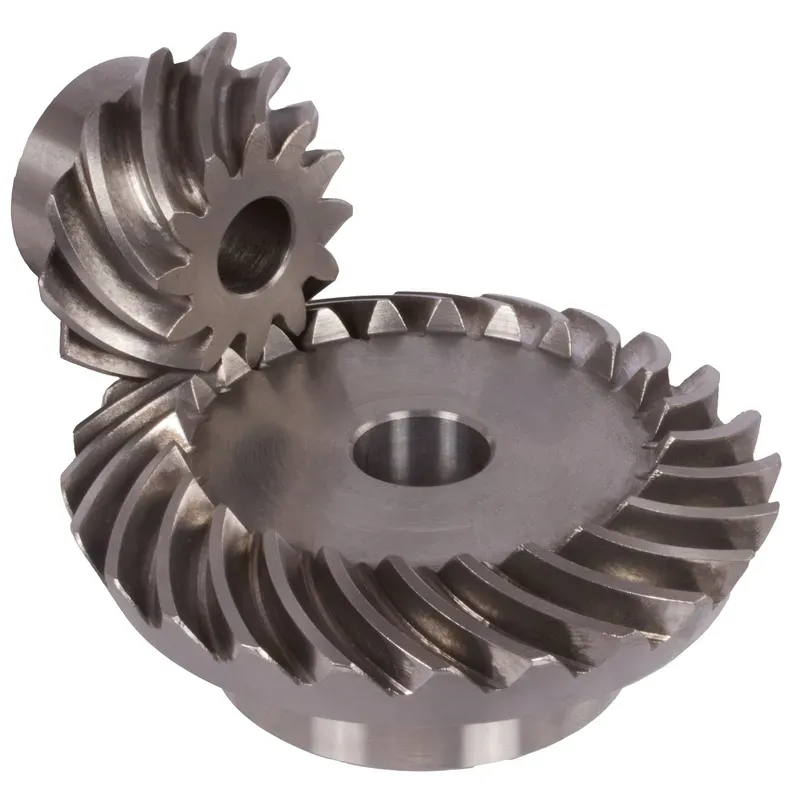
Steel Straight Bevel Gears Ratio 3.5:1 Straight Tooth System
The steel straight bevel gears ratio 3.5:1 straight tooth system refers to a specific type of mechanical gear configuration used in machinery to transfer rotational motion between two shafts that are usually at a right angle (90°) to each other. This straight bevel gear system is commonly used in applications requiring precise torque transmission, such as automotive differentials, industrial machinery, and power tools. The straight-tooth design is simpler and more cost-effective to manufacture than spiral bevel gears, but it tends to generate more noise and vibration during operation.
The steel straight bevel gears ratio 3.5:1 straight tooth system refers to a specific type of mechanical gear configuration used in machinery to transfer rotational motion between two shafts that are usually at a right angle (90°) to each other. These gears are made of steel for durability and strength, and they feature straight teeth that are cut radially along the gear’s cone-shaped surface. The gear ratio of 3.5:1 means that the driving gear (the smaller gear, called the pinion) must rotate 3.5 times to turn the larger gear (the driven gear) once.
This straight bevel gear system is commonly used in applications requiring precise torque transmission, such as automotive differentials, industrial machinery, and power tools. The straight-tooth design is simpler and more cost-effective to manufacture than spiral bevel gears, but it tends to generate more noise and vibration during operation. Steel construction ensures high load capacity and wear resistance, making these gears suitable for heavy-duty use. Because of their straightforward design, they are ideal for moderate-speed, high-torque applications where efficiency and reliability are critical.

