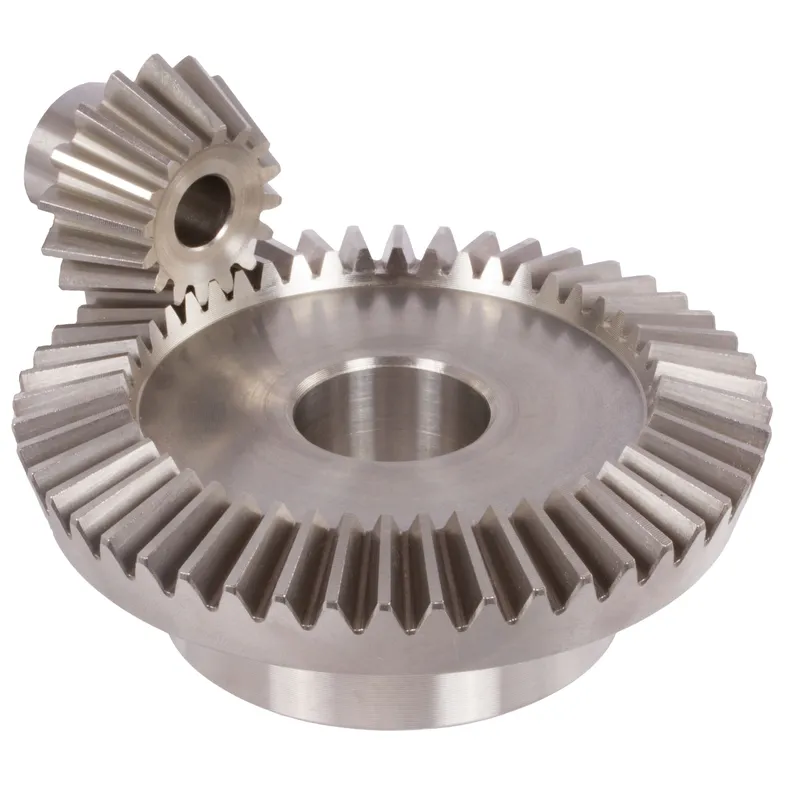
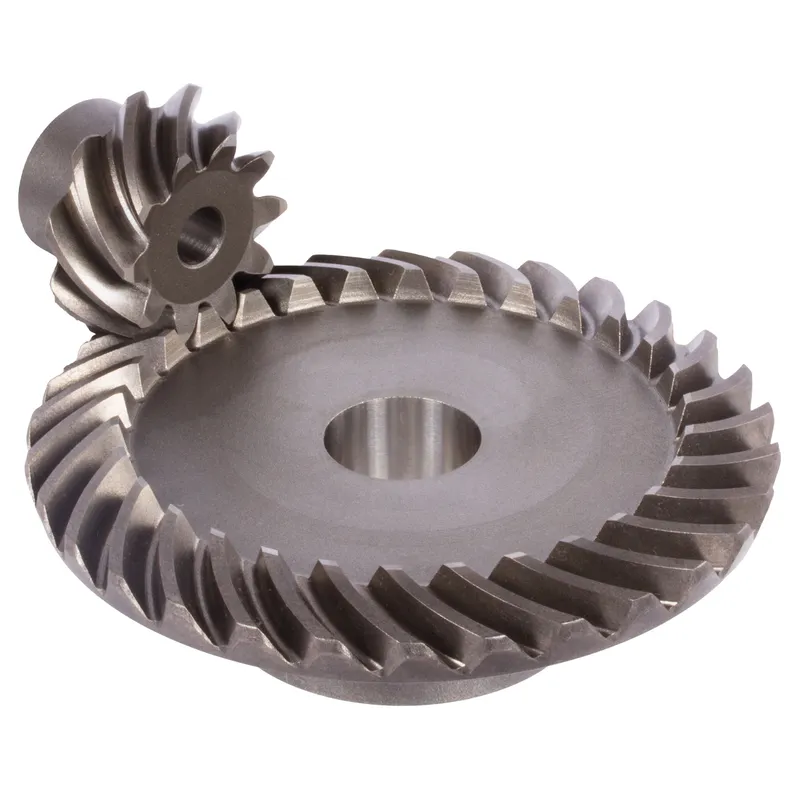
Steel Spiral Bevel Gears Ratio 2:1 Spiral Tooth System
Steel spiral bevel gears with a 2:1 ratio are conical gears designed to transmit power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, with a speed reduction where the driven gear rotates at half the speed of the driving gear. The spiral tooth system features curved, oblique teeth, often with a 35-degree helix angle, enabling smoother and quieter operation compared to straight bevel gears. Made from carbon or alloy steels like 42CrMo4 or 16MnCr5, these gears are heat-treated for enhanced durability and strength, ideal for high-load, high-speed applications such as automotive differentials or industrial machinery.
