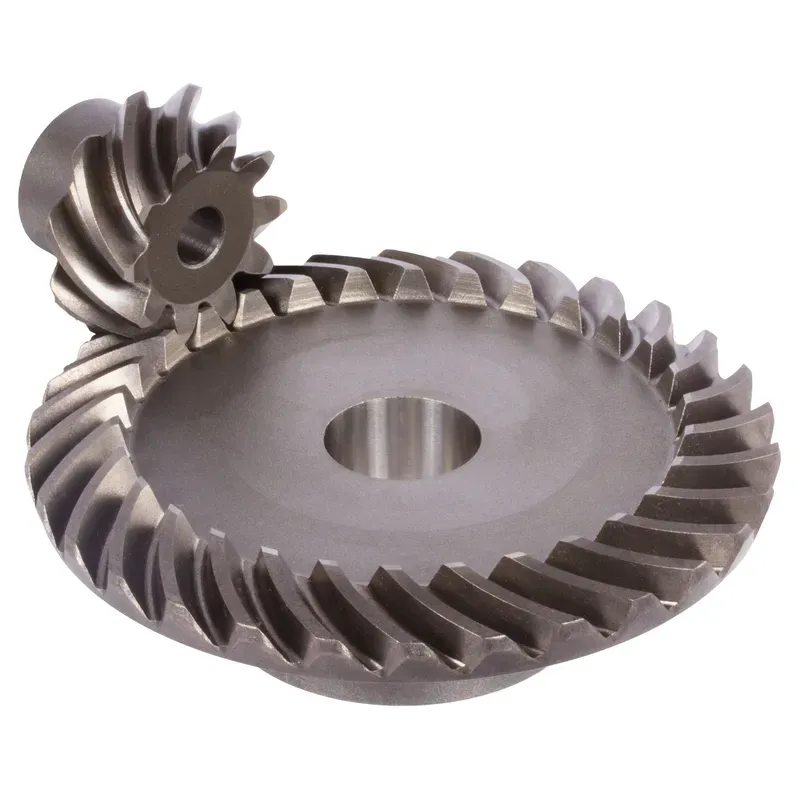
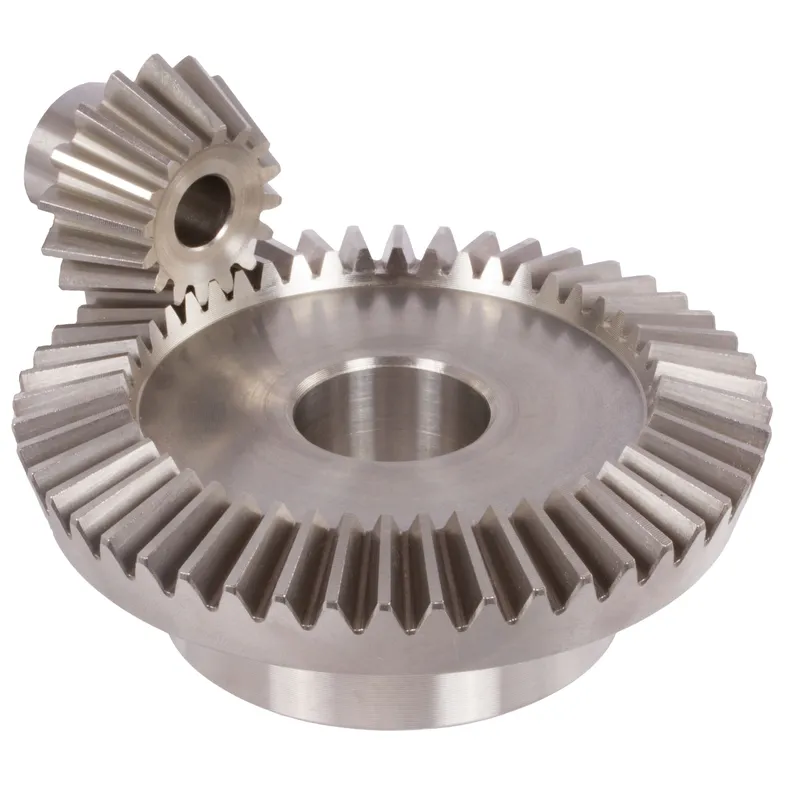
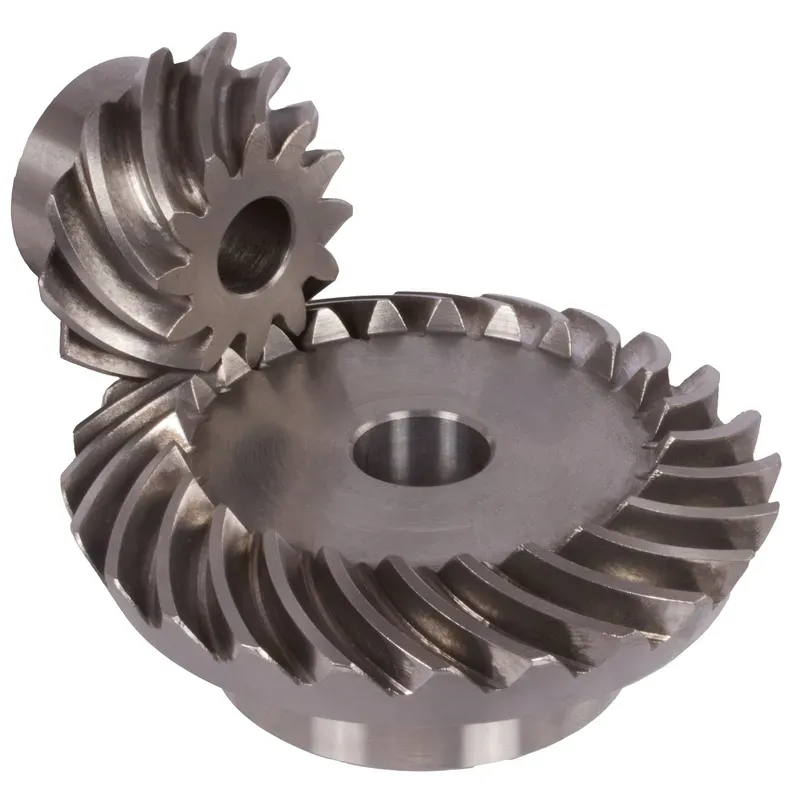
Steel Straight Bevel Gears Ratio 3:1 Straight Tooth System
Steel straight bevel gears with a ratio of 3:1 and a straight tooth system are mechanical components used to transmit rotational motion and power between two intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. These gears are characterized by their straight teeth, which are cut along the gear’s surface in a manner similar to a spur gear but positioned on a conical shape. These steel bevel gears are typically crafted from durable steel to ensure high strength, wear resistance, and longevity in demanding applications. They are widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing.
Steel straight bevel gears with a ratio of 3:1 and a straight tooth system are mechanical components used to transmit rotational motion and power between two intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. These gears are characterized by their straight teeth, which are cut along the gear's surface in a manner similar to a spur gear but positioned on a conical shape. The 3:1 ratio signifies that for every three revolutions of the driving gear (the smaller gear), the driven gear (the larger gear) completes one revolution.
These steel bevel gears are typically crafted from durable steel to ensure high strength, wear resistance, and longevity in demanding applications. They are widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing, where precise torque transfer and speed reduction are essential. The straight tooth design ensures simplicity in manufacturing and alignment, but it can produce higher noise levels compared to helical bevel gears.
