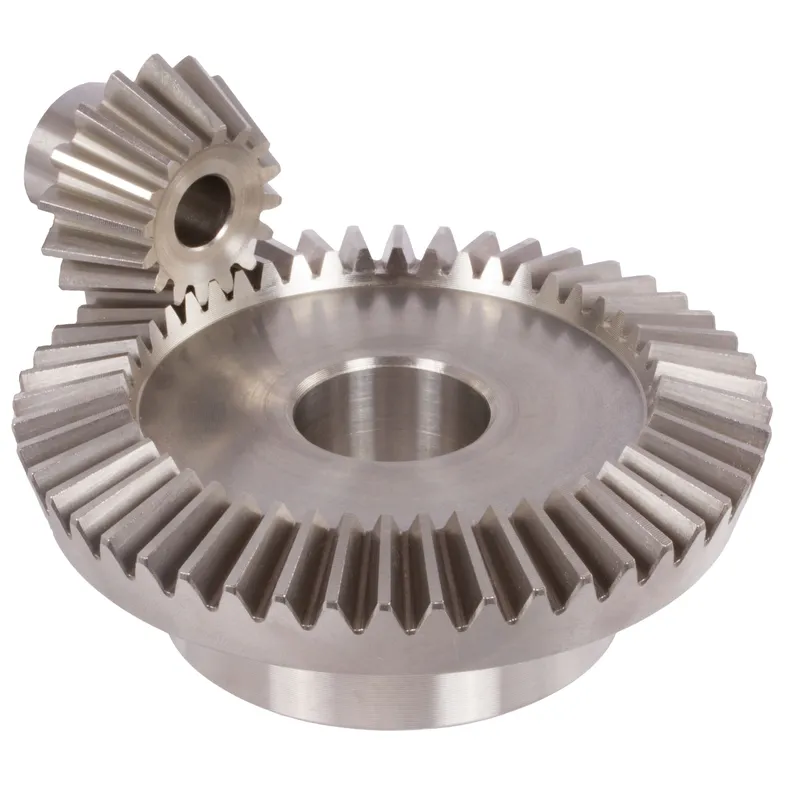
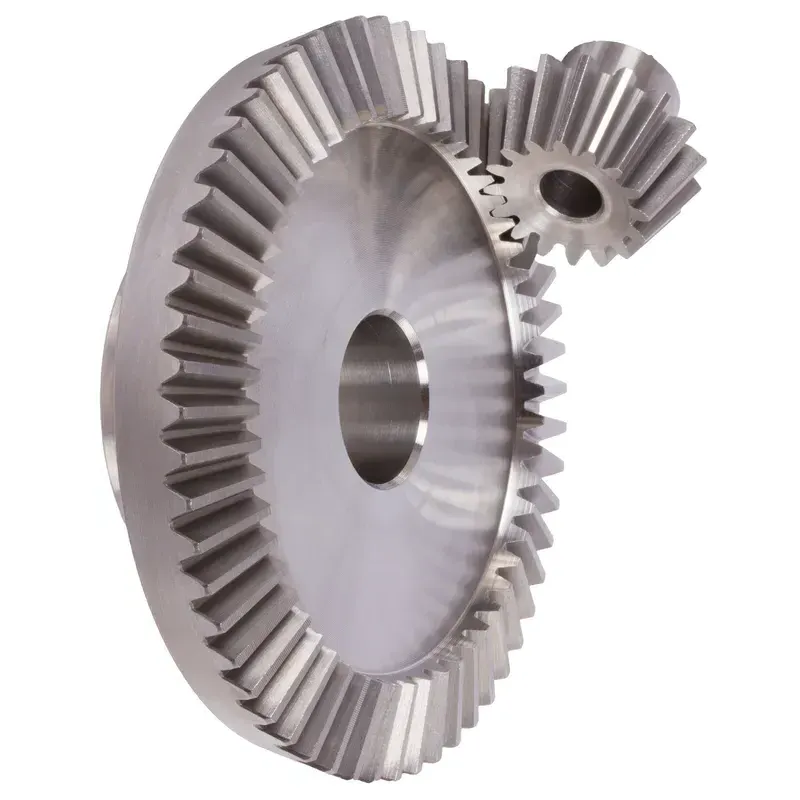
Steel Straight Bevel Gears Ratio 4:1 Straight Tooth System
The steel straight bevel gears ratio 4:1 straight tooth system refers to a specific type of mechanical gearing used to transfer motion and power between two shafts that intersect at an angle, typically 90 degrees. Bevel gears have a conical shape, and in this system, the teeth are straight rather than curved, enabling smooth and efficient transmission of torque. This straight bevel gear system is often made of steel for durability, high strength, and resistance to wear, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as industrial machinery, automotive differentials, or power tools.
