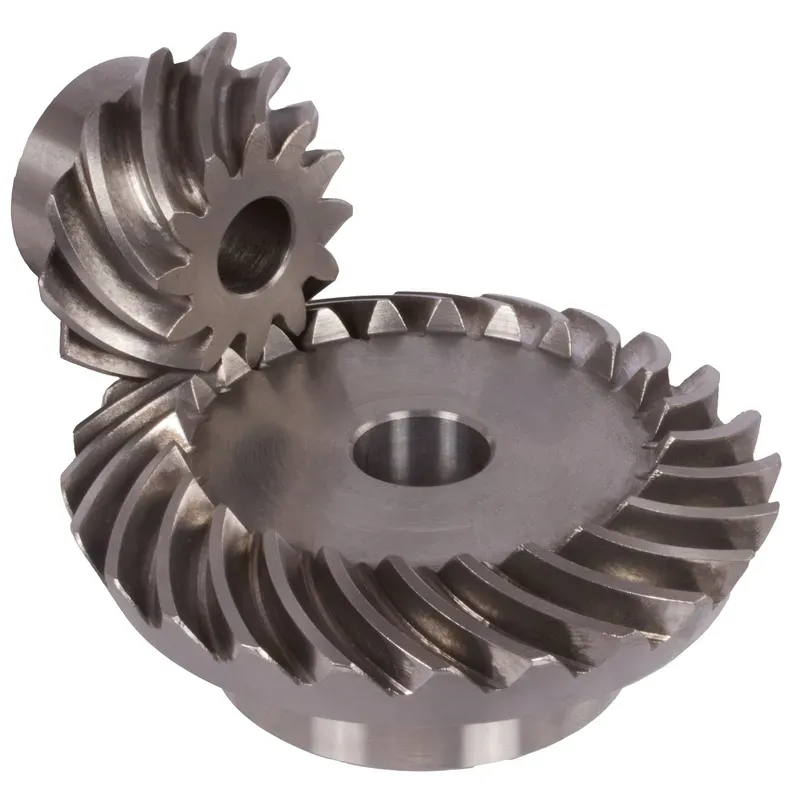
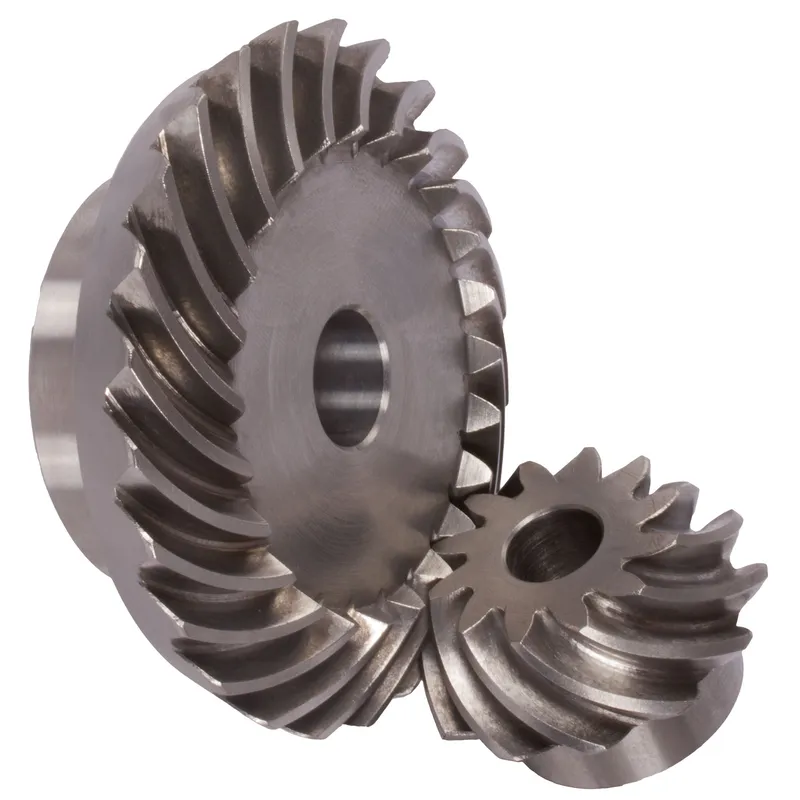
Stainless Steel Bevel Gears Ratio 1:1 – 4:1 Straight-Tooth System
Stainless steel bevel gears with ratios ranging from 1:1 to 4:1 in a straight-tooth system are mechanical components designed to transmit motion and torque between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. These gears feature straight teeth that are cut along the cone-shaped surface of the gear, enabling efficient power transfer while maintaining high precision and durability. The stainless steel bevel gears are suitable for demanding applications in industries such as food processing, marine, and chemical environments where hygiene and durability are critical.