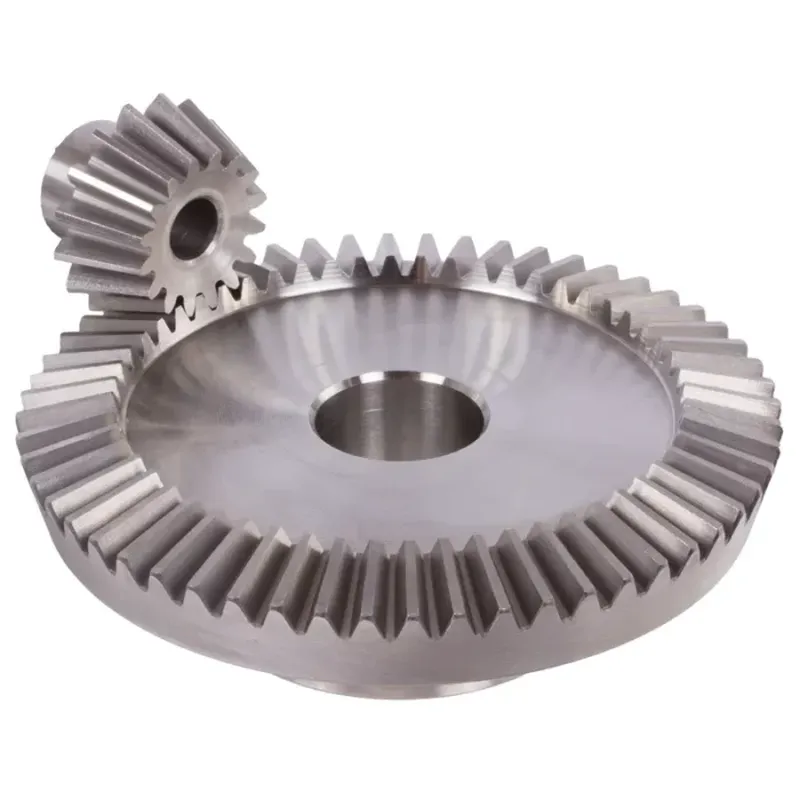

Steel Straight Bevel Gear Ratio 3:1
 | 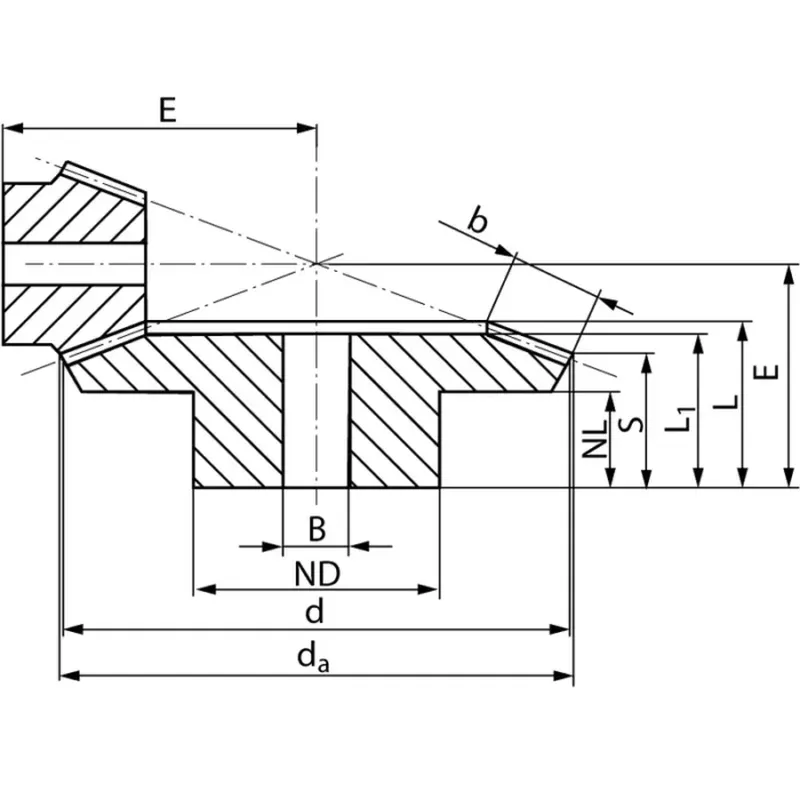 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 0,5 | 15 | 8,0 | 7,5 | 6 | 3,7 | 6,5 | 7,0 | 4,3 | 3 | 3 | 15,3 | 0,009 | 1 |
| 0,5 | 45 | 22,7 | 22,5 | 12 | 5,0 | 7,5 | 8,4 | 7,5 | 3 | 4 | 11,0 | 0,027 | 10 |
| 1 | 15 | 17,7 | 15 | 13 | 9,2 | 16 | 16,5 | 10,0 | 7,1 | 5 | 32 | 0,086 | 14 |
| 1 | 45 | 45,4 | 45 | 25 | 10 | 15 | 17,0 | 15,1 | 7,1 | 8 | 22 | 0,258 | 92 |
| 1,5 | 16 | 28 | 24 | 18 | 11 | 22 | 23,2 | 12,7 | 11,4 | 8 | 48 | 0,38 | 42 |
| 1,5 | 48 | 72,6 | 72 | 50 | 12 | 20 | 24,1 | 20,8 | 11,4 | 15 | 32 | 1,14 | 405 |
| 2 | 16 | 35,9 | 32 | 20 | 10 | 25 | 26,6 | 12,6 | 15 | 10 | 60 | 0,92 | 80 |
| 2 | 48 | 97,3 | 96 | 60 | 18 | 30 | 35,0 | 31,0 | 15 | 25 | 45 | 2,76 | 950 |
| 2,5 | 16 | 44,9 | 40 | 30 | 15,35 | 34 | 36,5 | 17,8 | 20 | 10 | 77 | 5,6 | 200 |
| 2,5 | 48 | 121,6 | 120 | 80 | 15 | 29 | 33,9 | 28,5 | 20 | 25 | 46 | 16,8 | 1600 |
| 3 | 16 | 53,9 | 48 | 40 | 12,5 | 36 | 38,3 | 15,0 | 25 | 15 | 86 | 10,0 | 310 |
| 3 | 48 | 145,9 | 144 | 70 | 18 | 34 | 38,7 | 32,0 | 25 | 30 | 53 | 30,0 | 2300 |
| 4 | 16 | 71,8 | 64 | 50 | 17 | 46 | 48,3 | 20,3 | 30 | 20 | 115 | 22,9 | 680 |
| 4 | 48 | 194,6 | 192 | 90 | 20 | 43 | 50,0 | 41,9 | 30 | 30 | 70 | 68,7 | 5700 |
| 5 | 15 | 84,9 | 75 | 60 | 15 | 53 | 56,4 | 19,1 | 40 | 20 | 130 | 39,3 | 1110 |
| 5 | 45 | 228,3 | 225 | 100 | 20 | 45 | 53,1 | 42,4 | 40 | 40 | 75 | 117,9 | 7920 |
| 5 | 16 | 89,8 | 80 | 60 | 16,5 | 55 | 59,0 | 21,6 | 40 | 20 | 140 | 47,7 | 1310 |
| 5 | 48 | 243,2 | 240 | 100 | 20 | 47 | 55,7 | 44,9 | 40 | 40 | 80 | 143,1 | 9640 |
| 6 | 15 | 101,4 | 90 | 70 | 20 | 67 | 73 | 26,2 | 50 | 30 | 159,2 | 70,7 | 1880 |
