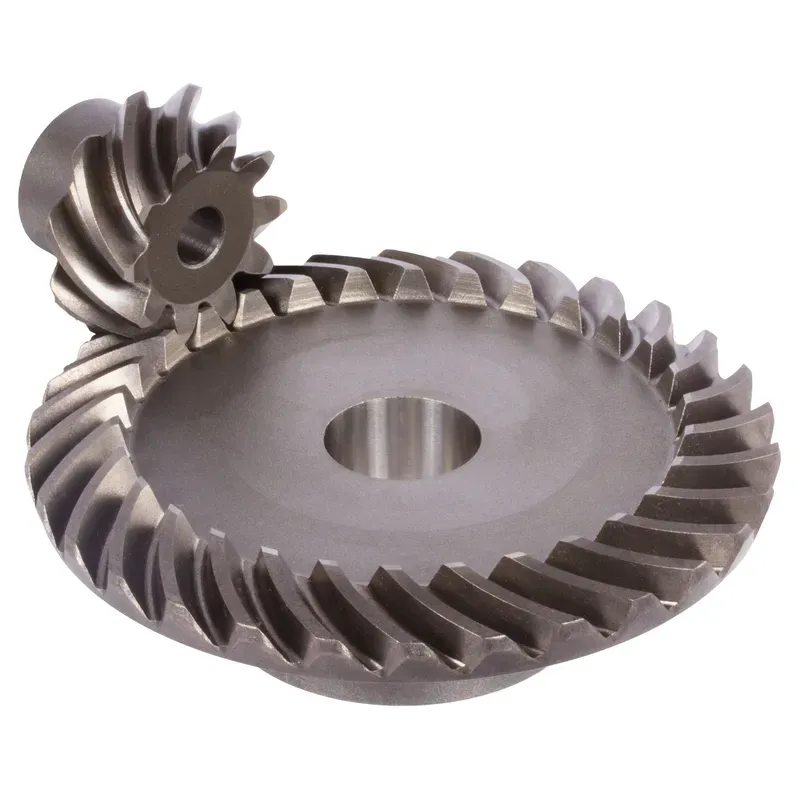
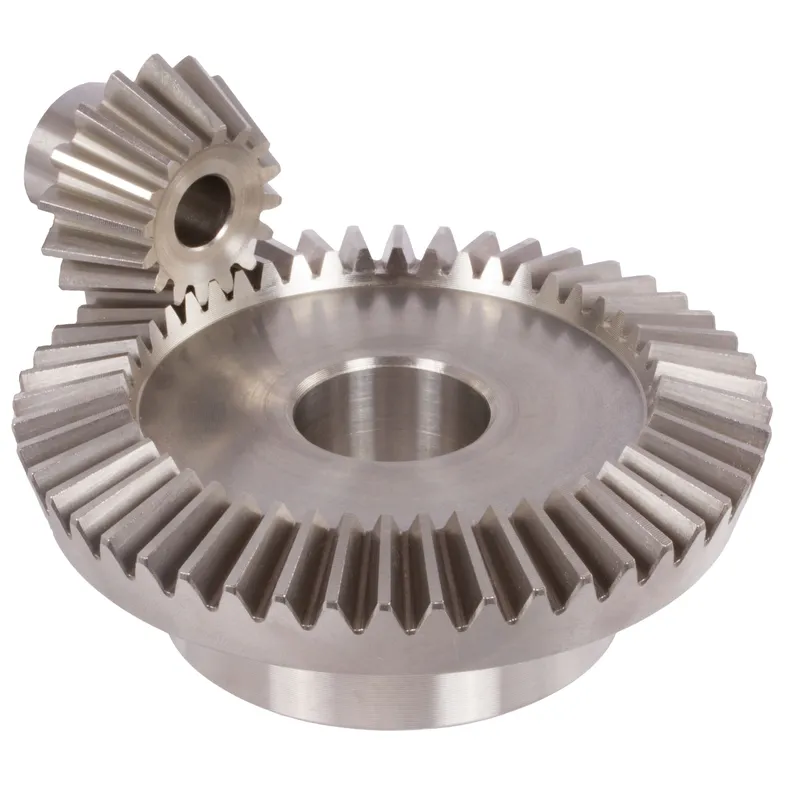
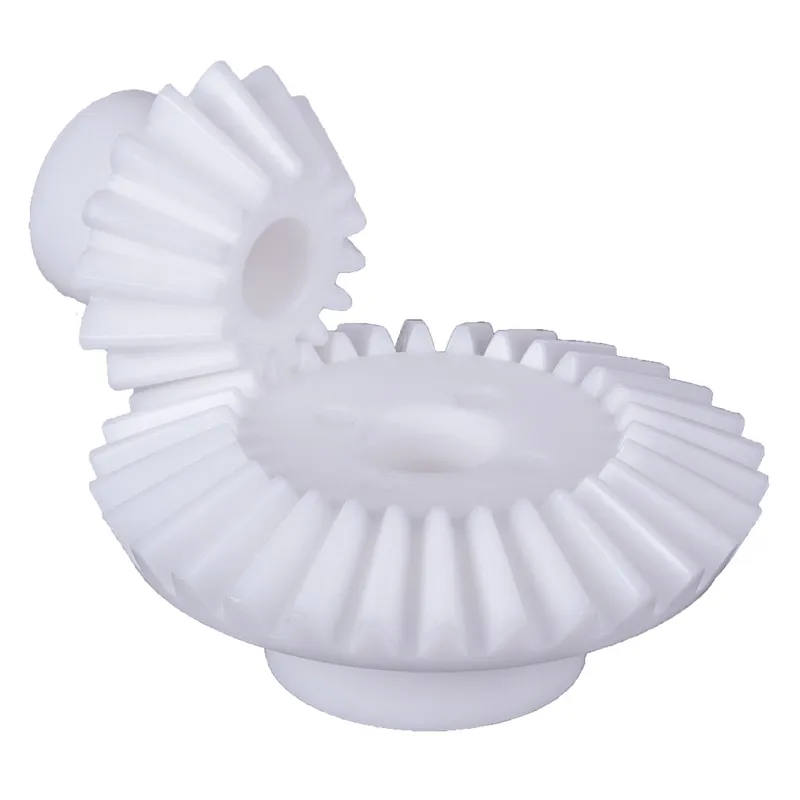
Steel Spiral Bevel Gears Ratio 1.615:1 Spiral Tooth System
Steel spiral bevel gears with a 1.615:1 ratio are specialized conical gears designed to transmit power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, with enhanced efficiency and smoothness compared to straight bevel gears. The spiral tooth system features curved, helical teeth that engage gradually, reducing noise, vibration, and impact stress, making them ideal for high-speed, high-torque applications.
Steel spiral bevel gears with a 1.615:1 ratio are specialized conical gears designed to transmit power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, with enhanced efficiency and smoothness compared to straight bevel gears. The spiral tooth system features curved, helical teeth that engage gradually, reducing noise, vibration, and impact stress, making them ideal for high-speed, high-torque applications.
The 1.615:1 ratio indicates that for every 1.615 rotations of the pinion (smaller gear), the mating gear completes one rotation, providing precise speed reduction or torque multiplication. Typically made from hardened steel like 42CrMo4 or 16MnCr5, these gears ensure durability and strength. They are commonly used in industrial machinery, automotive differentials, and power transmission systems requiring reliable, quiet operation.