Steel spiral bevel gears with a 2:1 ratio are conical gears designed to transmit power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, with a speed reduction where the driven gear rotates at half the speed of the driving gear. The spiral tooth system features curved, oblique teeth, often with a 35-degree helix angle, enabling smoother and quieter operation compared to straight bevel gears. Made from carbon or alloy steels like 42CrMo4 or 16MnCr5, these gears are heat-treated for enhanced durability and strength, ideal for high-load, high-speed applications such as automotive differentials or industrial machinery.
The 2:1 ratio is achieved by the driven gear having twice the number of teeth as the pinion, ensuring efficient torque transfer. Their design minimizes vibration, increases contact ratio, and requires robust bearings to handle axial thrust loads.
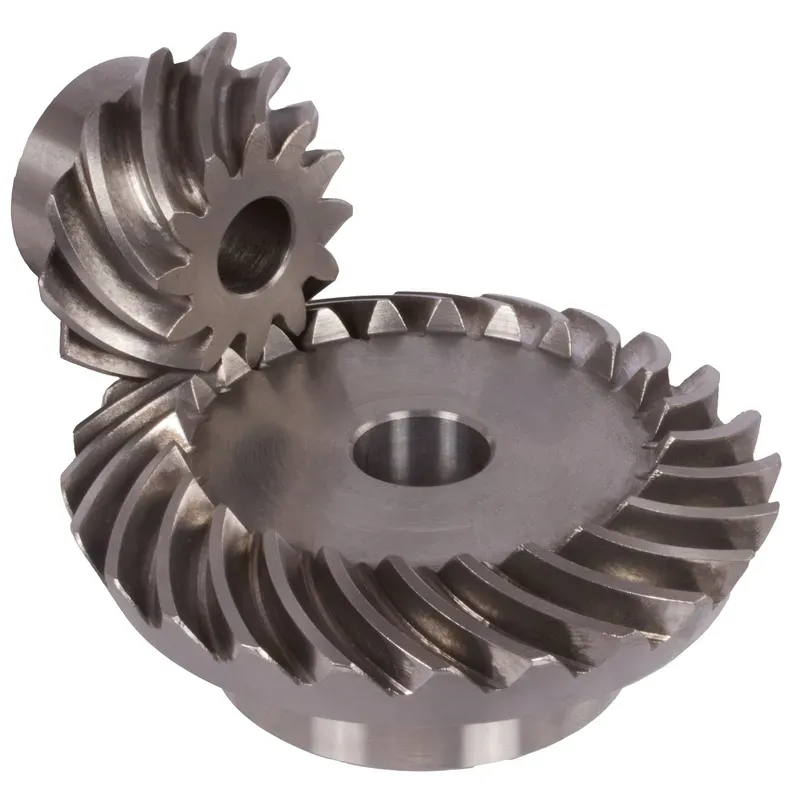

Steel Spiral Bevel Gear Ratio 2:1
 | 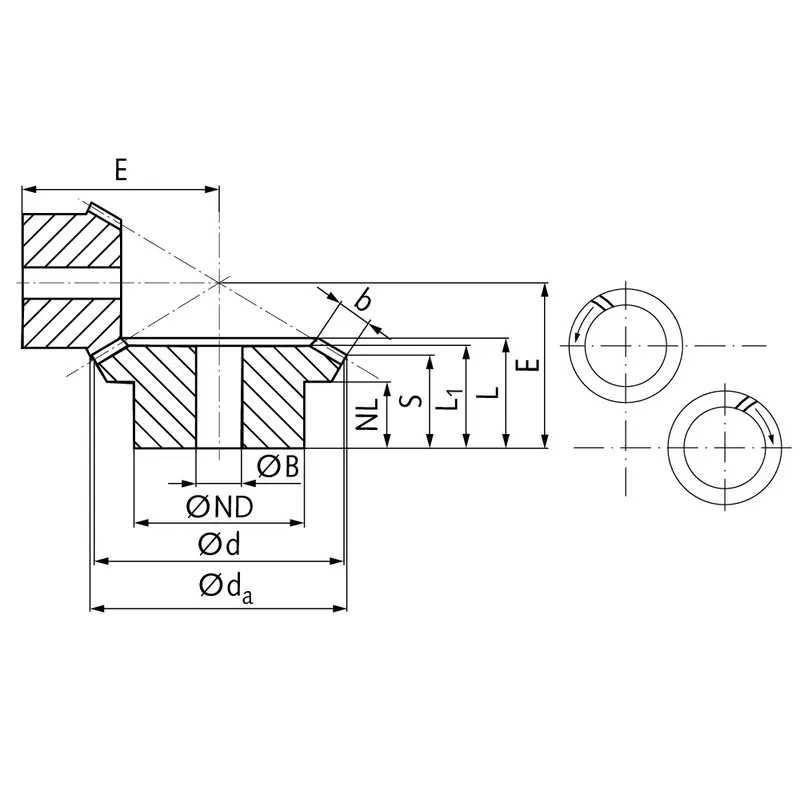 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 0,6 | 22 | 20,8 | 19,8 | 16 | 7,4 | 15 | 15,6 | 8,5 | 8 | 6 | 28 | 2,3 | 116 |