| 6 | 45 | 273,8 | 270 | 100 | 30 | 60 | 69 | 55,0 | 50 | 45 | 94,3 | 212,1 | 13170 |
Benefits of Steel Straight Bevel Gears
1. High Strength and Durability
Steel straight bevel gears are made from high-strength steel, making them highly resistant to wear, deformation, and heavy loads. This durability ensures reliable performance over extended periods, even in demanding industrial environments such as manufacturing machinery, automotive systems, and heavy-duty equipment.
2. Efficient Torque Transmission
These gears provide precise and efficient torque transfer between intersecting shafts. The straight tooth design minimizes energy losses, allowing for consistent power delivery. This makes them suitable for applications requiring high efficiency and reliable energy transfer without significant mechanical losses.
3. Simple Design
The straight tooth system is easier to design and manufacture compared to more complex helical or spiral bevel gears. This simplicity reduces production costs, making them an economical choice for industries that require durable and efficient gear systems without compromising quality.
4. Versatility in Applications
Steel bevel gears are versatile and can be used in various applications such as machining tools, automotive differentials, and power transmission systems. Their adaptability to different speed and torque requirements makes them invaluable in a range of mechanical systems.
5. High Resistance to Environmental Factors
Being made from steel, these gears are highly resistant to environmental factors such as corrosion, extreme temperatures, and heavy vibrations. This ensures their functionality and longevity in harsh environments, including outdoor machinery and industrial equipment exposed to challenging conditions.