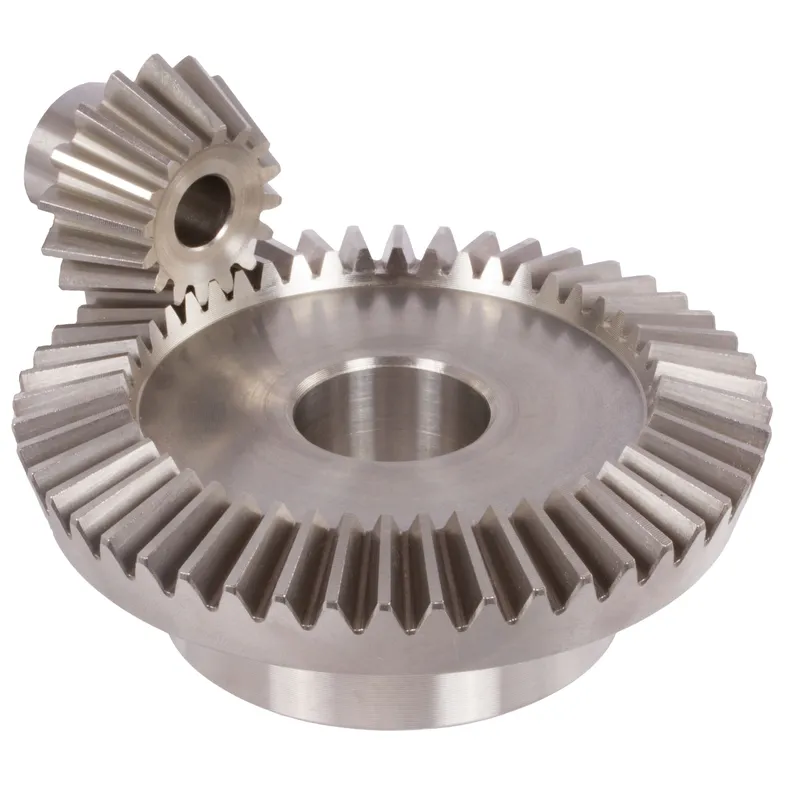
Steel Straight Bevel Gear Ratio 3.5:1
 | 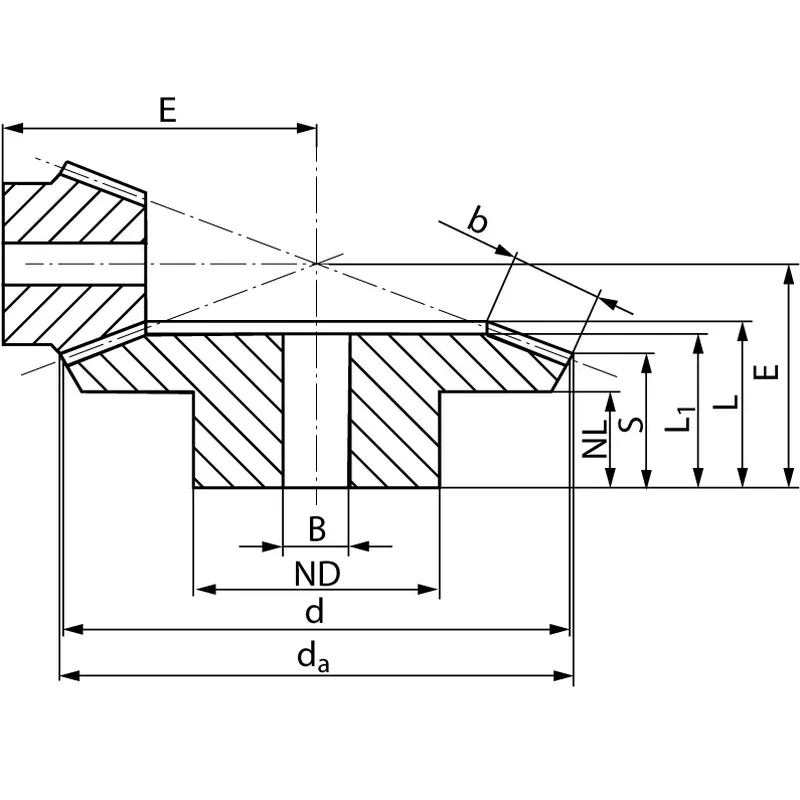 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 16 | 18,7 | 16 | 13 | 7,6 | 16 | 16,6 | 8,4 | 8,7 | 5 | 36 | 0,127 | 16 |
| 1 | 56 | 56,3 | 56 | 30 | 10,0 | 14 | 16,7 | 14,6 | 8,7 | 8 | 22 | 0,445 | 130 |
| 1,5 | 16 | 28,1 | 24 | 18 | 12,2 | 24 | 26 | 13,6 | 13,1 | 8 | 55 | 0,45 | 48 |
| 1,5 | 56 | 84,5 | 84 | 50 | 12 | 24 | 27,1 | 23,8 | 13,1 | 15 | 35 | 1,58 | 634 |
| 2 | 16 | 35,9 | 32 | 20 | 10 | 25 | 26,8 | 12,5 | 15 | 10 | 68 | 0,99 | 82 |
| 2 | 56 | 113,1 | 112 | 60 | 18 | 31 | 35,5 | 31,9 | 15 | 25 | 46 | 3,47 | 1200 |
| 2,5 | 16 | 44,9 | 40 | 30 | 16,5 | 36 | 37,7 | 18,7 | 20 | 10 | 88 | 6,0 | 220 |
| 2,5 | 56 | 141,4 | 140 | 80 | 18 | 32 | 37,2 | 32,4 | 20 | 25 | 50 | 21,0 | 2300 |
| 3 | 16 | 53,9 | 48 | 40 | 15 | 39 | 40,6 | 16,8 | 25 | 15 | 100 | 10,9 | 340 |
| 3 | 56 | 169,7 | 168 | 80 | 18 | 33 | 39,8 | 34,0 | 25 | 30 | 55 | 38,2 | 3100 |
| 4 | 16 | 71,9 | 64 | 50 | 13 | 42 | 44,6 | 16,1 | 30 | 20 | 127 | 24,7 | 660 |
| 4 | 56 | 226,3 | 224 | 90 | 20 | 40 | 49,0 | 42,0 | 30 | 30 | 70 | 86,5 | 6900 |
Straight Bevel Gear Material Selection
- Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a popular material for straight bevel gears due to its excellent balance of strength, durability, and affordability. It is ideal for heavy-duty applications as it provides good wear resistance and can handle high loads. However, it may require additional surface treatments, such as carburizing or hardening, to improve its performance in environments with high stress or friction. Carbon steel is widely used in industrial and automotive applications where cost-effectiveness and reliability are critical. - Alloy Steel
Alloy steel is chosen for gears that need enhanced mechanical properties, such as increased toughness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. By incorporating elements like chromium, molybdenum, or nickel, alloy steel delivers superior performance under high stresses and in extreme operating conditions. It is suitable for high-speed or heavy-load applications, such as machinery and aerospace systems. - Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is selected for its excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as marine, chemical, or food processing industries. It also provides good strength and durability, though it may not be as hard as carbon or alloy steel. Stainless steel gears are more expensive but are essential in scenarios where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures is a concern. - Plastic
Plastic gears are lightweight and cost-effective, making them suitable for low-load and low-speed applications, such as home appliances, toys, and medical devices. They operate quietly and require minimal lubrication, which reduces maintenance needs. While they offer excellent resistance to corrosion, they lack the strength and wear resistance of metal gears, making them unsuitable for heavy-duty applications. - Brass