The steel straight bevel gears ratio 4:1 straight tooth system refers to a specific type of mechanical gearing used to transfer motion and power between two shafts that intersect at an angle, typically 90 degrees. Bevel gears have a conical shape, and in this system, the teeth are straight rather than curved, enabling smooth and efficient transmission of torque. This straight bevel gear system is often made of steel for durability, high strength, and resistance to wear, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications such as industrial machinery, automotive differentials, or power tools.
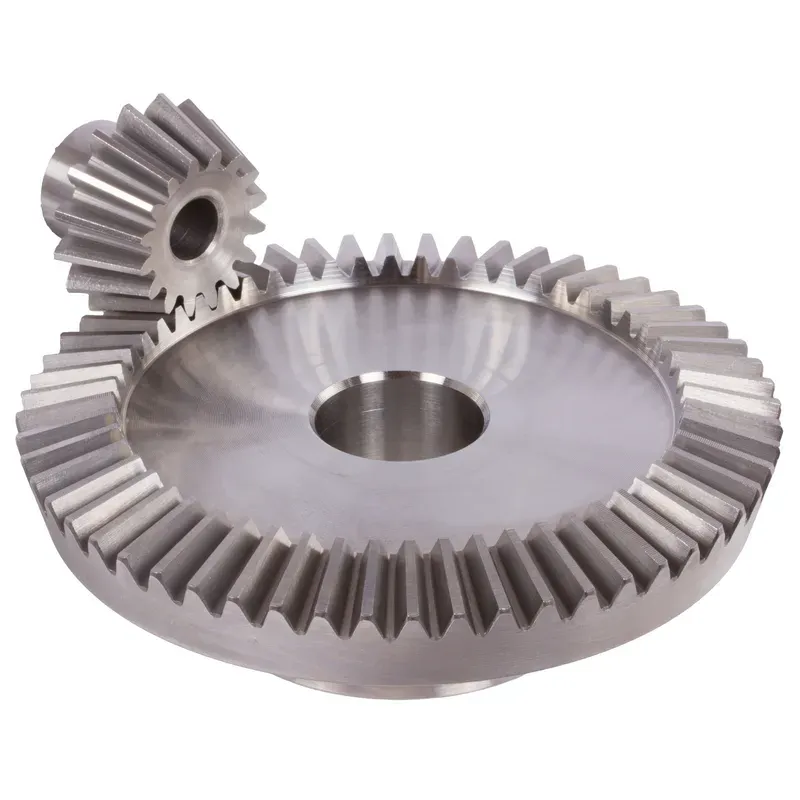

Steel Straight Bevel Gear Ratio 4:1
 | 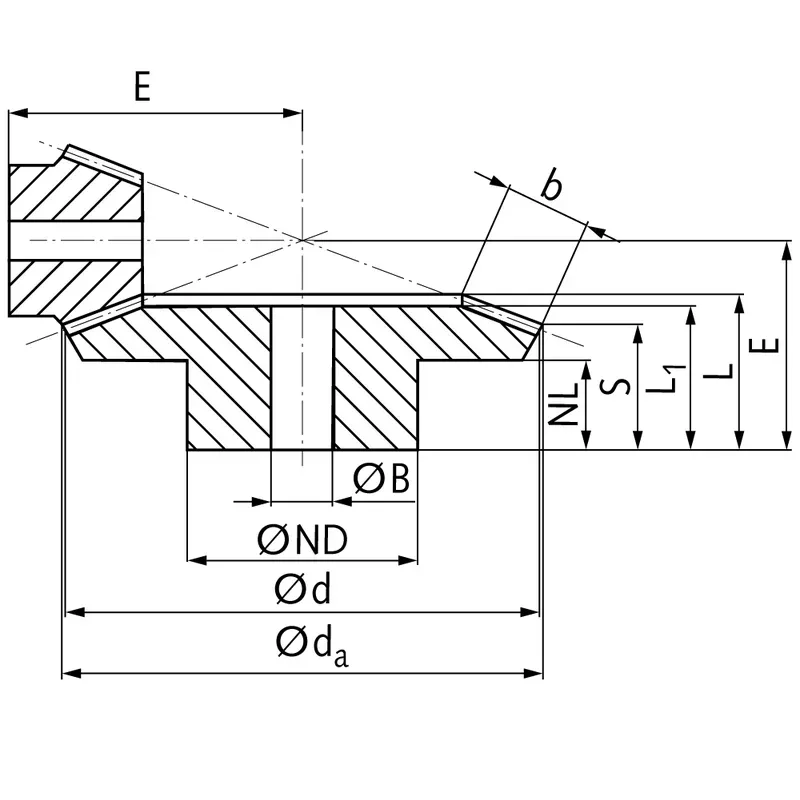 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 15 | 17,8 | 15 | 13 | 7,7 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 8,4 | 9,3 | 5 | 38 | 0,117 | 15 |
| 1 | 60 | 60,3 | 60 | 30 | 10,0 | 15 | 17,1 | 15,1 | 9,3 | 8 | 22 | 0,468 | 160 |
| 1,5 | 15 | 26,7 | 22,5 | 18 | 14,45 | 28 | 28,9 | 15,5 | 13,9 | 8 | 60 | 0,41 | 42 |
| 1,5 | 60 | 90,4 | 90 | 50 | 12,0 | 25 | 27,6 | 24,6 | 13,9 | 15 | 35 | 1,64 | 745 |
| 2 | 15 | 34,0 | 30 | 20 | 13,5 | 29 | 29,9 | 15,5 | 15 | 10 | 75 | 1,02 | 80 |
| 2 | 60 | 120,9 | 120 | 60 | 20,0 | 35 | 40,1 | 37,0 | 15 | 25 | 50 | 4,08 | 1600 |
| 2,5 | 15 | 42,5 | 37,5 | 30 | 16,1 | 35 | 36,8 | 17,6 | 20 | 10 | 92 | 5,3 | 190 |
| 2,5 | 60 | 151,2 | 150 | 80 | 18,0 | 33 | 37,8 | 33,8 | 20 | 25 | 50 | 21,2 | 2600 |
| 3 | 15 | 51,0 | 45 | 30 | 13,15 | 38 | 39,7 | 15,7 | 25 | 10 | 105 | 9,6 | 270 |
| 3 | 60 | 181,5 | 180 | 80 | 18,0 | 35 | 40,6 | 35,5 | 25 | 30 | 55 | 38,4 | 3800 |
| 4 | 15 | 68,0 | 60 | 40 | 12,5 | 43 | 44,8 | 16,0 | 30 | 20 | 135 | 21,7 | 520 |