Stainless steel bevel gears with ratios ranging from 1:1 to 4:1 in a straight-tooth system are mechanical components designed to transmit motion and torque between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. These gears feature straight teeth that are cut along the cone-shaped surface of the gear, enabling efficient power transfer while maintaining high precision and durability.
The 1:1 ratio means the input and output shafts rotate at the same speed, whereas ratios like 2:1, 3:1, or 4:1 allow for speed reduction or torque multiplication. Made from stainless steel, these bevel gears offer excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and longevity, making them suitable for demanding applications in industries such as food processing, marine, and chemical environments where hygiene and durability are critical.
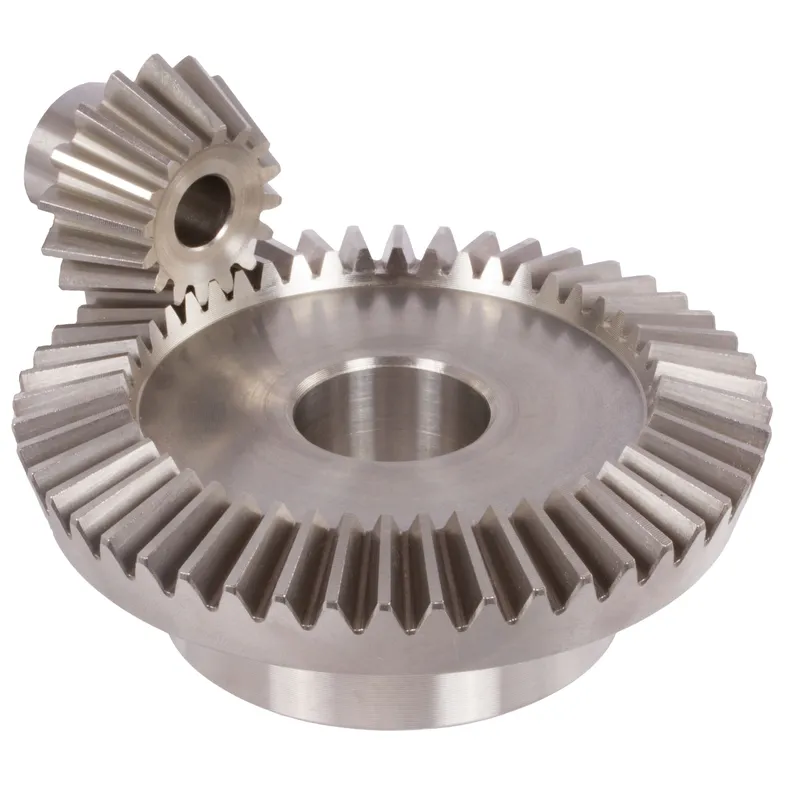

Stainless Steel Bevel Gear Ratio 1:1
 | 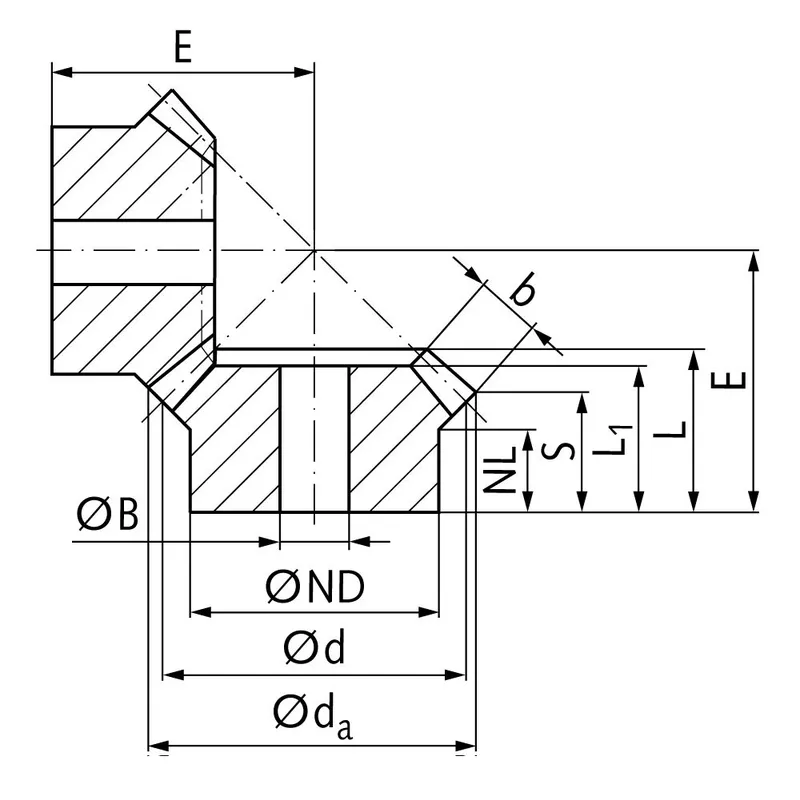 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 16 | 17,4 | 16 | 14 | 7 | 10 | 11,2 | 8,7 | 4,0 | 5 | 16 | 0,06 | 9 |
| 1,5 | 16 | 26,1 | 24 | 20 | 11 | 15 | 17,3 | 14,1 | 5,1 | 8 | 25 | 0,19 | 32 |
| 2 | 16 | 34,8 | 32 | 25 | 11,5 | 18 | 20,7 | 16,4 | 6,8 | 10 | 31 | 0,46 | 66 |
| 2,5 | 16 | 43,7 | 40 | 30 | 10 | 21 | 23,8 | 16,8 | 11 | 10 | 35 | 1,1 | 120 |
| 3 | 16 | 52,4 | 48 | 40 | 12 | 24 | 27,7 | 18,2 | 15 | 10 | 40 | 2,0 | 240 |
| 4 | 16 | 70,0 | 64 | 50 | 11 | 29 | 32,9 | 21,0 | 19 | 20 | 50 | 4,8 | 420 |
Stainless Steel Bevel Gear Ratio 2:1
 |  |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 15 | 17,4 | 15 | 13 | 6,5 | 11 | 11,9 | 7,6 | 5,0 | 5 | 22 | 0,08 | 10 |
| 1 | 30 | 30,6 | 30 | 20 | 9,0 | 13 | 15,1 | 13,1 | 5,0 | 5 | 20 | 0,16 | 40 |
| 1,5 | 15 | 26,1 | 22,5 | 18 | 6,5 | 13 | 14,8 | 8,4 | 7,6 | 8 | 30 | 0,27 | 26 |
| 1,5 | 30 | 45,9 | 45 | 30 | 12,0 | 18 | 20,7 | 17,6 | 7,6 | 10 | 28 | 0,54 | 124 |