Brass is used for gears requiring good machinability, corrosion resistance, and moderate strength. It is commonly applied in precision instruments, clocks, and marine equipment because it performs well in environments with moisture and does not rust. Brass gears are quieter than steel gears and offer smooth operation, but they are not suitable for high-load or high-speed applications due to their lower strength and wear resistance.
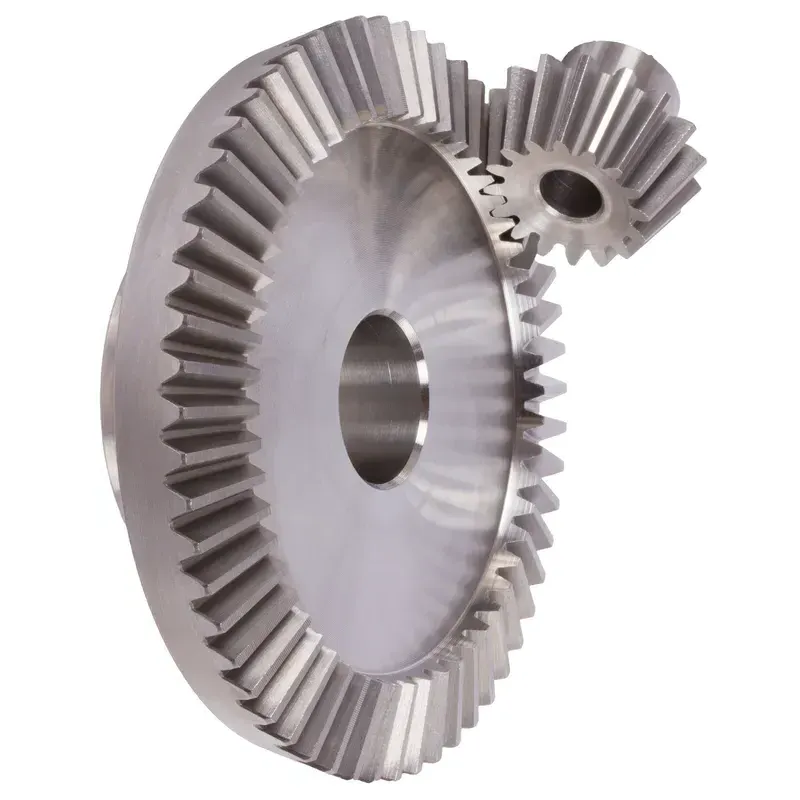

Steel Straight Bevel Gear Purpose and Applications
- Automotive Industry
Steel straight bevel gears are extensively used in the automotive sector for their ability to transfer torque between perpendicular shafts efficiently. They are commonly found in differential systems, where they help distribute power between wheels, ensuring smooth cornering and stability. Their durability and high load capacity make them ideal for handling the stresses of continuous use in vehicles. Additionally, they are used in steering systems and transmission assemblies, where precise torque control is essential for vehicle performance and safety. - Industrial Machinery
In industrial machinery, steel straight bevel gears play a key role in power transmission systems for heavy-duty equipment such as conveyor belts, mixers, and crushers. Their robust construction and ability to handle high loads and torque make them essential for reliable operation in harsh environments. These gears are particularly valued in industries like mining, construction, and manufacturing, where efficiency and durability are crucial. - Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry relies on steel straight bevel gears for applications requiring precise and reliable power transmission under extreme conditions. They are used in aircraft landing gear systems, propulsion systems, and control actuators, where their strength and resistance to wear are critical. Aerospace environments demand materials that can endure high speeds, vibrations, and temperature fluctuations, and steel straight bevel gears meet these requirements effectively. - Marine Applications
Marine equipment, such as ship propulsion systems, winches, and steering mechanisms, often employs steel straight bevel gears for their high strength and corrosion resistance when treated appropriately. These gears are critical for transferring power in shipboard machinery, often operating under heavy loads and in wet or corrosive environments. Their ability to deliver reliable performance with minimal maintenance ensures smooth operation in demanding maritime conditions. - Robotics and Automation
In the robotics and automation industry, steel straight bevel gears are essential for creating precise, controlled motion in robotic arms, actuators, and automated systems. Their high efficiency and ability to handle variable loads make them suitable for sophisticated machinery requiring accurate and repeatable movements. These gears are used in pick-and-place robots, assembly lines, and even autonomous vehicles.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Automotive Differentials | Bevel Gear for Robotics |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Industrial Equipments | Bevel Gear for Marine Industry |