| 0,6 | 44 | 40,1 | 39,6 | 25 | 8 | 15 | 17,2 | 13,6 | 8 | 10 | 23 | 4,6 | 116 |
| 1 | 20 | 31,8 | 30 | 25 | 8 | 19 | 20,2 | 9,4 | 12 | 8 | 39 | 9,8 | 323 |
| 1 | 40 | 60,9 | 60 | 40 | 8 | 18 | 21,2 | 15,9 | 12 | 12 | 30 | 19,6 | 323 |
| 1,3 | 16 | 34,4 | 32 | 25 | 7 | 20 | 22,1 | 9,6 | 14 | 8 | 41 | 12,0 | 397 |
| 1,3 | 32 | 65,1 | 64 | 40 | 8 | 20 | 23,3 | 17,1 | 14 | 12 | 32 | 24,0 | 397 |
| 1,5 | 16 | 38,0 | 35,2 | 30 | 8,4 | 19 | 21,2 | 10,5 | 12 | 10 | 45 | 14,4 | 435 |
| 1,5 | 32 | 71,7 | 70,4 | 45 | 8 | 17 | 21,0 | 15,7 | 12 | 12 | 32 | 28,8 | 435 |
| 2,269 | 12 | 44,0 | 41,5 | 30 | 12 | 28,23 | 28,23 | 17,6 | 15 | 12 | 55 | 10,1 | 846 |
| 2,269 | 24 | 83,0 | 83 | 50 | 15 | 27 | 32,41 | 26,0 | 15 | 16 | 45 | 20,2 | 846 |
| 2,321 | 13 | 47,0 | 45 | 30 | 15 | 30 | 33,0 | 21,7 | 15 | 10 | 63,65 | 49 | 818 |
| 2,321 | 26 | 91,0 | 90 | 40 | 22 | 30 | 35,5 | 29,8 | 15 | 16 | 50 | 98 | 818 |
| 2,5 | 11 | 57,0 | 52,5 | 40 | 15 | 36,72 | 36,72 | 19,7 | 20 | 16 | 70 | 17,8 | 2000 |
| 2,5 | 22 | 106,0 | 105 | 70 | 20 | 39 | 44,65 | 35,8 | 20 | 20 | 60 | 35,6 | 2000 |