| 2 | 15 | 33,7 | 30 | 20 | 7,5 | 22 | 23,0 | 10,9 | 14 | 10 | 40 | 0,78 | 58 |
| 2 | 30 | 61,8 | 60 | 40 | 12,0 | 24 | 27,2 | 21,9 | 14 | 15 | 35 | 1,56 | 312 |
| 2,5 | 15 | 42,2 | 37,5 | 30 | 15,6 | 31 | 33,3 | 18,6 | 17 | 10 | 55 | 1,6 | 160 |
| 2,5 | 30 | 77,3 | 75 | 50 | 10,0 | 24 | 28,1 | 21,6 | 17 | 15 | 38 | 3,2 | 530 |
| 3 | 15 | 50,6 | 45 | 30 | 11,5 | 33 | 35,4 | 16,4 | 22 | 10 | 60 | 2,8 | 270 |
| 3 | 30 | 92,8 | 90 | 50 | 10,0 | 26 | 30,7 | 22,3 | 22 | 20 | 42 | 5,6 | 750 |
| 4 | 15 | 67,5 | 60 | 40 | 10,0 | 38 | 41,0 | 16,9 | 28 | 20 | 75 | 6,0 | 410 |
| 4 | 30 | 123,8 | 120 | 60 | 15,0 | 33 | 39,4 | 28,8 | 28 | 25 | 55 | 12,0 | 1600 |
Stainless Steel Bevel Gear Ratio 3:1
 |  |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 15 | 17,7 | 15 | 13 | 9,2 | 16 | 16,5 | 10,0 | 7,1 | 5 | 32 | 0,10 | 14 |
| 1 | 45 | 45,4 | 45 | 25 | 10 | 15 | 17,0 | 15,1 | 7,1 | 8 | 22 | 0,30 | 92 |
| 1,5 | 16 | 28,0 | 24 | 18 | 11 | 22 | 23,2 | 12,7 | 11,4 | 8 | 48 | 0,45 | 42 |
| 1,5 | 48 | 72,6 | 72 | 50 | 12 | 20 | 24,1 | 20,8 | 11,4 | 15 | 32 | 1,35 | 405 |
| 2 | 16 | 35,9 | 32 | 20 | 10 | 25 | 26,6 | 12,6 | 15 | 10 | 60 | 1,21 | 80 |
| 2 | 48 | 97,3 | 96 | 60 | 18 | 30 | 35,0 | 31,0 | 15 | 25 | 45 | 3,63 | 95 |
| 2,5 | 16 | 44,9 | 40 | 30 | 15 | 34 | 36,5 | 17,8 | 20 | 10 | 77 | 2,6 | 200 |
| 2,5 | 48 | 121,6 | 120 | 80 | 15 | 29 | 33,9 | 28,5 | 20 | 25 | 46 | 7,8 | 1600 |
| 3 | 16 | 53,9 | 48 | 40 | 12,5 | 36 | 38,3 | 15,0 | 25 | 15 | 86 | 4,6 | 310 |
| 3 | 48 | 145,9 | 144 | 70 | 18 | 34 | 38,7 | 32,0 | 25 | 30 | 53 | 13,8 | 2300 |
| 4 | 16 | 71,8 | 64 | 50 | 17 | 46 | 48,3 | 20,3 | 30 | 20 | 115 | 9,4 | 680 |
| 4 | 48 | 194,6 | 192 | 90 | 20 | 43 | 50,0 | 41,9 | 30 | 30 | 70 | 28,2 | 5700 |
Stainless Steel Bevel Gear Ratio 4:1
 |  |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 15 | 17,8 | 15 | 13 | 7,7 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 8,4 | 9,3 | 5 | 38 | 0,14 | 15 |