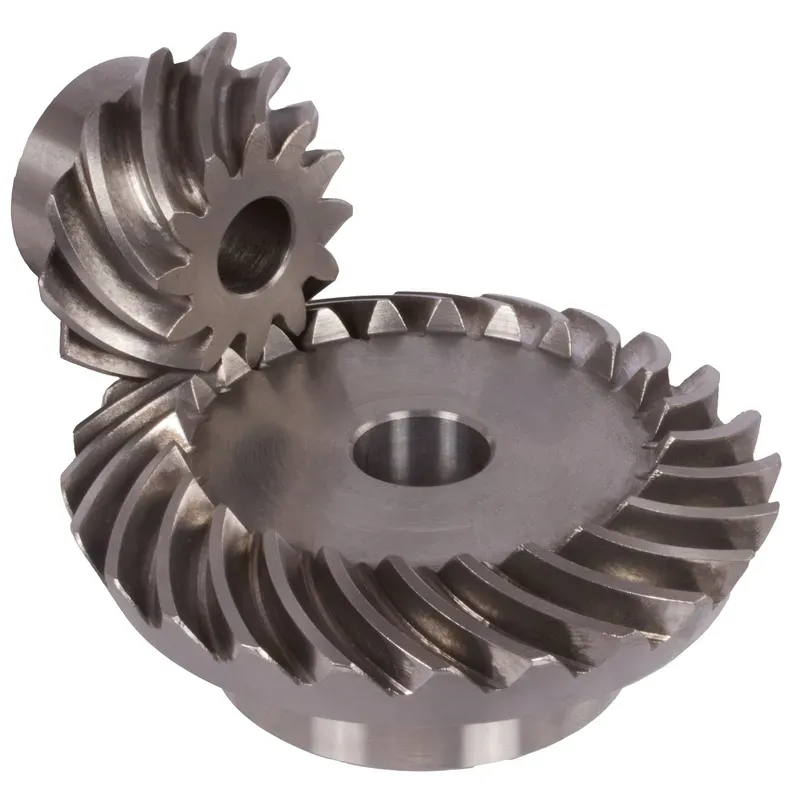

Steel Spiral Bevel Gear Ratio 1.615:1
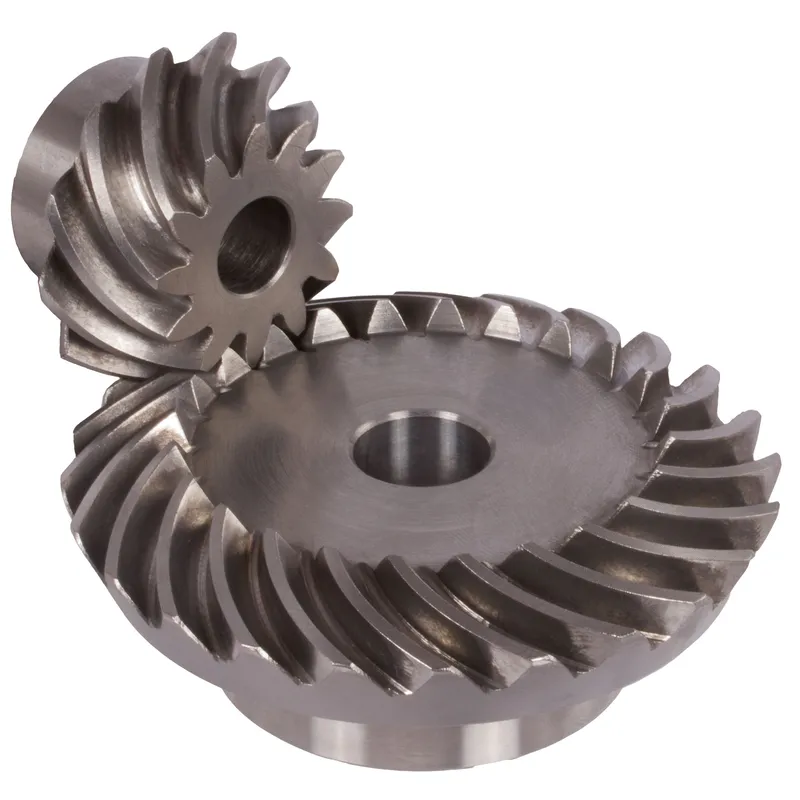 | 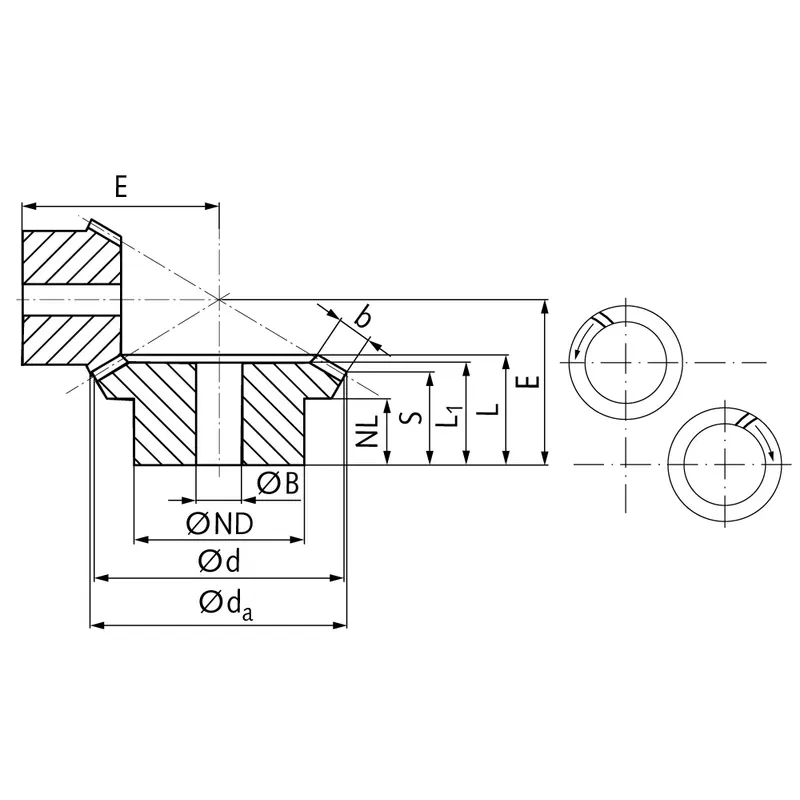 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 13 | 20,8 | 18,6 | 16 | 8,2 | 12 | 13,9 | 9,3 | 5 | 8 | 24 | 2,4 | 45 |
| 1 | 21 | 30,8 | 30,0 | 20 | 6 | 10,5 | 12,0 | 9,3 | 5 | 10 | 18 | 3,9 | 45 |
Steel Spiral Bevel Gear Function
Steel spiral bevel gears serve a crucial function in mechanical systems, particularly in transmitting rotational motion and torque between two shafts that are typically arranged at a 90-degree angle. These gears are designed with helical, curved teeth that are cut at an angle, allowing for a gradual engagement of teeth during operation. This unique design results in smoother, quieter, and more efficient power transmission compared to straight bevel gears, which can be noisy and less durable under heavy loads.
