mm-250mm |
| Maximum pressure: | 20MPa |
| Maximum thrust: | 39KN |
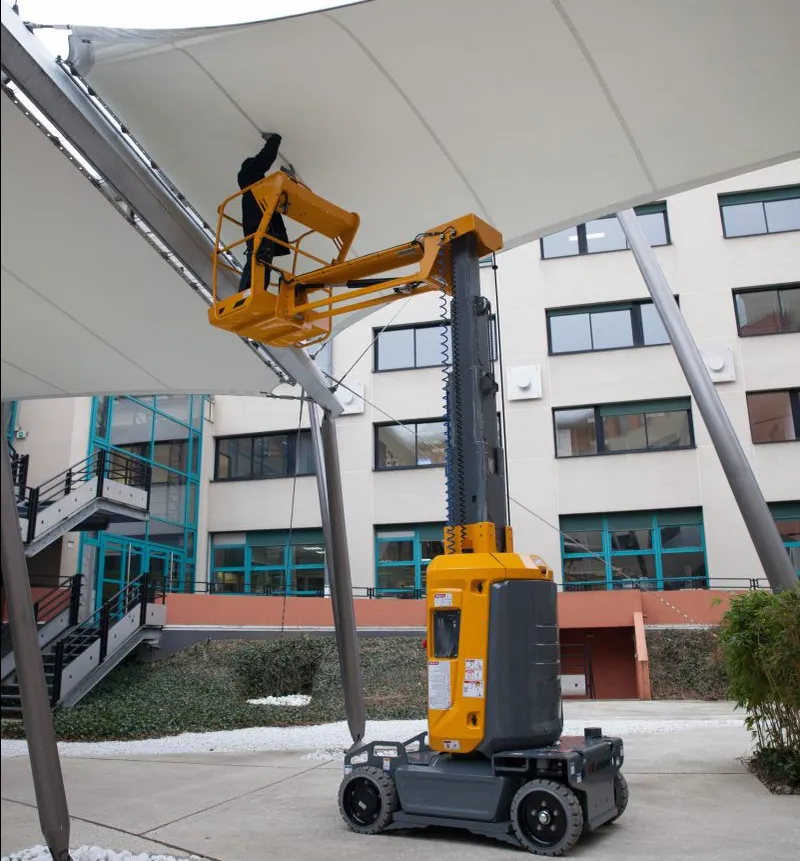
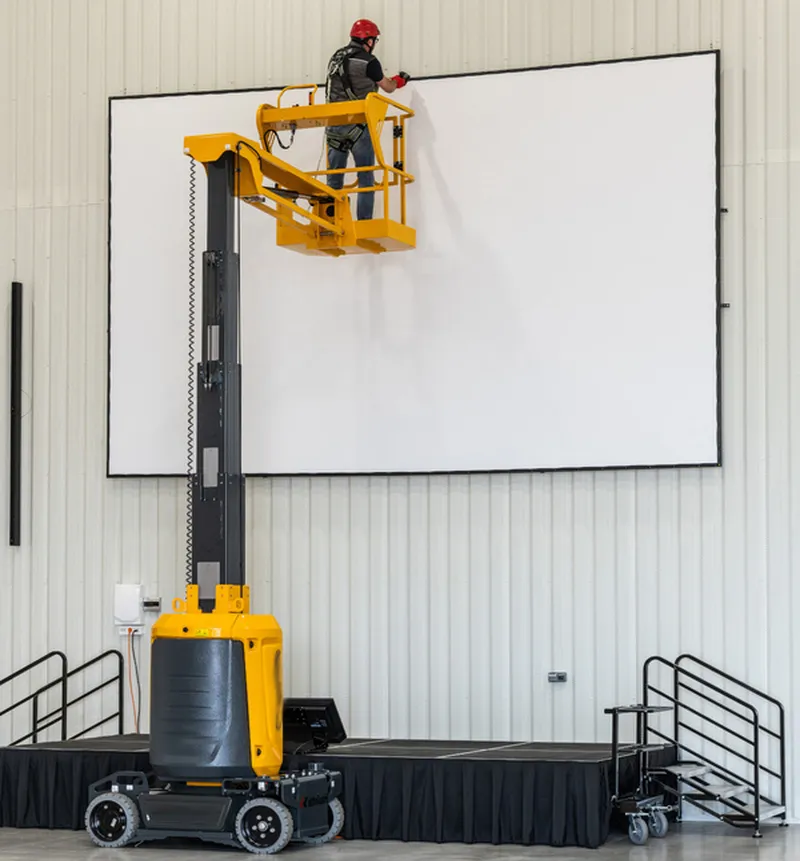
Mast Type Aerial Work Platform Hydraulic Cylinder Types
- Hydraulic Steering Cylinders
Hydraulic steering cylinders are essential for controlling the directional movement of mast-type aerial work platforms. These cylinders convert hydraulic pressure into linear motion, assisting in the smooth and precise steering of the platform. Built from durable materials, they are designed to handle heavy loads and ensure reliable operation in tight spaces or challenging environments. Their ability to provide accurate directional control enhances safety and efficiency during maneuvers. - Hydraulic Lifting Cylinders
Hydraulic lifting cylinders are responsible for the vertical movement of the mast-type aerial work platform. These cylinders generate the lifting force required to raise and lower the platform by pressurizing hydraulic fluid. They are engineered to handle substantial loads while maintaining stability and smooth operation at various heights. Properly functioning lifting cylinders are critical to ensuring the safety of workers and the overall reliability of the platform. - Hydraulic Swing Rod Cylinders
Hydraulic swing rod cylinders allow the mast-type aerial work platform to perform rotational or swinging movements. These cylinders use hydraulic power to move swing rods, enabling the platform to reach extended positions effectively. They are designed for precision and durability, ensuring smooth rotational action even under heavy-duty conditions. This capability improves the platform's overall flexibility and operational range in confined or elevated workspaces.
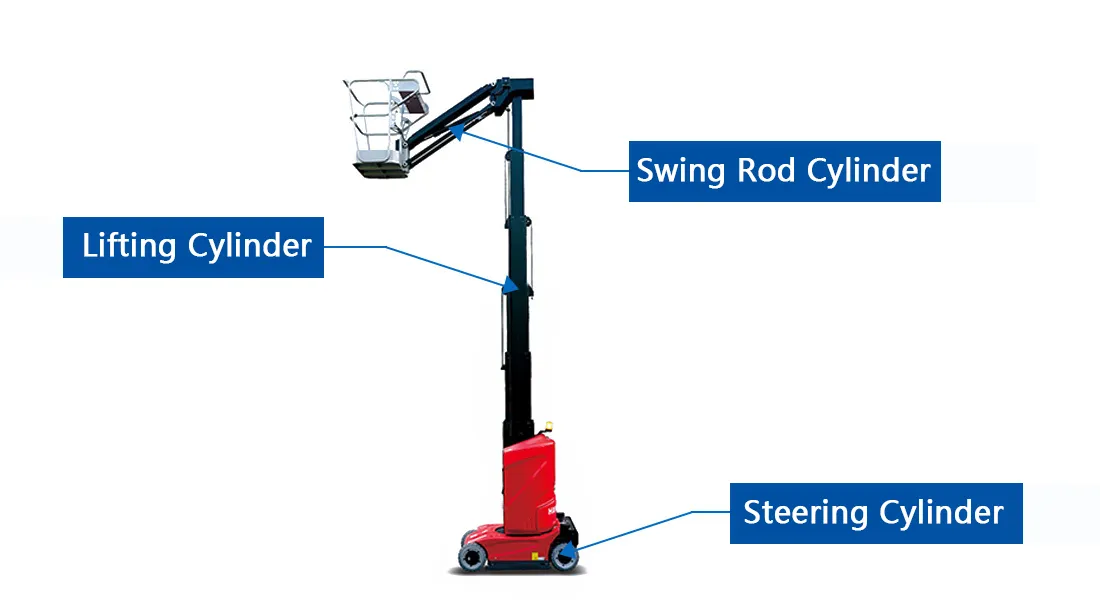