| 1 | 60 | 60,3 | 60 | 30 | 10,0 | 15 | 17,1 | 15,1 | 9,3 | 8 | 22 | 0,56 | 160 |
| 1,5 | 15 | 26,7 | 22,5 | 18 | 14,45 | 28 | 28,9 | 15,5 | 13,9 | 8 | 60 | 0,48 | 42 |
| 1,5 | 60 | 90,4 | 90 | 50 | 12,0 | 25 | 27,6 | 24,6 | 13,9 | 15 | 35 | 1,92 | 745 |
| 2 | 15 | 34,0 | 30 | 20 | 13,5 | 29 | 29,9 | 15,5 | 15 | 10 | 75 | 1,34 | 80 |
| 2 | 60 | 120,9 | 120 | 60 | 20,0 | 35 | 40,1 | 37,0 | 15 | 25 | 50 | 5,36 | 1600 |
| 2,5 | 15 | 42,5 | 37,5 | 30 | 16,1 | 35 | 36,8 | 17,6 | 20 | 10 | 92 | 2,5 | 190 |
| 2,5 | 60 | 151,2 | 150 | 80 | 18,0 | 33 | 37,8 | 33,8 | 20 | 25 | 50 | 10,0 | 2600 |
| 3 | 15 | 51,0 | 45 | 30 | 13,15 | 38 | 39,7 | 15,7 | 25 | 10 | 105 | 4,4 | 270 |
| 3 | 60 | 181,5 | 180 | 80 | 18,0 | 35 | 40,6 | 35,5 | 25 | 30 | 55 | 17,6 | 3800 |
| 4 | 15 | 68,0 | 60 | 40 | 12,5 | 43 | 44,8 | 16,0 | 30 | 20 | 135 | 8,9 | 520 |
| 4 | 60 | 242,0 | 240 | 90 | 20,0 | 41 | 50,1 | 44,0 | 30 | 30 | 70 | 35,6 | 8300 |
Stainless Steel Bevel Gear Advantages
- Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel bevel gears, often made from grades like SUS303 or 1.4305, resist rust and chemical degradation. This makes them ideal for harsh environments such as marine, food processing, or chemical industries, ensuring long-term durability and minimal maintenance. - High Strength and Durability
The robust nature of stainless steel provides exceptional strength, allowing these gears to handle significant loads and stresses. This durability ensures reliable performance in demanding applications, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintaining operational efficiency over extended periods. - Precision Power Transmission
With gear ratios from 1:1 to 4:1, straight-tooth bevel gears deliver precise speed and torque transfer between intersecting shafts, typically at 90 degrees. This accuracy is critical for machinery requiring consistent rotational motion, enhancing overall system reliability and performance. - Hygienic Properties