| 2,5 | 13 | 59,0 | 56 | 39 | 15 | 34 | 38,37 | 22,9 | 20 | 16 | 75,13 | 95 | 1400 |
| 2,5 | 26 | 113,0 | 112 | 54 | 21 | 30 | 37,72 | 29,0 | 20 | 25 | 55 | 190 | 1400 |
| 3 | 13 | 68,0 | 64 | 45 | 16 | 37 | 41,95 | 24,9 | 22 | 20 | 84,62 | 133 | 2000 |
| 3 | 26 | 128,0 | 128 | 54 | 20 | 32 | 39,9 | 30,6 | 22 | 25 | 60 | 266 | 2000 |
| 3 | 14 | 76,0 | 72,5 | 55 | 25 | 51,46 | 51,46 | 32,0 | 25 | 20 | 100 | 644 | 4800 |
| 3 | 28 | 146,0 | 145 | 90 | 25 | 50 | 57,1 | 46,2 | 25 | 30 | 80 | 128 | 4800 |
| 3,5 | 13 | 77,0 | 72 | 54 | 12 | 34 | 39,8 | 21,1 | 24 | 20 | 88,38 | 197 | 2800 |
| 3,5 | 26 | 146,0 | 144 | 64 | 25 | 38 | 47,1 | 36,5 | 24 | 30 | 70 | 394 | 2800 |
Different Types of Bevel Gears
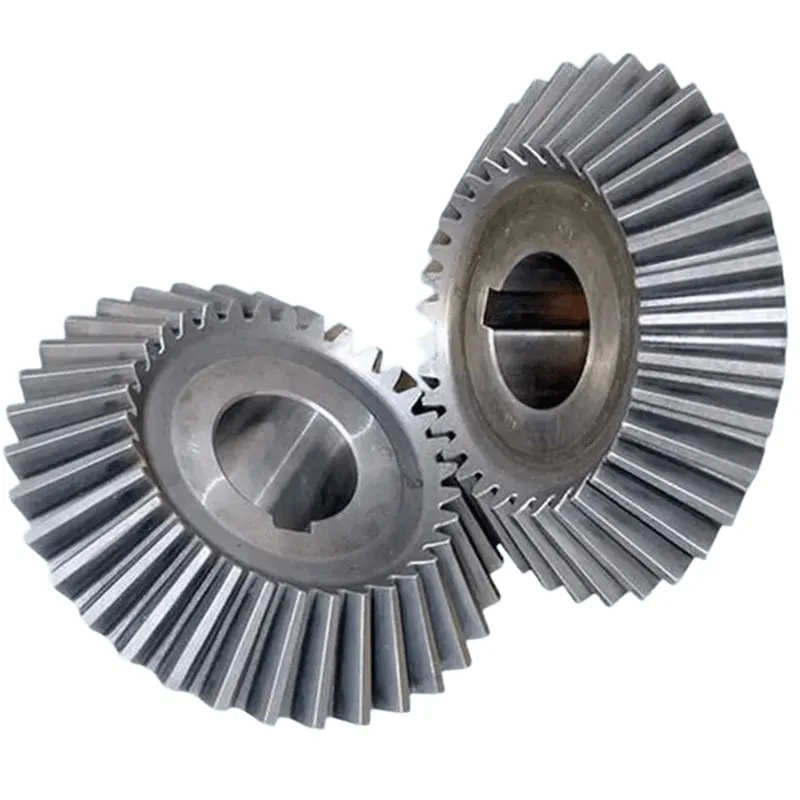
Straight Bevel Gears
Straight bevel gears are the simplest type of bevel gears, featuring straight teeth that are parallel to the generatrix of the pitch cone. They are used in applications where high speeds and low to medium loads are present. However, straight bevel gears may generate more noise compared to other types of bevel gears due to the sudden engagement of the teeth.