Difference Between Bevel Gear and Helical Gear
Helical gears and bevel gears are both important types of gears commonly used in various mechanical systems. While they share some similarities, they also have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications.
1. Tooth Orientation:
Helical Gears: Helical gears have teeth that are cut at an angle, resulting in a helix shape. The teeth are oriented at an angle to the gear axis, allowing for gradual engagement, which reduces noise and vibrations.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears have teeth that are cut on conical surfaces. The teeth are oriented at an angle to the gear axis, enabling power transmission between intersecting shafts.
2. Axial Thrust:
Helical Gears: Due to the helix angle, helical gears generate axial thrust along the gear axis during operation. This thrust needs to be accommodated by suitable thrust bearings.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears also produce axial thrust, but it is typically lower compared to helical gears.
3. Efficiency:
Helical Gears: Helical gears provide higher efficiency than bevel gears due to their gradual engagement and larger contact area between teeth.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears have slightly lower efficiency compared to helical gears due to the sliding action between teeth during meshing.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Helical Gears: The helical tooth design helps in reducing noise and vibration by distributing the load over multiple teeth during engagement.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears tend to generate more noise and vibration compared to helical gears, particularly at higher speeds.
5. Applications:
Helical Gears: Helical gears are commonly used in applications that require high-speed and high-load transmission, such as automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and power generation systems.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears are suitable for applications where power transmission is required between intersecting shafts, such as differential gears in vehicles, angle drives, and hand drills.
6. Gearbox Arrangement:
Helical Gears: Helical gears are often used in parallel shaft arrangements, where the gears are placed on parallel axes.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears are commonly employed in perpendicular shaft arrangements, where the gears are placed on intersecting axes.
7. Manufacturing Complexity:
Helical Gears: Manufacturing helical gears can be more complex than bevel gears due to the angled teeth, requiring specific cutting techniques and specialized machinery.
Bevel Gears: Bevel gears are relatively easier to manufacture compared to helical gears, as they can be cut using standard gear cutting methods.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear | Helical Gear |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|