The primary function of steel spiral bevel gears is to transfer power between intersecting shafts with minimal energy loss, providing precise motion control and high torque transmission. Their curved tooth design ensures a larger contact area between the gear teeth, which distributes load more evenly and reduces stress points. This enhances durability and prolongs the lifespan of the gears, especially in high-speed or high-load applications.
The use of steel as the material adds significant strength, wear resistance, and the ability to withstand harsh operating conditions, such as high temperatures, heavy loads, or corrosive environments. Steel spiral bevel gears are commonly found in applications like automotive differentials, where they enable wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns, ensuring better handling and safety. They are also used in industrial machinery, aerospace systems, robotics, and marine equipment, where precise torque control and reliable performance are essential. Their ability to operate efficiently in demanding environments makes them indispensable in modern mechanical systems.
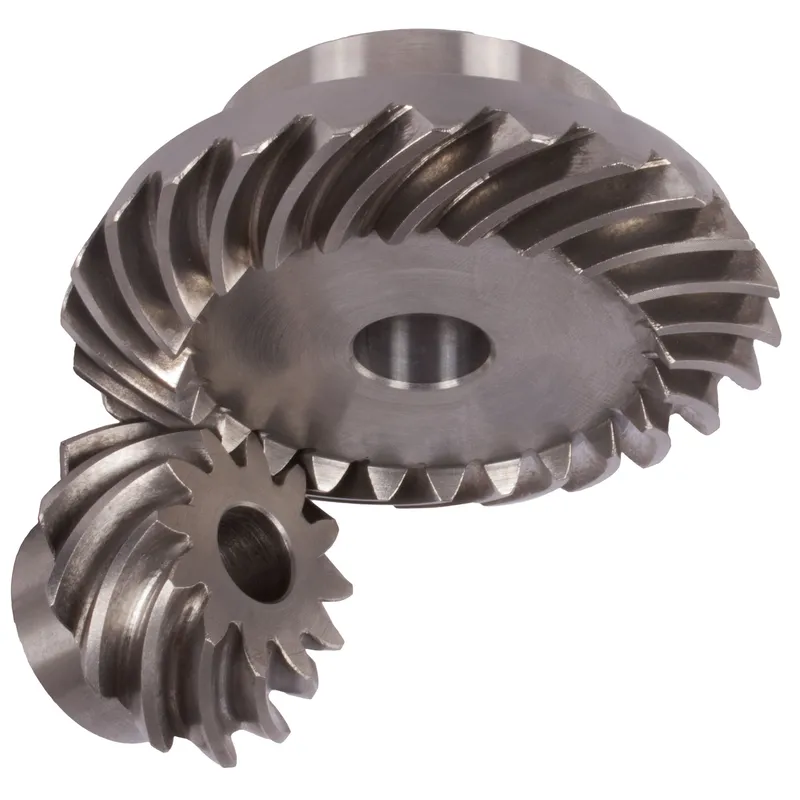

Applications of Steel Spiral Bevel Gears
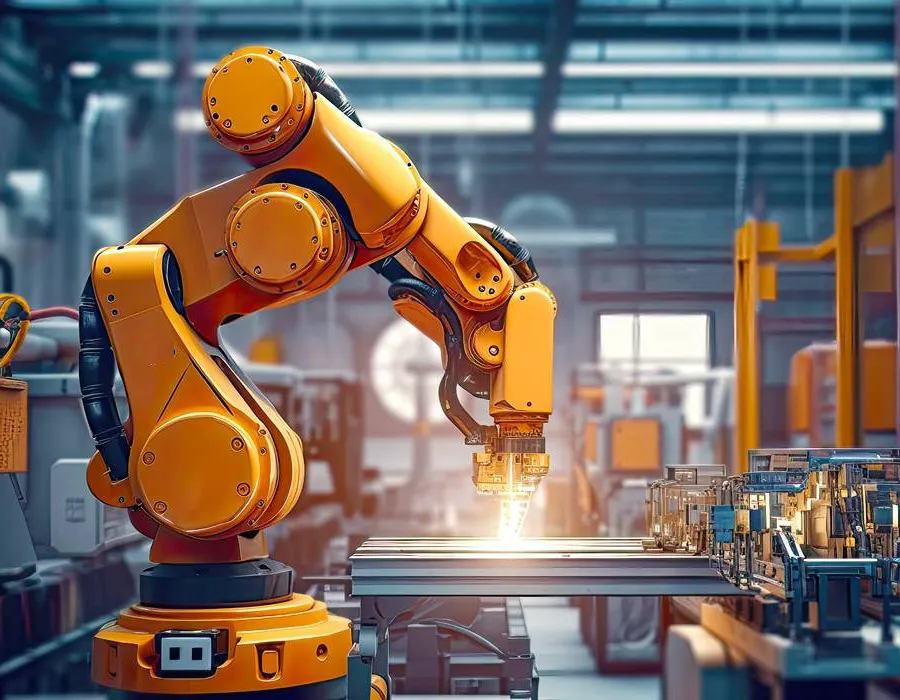
1. Automotive Differentials
Steel spiral bevel gears are widely used in automotive differentials to transfer power from the driveshaft to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds during turns. Their smooth operation ensures efficient torque distribution, improved handling, and reduced mechanical noise.