6. Low Maintenance Requirements
With proper lubrication and alignment, straight bevel gears require minimal maintenance over their operational lifespan. This reduces downtime and repair costs, offering long-term reliability and efficiency for industries looking to maximize productivity and minimize operational expenses.

Applications of Straight Bevel Gears
1. Automotive Differentials
Straight bevel gears are commonly used in automotive differentials to transfer torque from the drive shaft to the wheels. They enable smooth power distribution between the left and right wheels, ensuring better traction and handling during turns or uneven road conditions.
2. Machining Tools and Equipment
These gears are vital in machine tools such as lathes, milling machines, and drills. They help transmit power at specific angles, enabling precision movement and operation of cutting or shaping tools in various manufacturing and machining processes.
3. Industrial Conveyor Systems
Straight bevel gears are used in conveyor systems to transmit power between intersecting shafts, ensuring smooth operation. They are essential in industries such as mining, packaging, and material handling, where efficient power transfer and durability are critical for productivity.
4. Railway and Locomotive Systems
In railway systems, steel bevel gears are utilized in braking mechanisms and power transmission units. Their ability to handle heavy loads and transmit torque efficiently makes them ideal for the demanding requirements of locomotives and railcar systems.
5. Aerospace Applications
These gears are used in aerospace applications for actuating components such as landing gear systems and control surfaces. Their strength, precision, and ability to operate under extreme conditions make them suitable for use in high-performance and safety-critical aerospace systems.
6. Agricultural Machinery
Steel bevel gears are widely used in agricultural equipment like harvesters, tractors, and plows. They enable efficient power transmission to various components, ensuring the reliable and smooth operation of machinery in rugged environments and under heavy workloads in farming applications.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Power Tools | Bevel Gear for Automotive Differentials |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Marine Industry | Bevel Gear for Agricultural Machinery |
Spiral Bevel Gear Vs Straight Bevel Gear
| Aspect | Spiral Bevel Gear | Straight Bevel Gear |
|---|---|---|
| Tooth Design | Teeth are curved and angled, forming a spiral shape. | Teeth are straight and cut along the cone's surface, similar to spur gears. |