Stainless steel’s non-porous surface resists bacterial growth, making these gears suitable for food and beverage or pharmaceutical applications. Their ability to withstand frequent cleaning with harsh chemicals ensures compliance with strict hygiene standards without compromising structural integrity. - Versatility in Applications
These bevel gears are adaptable to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Their ability to function effectively in diverse conditions, from high-humidity environments to heavy-duty mechanical systems, makes them a versatile choice for engineers and designers. - Ease of Maintenance
Stainless steel bevel gears require minimal upkeep due to their corrosion-resistant and wear-resistant properties. This reduces downtime and maintenance costs, as the gears can endure prolonged use without significant wear, even in challenging operating conditions.
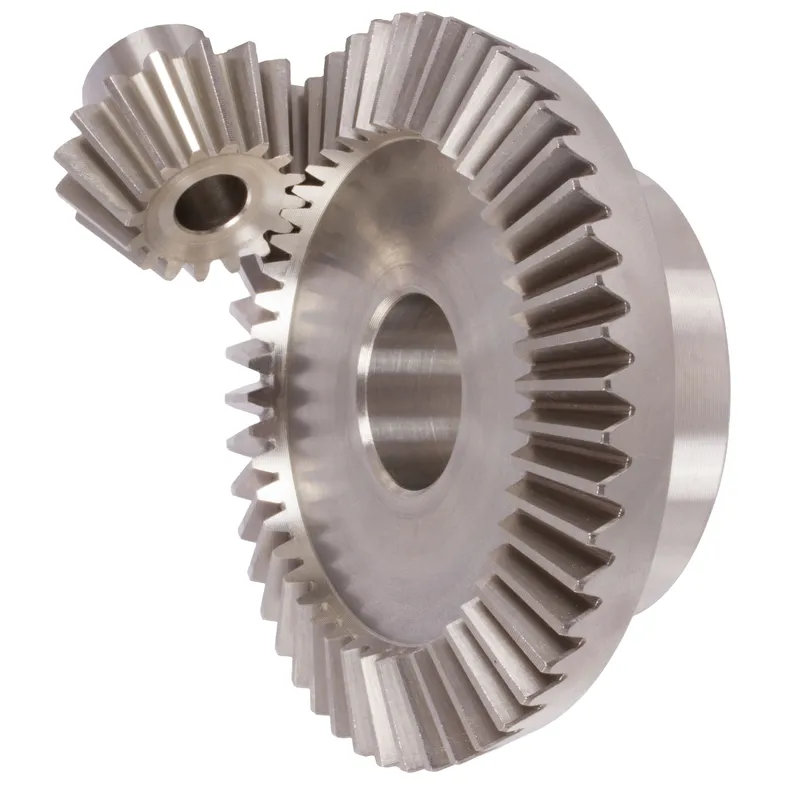

How Do Bevel Gears Work
Bevel gears are designed to transmit power and motion between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. The teeth of bevel gears are formed on conical surfaces, allowing them to mesh and transfer torque efficiently.
The working principle of bevel gears involves the meshing of teeth on two cone-shaped gear wheels. The cone angles of these gears are designed such that the pitch surfaces of the teeth roll on each other without slipping. This rolling action enables the smooth transmission of power and rotation between the intersecting shafts.
In a bevel gear system, the pinion is the smaller gear that drives the larger gear, known as the crown gear or ring gear. The pinion is typically mounted on the input shaft, while the crown gear is attached to the output shaft. As the pinion rotates, its teeth engage with the teeth of the crown gear, causing it to rotate as well.