| 4 | 60 | 242,0 | 240 | 90 | 20,0 | 41 | 50,1 | 44,0 | 30 | 30 | 70 | 86,8 | 8300 |
Steel Straight Bevel Gear Design Benefits
- High Strength and Durability
Steel straight bevel gears are made from robust materials, providing exceptional resistance to wear and tear. Their durability ensures they can handle high torque and heavy loads in demanding industrial applications over long periods. - Efficient Power Transmission
The straight tooth design allows for effective power transfer between intersecting shafts. This efficiency minimizes energy losses during operation and ensures consistent performance, making these gears suitable for critical mechanical systems. - Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Compared to spiral bevel gears, the straight tooth design is simpler to produce. This simplicity reduces manufacturing costs while still maintaining reliable performance, making them an economical choice for many mechanical systems. - Versatility in Applications
These steel bevel gears are used in a wide range of industries, from automotive systems to heavy machinery. Their ability to work in intersecting shaft configurations offers flexibility for various mechanical designs and engineering solutions. - Precise Motion Control
The design of bevel gears ensures accurate motion transfer between shafts. This precision is crucial in applications requiring exact positioning, such as in robotics, conveyor systems, and precision machining tools. - Resistance to Thermal Stress
Steel construction provides excellent resistance to heat generated during operation. This feature makes them suitable for high-temperature applications, ensuring consistent performance without compromising the gear’s structural integrity over time.