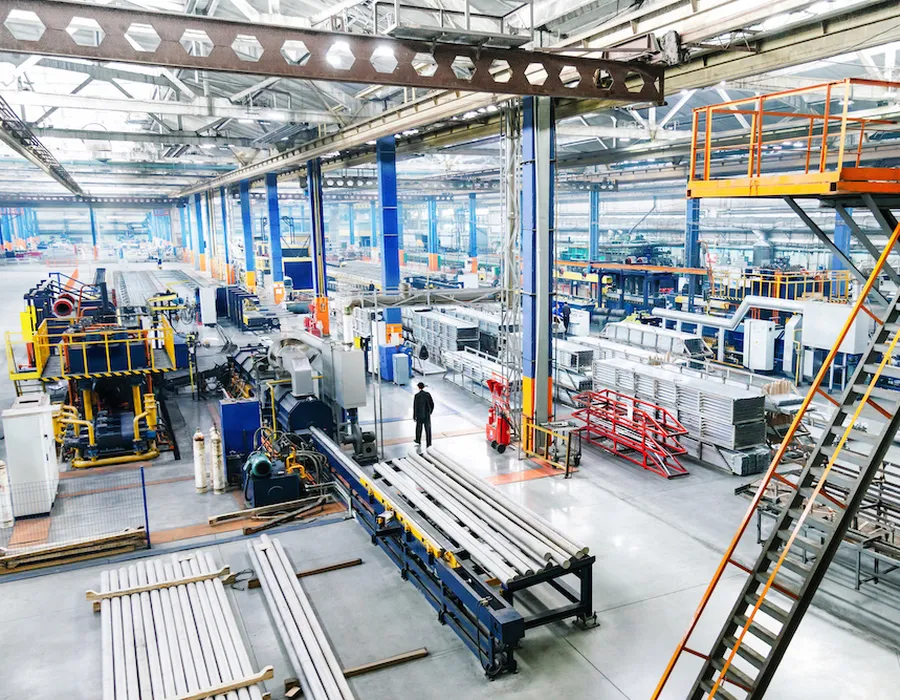
2. Industrial Machinery
In heavy-duty industrial equipment such as conveyor systems, compressors, and milling machines, spiral bevel gears provide reliable torque transmission between intersecting shafts. Their high durability and ability to handle significant loads make them indispensable in demanding manufacturing and processing environments.
3. Aerospace Systems
Aerospace applications require precision and reliability, and spiral bevel gears are used in helicopter transmissions and other aircraft components. Their curved teeth reduce vibration, ensure smooth operation, and withstand extreme conditions, including temperature fluctuations and high-pressure environments.
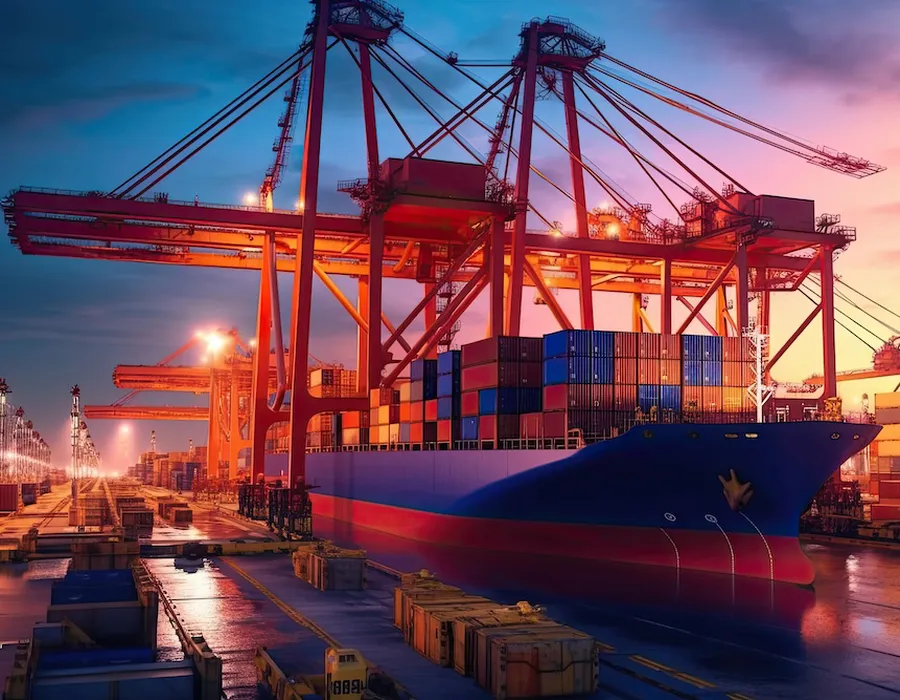
4. Marine Equipment
Marine propulsion systems, such as ship engines and thrusters, rely on spiral bevel gears to transfer power between engines and propellers. Their resistance to wear and corrosion, combined with smooth torque delivery, ensures reliable operation in harsh saltwater environments.
5. Robotics and Automation
In robotics and automated systems, spiral bevel gears allow for precise motion control and torque transmission in compact designs. Their ability to operate quietly and efficiently makes them ideal for sensitive applications like robotic arms, positioning systems, and servo mechanisms.