Mast Type Aerial Work Platform Hydraulic Steering Cylinder Features
- High Precision Control
The hydraulic steering cylinder ensures precise directional control by converting hydraulic fluid pressure into smooth linear motion, allowing operators to navigate tight spaces with accuracy, enhancing safety and efficiency during high-altitude tasks on mast-type aerial work platforms. - Robust Construction
Built with high-strength materials like steel or aluminum, the steering cylinder features a durable piston, rod, and high-quality seals, designed to withstand pressures up to 20MPa, ensuring long-term reliability under demanding operational conditions. - Compact Design
The steering hydraulic cylinder’s compact structure, with typical diameters of 40mm–50mm and stroke lengths of 140mm-250mm, optimizes space on the platform, enabling efficient integration into the steering system without compromising performance or maneuverability. - Leak-Proof Sealing System
Advanced sealing technology prevents hydraulic fluid leaks, maintaining consistent pressure and performance while reducing maintenance needs and ensuring safe operation in high-altitude environments, even during extended or intensive steering tasks. - High Load Capacity
Engineered to handle significant steering forces, the hydraulic cylinder for steering supports the platform’s weight and dynamic loads, ensuring stable and responsive steering, critical for safe navigation in construction or maintenance applications. - Corrosion Resistance
Coated with anti-corrosive materials or finishes, the hydraulic steering cylinders resist environmental wear from moisture, dust, or chemicals, extending their lifespan and maintaining functionality in harsh outdoor conditions typical of aerial work platform operations.