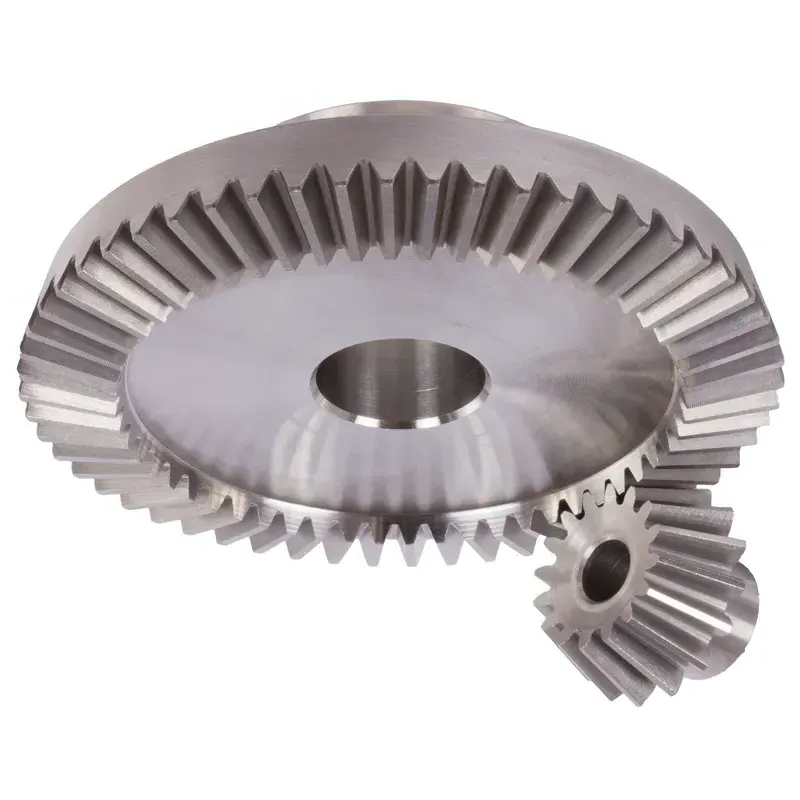

Uses of Straight Bevel Gears
- Automotive Differentials
Straight bevel gears are widely used in automotive differentials to transfer power from the driveshaft to the wheels. Their ability to handle torque at right angles ensures smooth cornering and efficient power distribution between the wheels. - Industrial Machinery
These gears are essential in heavy-duty industrial machines, such as conveyor systems and material handling equipment. Their durability and capacity to transmit high torque make them ideal for operations that require reliable and consistent performance. - Robotics and Automation
Robotics heavily relies on steel bevel gears for transferring motion between different axes. Their precise motion control and adaptability to various configurations make them critical in robotic arms, automated systems, and other precision-driven applications. - Power Tools and Drills
Straight bevel gears are used in power tools, like hand drills and grinders, to transfer motion between perpendicular shafts. Their simple design ensures efficient power delivery in compact spaces, enhancing the tool's overall effectiveness. - Marine and Aerospace Applications
In marine propulsion systems and aerospace mechanisms, these gears enable torque transmission in compact spaces. Their ability to work under stress and maintain precision makes them suitable for handling extreme environmental conditions and high operational demands. - Agricultural Equipment
Straight bevel gears are used in agricultural machinery like harvesters and tractors for efficient torque transmission. Their robust construction and ability to function in harsh environments help improve the reliability and productivity of farming operations.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Automotive Differentials | Bevel Gear for Robotics |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Agricultural Machinery | Bevel Gear for Marine Industry |
Steel Straight Bevel Gear Troubleshooting
- Excessive Noise During Operation
Excessive noise typically indicates improper alignment between the gears. Misalignment results in uneven contact across the teeth, causing vibrations and loud operation. Regularly inspect gear positioning and ensure proper alignment to reduce noise and maintain smooth performance. - Premature Wear or Damage to Teeth
Premature wear often stems from inadequate lubrication or the use of incorrect lubricants. This increases friction and accelerates tooth damage. To address this issue, use the recommended lubricant type and maintain proper lubrication schedules to extend gear life. - Overheating During Use
Overheating can occur due to excessive load or insufficient lubrication. High operational temperatures may weaken the material and damage the gear. Regularly monitor operating conditions, reduce loads if necessary, and ensure proper lubrication to prevent overheating. - Tooth Breakage Under Load
Tooth breakage is often caused by overloading or material fatigue. If the gear is subjected to forces beyond its capacity, it may fracture. Review load requirements, replace damaged gears, and ensure the gear selection matches the application needs. - Poor Gear Engagement
Improper engagement between gears can lead to slipping or inefficient power transfer. This issue is often due to incorrect installation or wear on the mating surfaces. Inspect gear alignment, check for wear, and replace damaged components to resolve the problem. - Corrosion or Surface Deterioration
Corrosion results from exposure to moisture, chemicals, or improper storage. It weakens the gear and reduces its efficiency. To prevent corrosion, use protective coatings, store gears in dry conditions, and regularly inspect for signs of surface deterioration.

Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|