The gear ratio of bevel gears is determined by the number of teeth on the pinion and the crown gear. A higher gear ratio indicates that the crown gear has more teeth than the pinion, resulting in a speed reduction and torque multiplication. Conversely, a lower gear ratio means that the pinion has more teeth than the crown gear, leading to a speed increase and torque reduction.
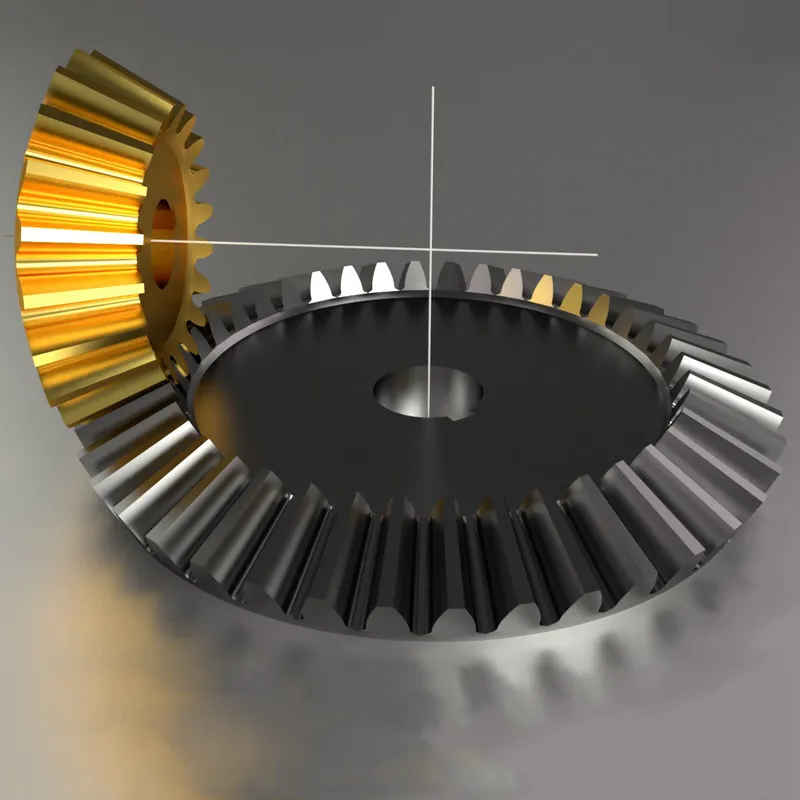

Stainless Steel Bevel Gear Applications
Food and Beverage Industry
Stainless steel bevel gears are widely used in food processing equipment due to their hygienic properties and resistance to corrosion. They are ideal for applications requiring frequent cleaning, such as mixers, conveyors, and packaging machines, ensuring compliance with stringent hygiene standards.
Power Transmission in Automobiles
Bevel gears find extensive use in the automotive industry, particularly in differential drives. In a differential, bevel gears are used to split the power from the driveshaft and transmit it to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds. This enables smooth cornering and improved traction control. Bevel gears are also used in various other automotive applications, such as transfer cases and steering systems.
Industrial Machinery
Stainless steel bevel gears are commonly used in industrial machinery where power needs to be transmitted between intersecting shafts. They are found in a wide range of equipment, including gearboxes, speed reducers, and power transmission systems. Industrial applications that utilize bevel gears include mining machinery, construction equipment, printing presses, and textile machinery.
Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace and aviation industries rely on stainless steel bevel gears for power transmission in various applications. Bevel gears are used in aircraft engines, rotor drive systems, and accessory gearboxes. They are designed to handle high loads and provide reliable performance in demanding operating conditions. The compact design and ability to transmit power between non-parallel shafts make bevel gears well-suited for aerospace applications where space is limited.
Marine Applications
Bevel gears are employed in marine applications for power transmission in propulsion systems, steering systems, and deck machinery. They are used in marine gearboxes, thrusters, and winches. The ability of bevel gears to handle high torque loads and withstand harsh marine environments makes them suitable for these applications. Marine bevel gears are often manufactured from corrosion-resistant materials to ensure durability and reliability.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Automotive Industry | Bevel Gear for Marine Industry |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Aerospace Industry | Bevel Gear for Food Industry |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|