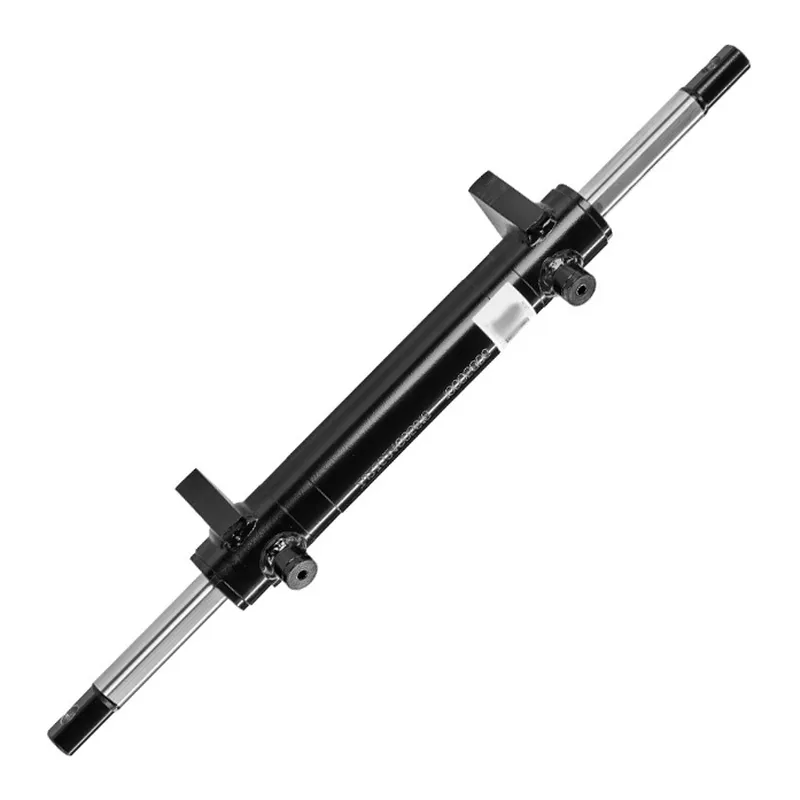

Mast Type Aerial Work Platform Steering Hydraulic Cylinder Troubleshooting
- Steering Cylinder Leakage
If hydraulic fluid leaks from the steering hydraulic cylinder, inspect the seals, fittings, and hoses for damage or wear. Replace faulty seals or tighten connections to prevent further fluid loss and ensure proper pressure maintenance. - Reduced Steering Response
A sluggish or delayed steering response can indicate low hydraulic fluid levels, air in the system, or a worn piston. Check fluid levels, bleed the system to remove air, and inspect the piston for wear or damage. - Excessive Noise During Operation
Unusual noises, such as squealing or knocking, could result from contaminated hydraulic fluid, misaligned components, or internal damage. Flush the system, replace the fluid if needed, and inspect the hydraulic steering cylinder for alignment or internal wear. - Steering Cylinder Overheating
Overheating typically occurs due to excessive load, prolonged operation, or insufficient fluid flow. Check for blockages in the hydraulic lines, ensure proper fluid levels, and avoid exceeding the platform’s recommended operating limits to reduce heat buildup. - Uneven or Jerky Steering Movement
Jerky motion or uneven steering can result from air trapped in the hydraulic system, damaged seals, or improper fluid flow. Bleed the system, inspect the seals for wear, and ensure the fluid supply is unobstructed. - Cylinder Fails to Move
If the hydraulic cylinder for steering fails to function, check for hydraulic fluid blockages, damaged hoses, or a malfunctioning pump. Inspect the valve connections and ensure the hydraulic power unit is delivering adequate pressure for proper operation.
 |
 |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|