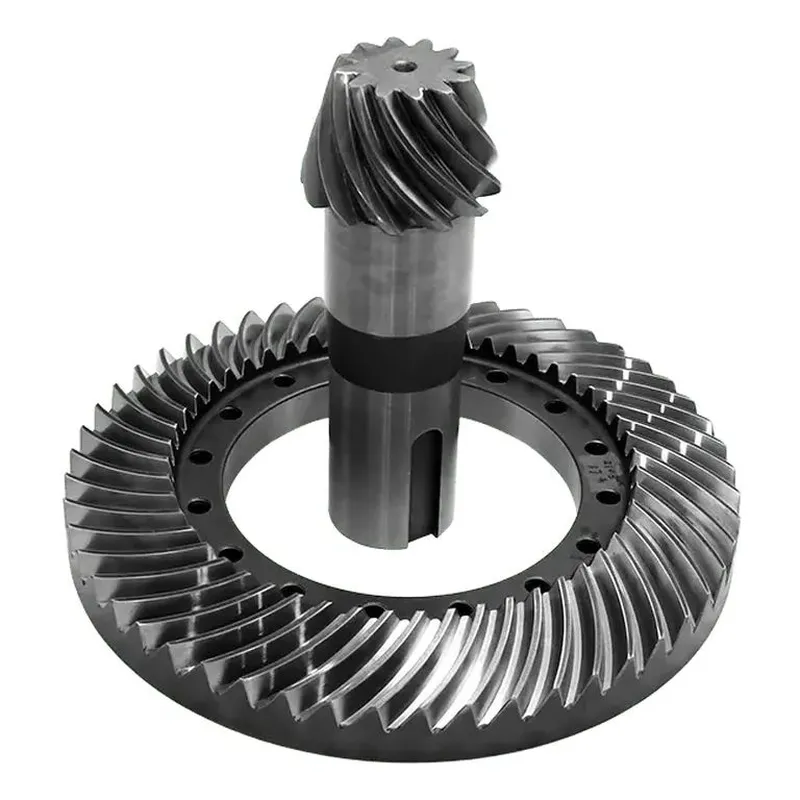
Spiral Bevel Gears
Spiral bevel gears have curved teeth that are oblique to the generatrix of the pitch cone. The spiral angle of the teeth provides a gradual and smooth engagement, resulting in quieter operation and higher load capacity compared to straight bevel gears. Spiral bevel gears are commonly used in automotive differentials and industrial applications that require high speeds and heavy loads.
Hypoid Bevel Gears
Hypoid bevel gears are similar to spiral bevel gears but with a notable difference: the pitch cones of the gears do not intersect. Instead, the axes of the gears are offset, allowing for larger pinion diameters and improved tooth contact. This offset configuration provides several advantages, such as higher torque capacity, reduced noise, and more compact designs. Hypoid gears are frequently used in automotive rear axles and industrial gearboxes.
Zerol Bevel Gears
Zerol bevel gears are a special case of spiral bevel gears, where the spiral angle is zero. This means that the teeth are parallel to the axis of rotation, similar to straight bevel gears. However, unlike straight bevel gears, Zerol bevel gears have a curved tooth profile that allows for smooth and gradual engagement. Zerol bevel gears offer a balance between the benefits of straight and spiral bevel gears, providing improved load capacity and quieter operation compared to straight bevel gears.
Miter Gears
Miter gears are a specific type of bevel gear where the number of teeth on both gears is equal, and the shaft angle is 90°. This configuration results in a 1:1 gear ratio, making miter gears ideal for applications that require a change in the direction of rotation without altering the speed or torque. Miter gears can have straight, spiral, or Zerol teeth.
 |  |
| Straight Bevel Gears | Spiral Bevel Gears |
 |  |
| Hypoid Bevel Gears | Zerol Bevel Gears |
Applications of Spiral Bevel Gears
1. Automotive Differentials
Spiral bevel gears are widely used in automotive differentials to transmit torque from the driveshaft to the wheels while allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds. Their smooth operation and quiet performance make them ideal for high-speed vehicles and heavy-duty trucks.
2. Industrial Machinery
In heavy-duty industrial machines such as conveyors, crushers, and mixers, spiral bevel gears ensure efficient power transmission between perpendicular shafts. Their ability to handle high torque loads with minimal vibration makes them suitable for applications requiring reliable and long-lasting operation under constant stress.
3. Aerospace Systems
Spiral bevel gears are integral to aerospace applications such as helicopter transmission systems and jet engines. They ensure precise and smooth power transfer in compact spaces while withstanding extreme conditions like high temperatures, heavy loads, and demanding operational environments, ensuring safety and reliability.
4. Marine Propulsion Systems
In marine applications, spiral bevel gears are used in propulsion systems to transfer power from engines to propellers. Their smooth engagement and high torque capacity allow for efficient power delivery, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environments, including prolonged exposure to saltwater and vibration.
5. Power Tools and Robotics
Spiral bevel gears are common in high-performance power tools and robotic systems where compact design and precision are essential. Their ability to transmit power smoothly in small spaces ensures accuracy and durability, especially in applications requiring continuous operation or varying load conditions.
6. Wind Turbines
Spiral bevel gears are used in wind turbine gearboxes to transfer rotational energy from the blades to the generator. Their smooth operation enhances energy efficiency, while their robust design ensures they can endure high torque loads and fluctuating wind conditions over extended periods.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Automotive Industry | Bevel Gear for Robotics |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Marine Industry | Bevel Gear for Power Tools |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|