| Efficiency | Slightly lower efficiency due to sliding contact between teeth. | Higher efficiency as the teeth experience less sliding friction during operation. |
| Noise Level | Operates more quietly due to gradual tooth engagement and smoother contact. | Produces more noise due to sudden tooth engagement and impact during operation. |
| Load Capacity | Handles higher loads and torque due to multiple teeth in contact at all times. | Handles moderate loads as only one pair of teeth are in contact at a time. |
| Durability | More durable under high-speed and heavy-load conditions. | Suitable for lighter-duty applications where extreme durability is not required. |
| Gear Mesh | Provides smoother meshing and less vibration due to gradual tooth engagement. | Results in more vibration and less smooth meshing due to abrupt tooth contact. |
| Manufacturing Complexity | More complex and expensive to manufacture due to the spiral tooth design. | Simpler and cheaper to manufacture due to straight tooth geometry. |
| Applications | Common in automotive differentials, aerospace, and heavy machinery. | Used in tools, agricultural machinery, and low-speed systems. |
| Axial Thrust | Generates axial thrust due to the spiral angle, requiring proper thrust bearings. | Does not generate significant axial thrust, reducing the need for special bearings. |
| Speed Capability | Better suited for high-speed applications due to reduced noise and vibration. | More suitable for low- to moderate-speed applications due to abrupt tooth contact. |
| Contact Surface | Larger contact area between teeth, reducing wear and improving load distribution. | Smaller contact area, leading to higher localized stresses and wear. |
| Power Transmission | Can transmit higher power levels more efficiently. | Limited to transmitting moderate power levels. |
| Alignment Sensitivity | More tolerant to minor misalignments due to gradual engagement. | Requires precise alignment; misalignment can cause significant wear or damage. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to complex design and precise manufacturing requirements. | Lower cost due to simpler design and easier manufacturing. |
| Maintenance | Requires more maintenance due to higher complexity and thrust-related forces. | Easier to maintain due to simpler design and fewer operational stresses. |
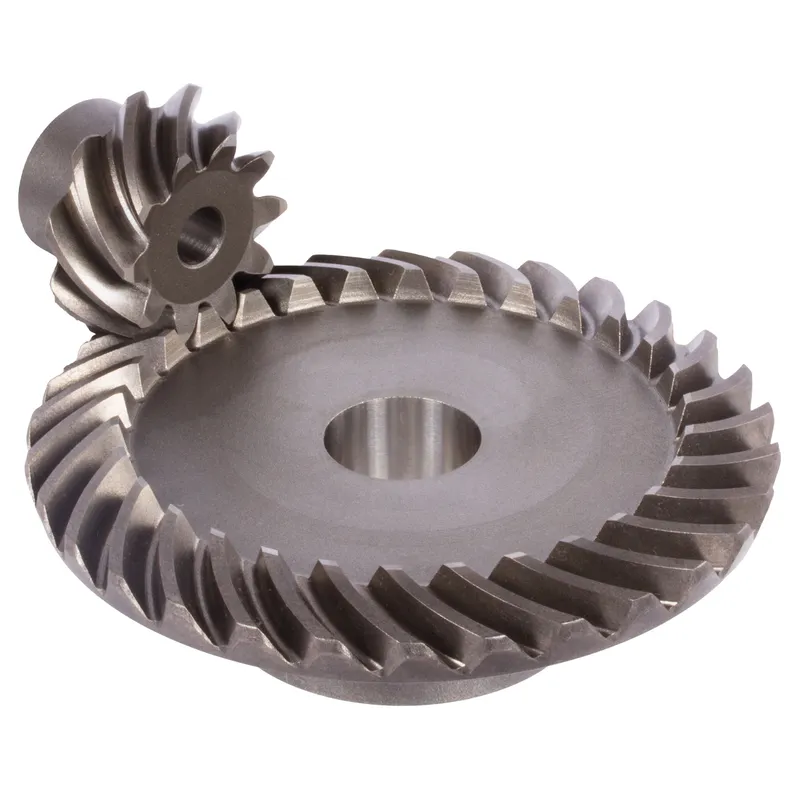 |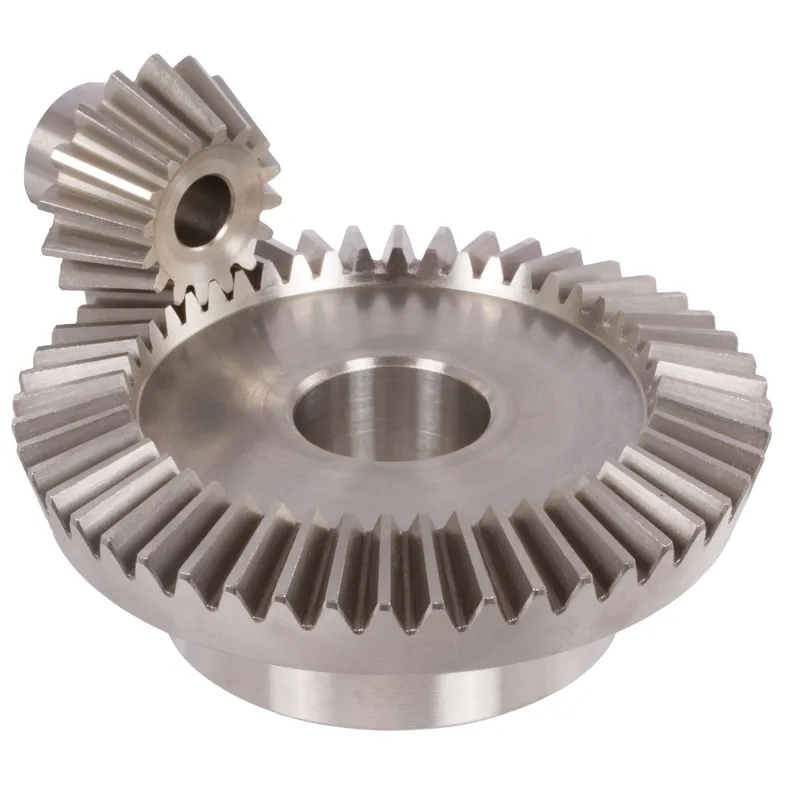  |
| Spiral Bevel Gear | Straight Bevel Gear |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|