6. Power Generation Equipment
Spiral bevel gears are used in turbines and generators to transfer rotational motion between perpendicular shafts. Their robust construction ensures reliable performance, even under intense loads and high speeds, making them crucial in wind turbines and hydroelectric systems.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Automotive Differentials | Bevel Gear for Robotics |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Marine Equipment | Bevel Gear for Industrial Machinery |
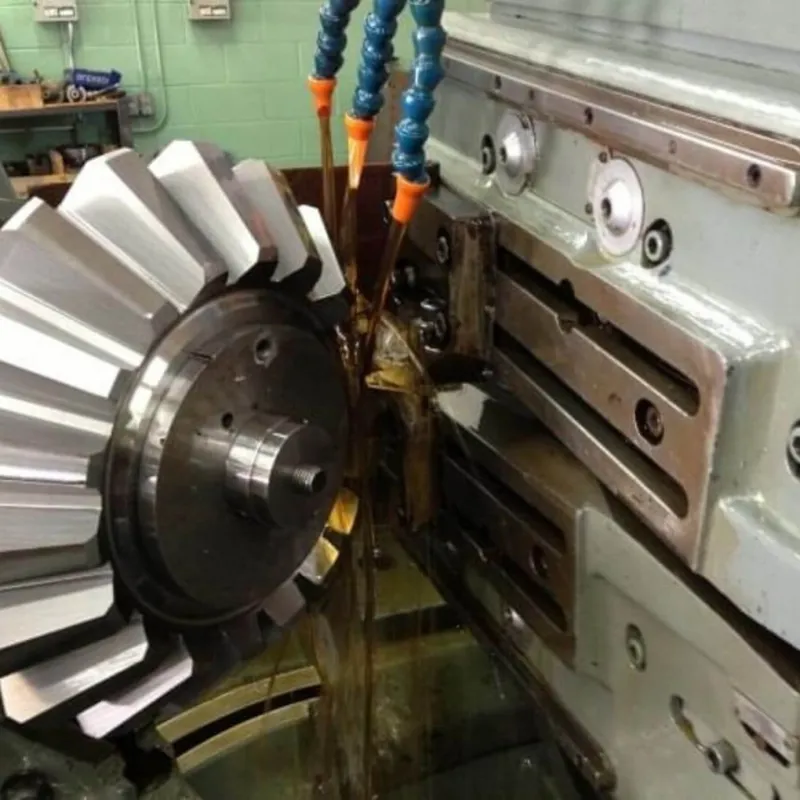
Spiral Bevel Gear Lubrication Steps
1. Select the Right Lubricant
Choose a lubricant specifically designed for spiral bevel gears. Consider factors such as viscosity, load-carrying capacity, temperature range, and anti-wear properties.
2. Ensure Adequate Lubricant Supply
It is important to ensure a sufficient amount of lubricant is supplied to the gear meshing area. This can be achieved through proper lubricant reservoir design, gear housing design, and lubricant distribution systems. The lubricant should reach all critical areas, including the gear teeth and the contact zone, to provide effective lubrication and cooling.
3. Maintain Proper Lubricant Viscosity
The lubricant’s viscosity should be suitable for the operating conditions, including the speed, load, and temperature of the gear system. Viscosity directly affects the lubrication film thickness and the ability to separate the gear surfaces, reducing friction and wear.
4. Monitor Lubricant Condition
Regularly monitor the condition of the lubricant to ensure its effectiveness. Check for contamination, degradation, or depletion of additives. Conduct oil analysis to assess the lubricant’s viscosity, acidity, and presence of wear particles. Replace the lubricant at recommended intervals or when it no longer meets the required specifications.
5. Maintain Proper Lubricant Cleanliness
Keep the lubricant clean and free from contaminants. Implement effective filtration systems, such as oil filters or magnetic separators, to remove dirt, debris, and metallic particles from the lubricant. Contaminants can accelerate wear and reduce gear performance.
6. Proper Lubricant Application
Apply the lubricant correctly to ensure complete coverage and effective lubrication. Follow the gear manual’s recommendations for the lubrication method, whether it is through oil bath, oil mist, oil jet, or forced lubrication systems. Pay attention to lubricant distribution across the gear surfaces and gear teeth, ensuring adequate coverage and film formation.

Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|


