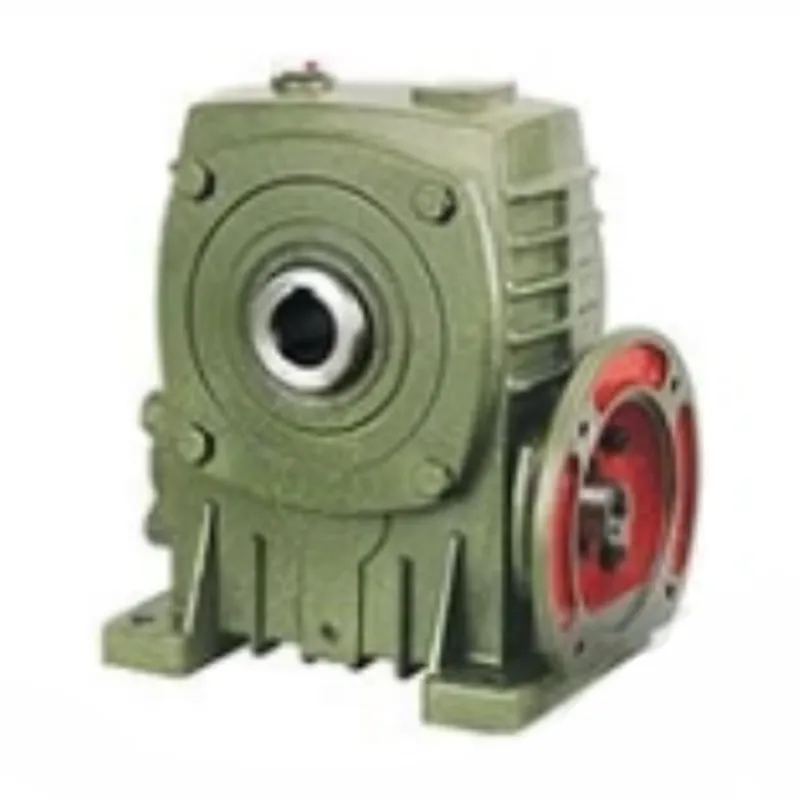
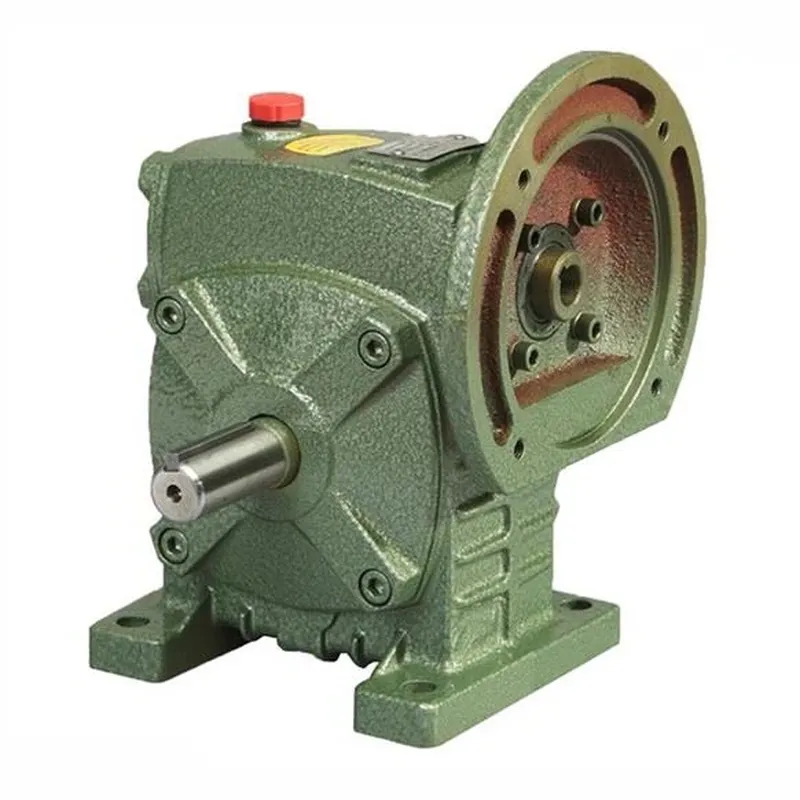
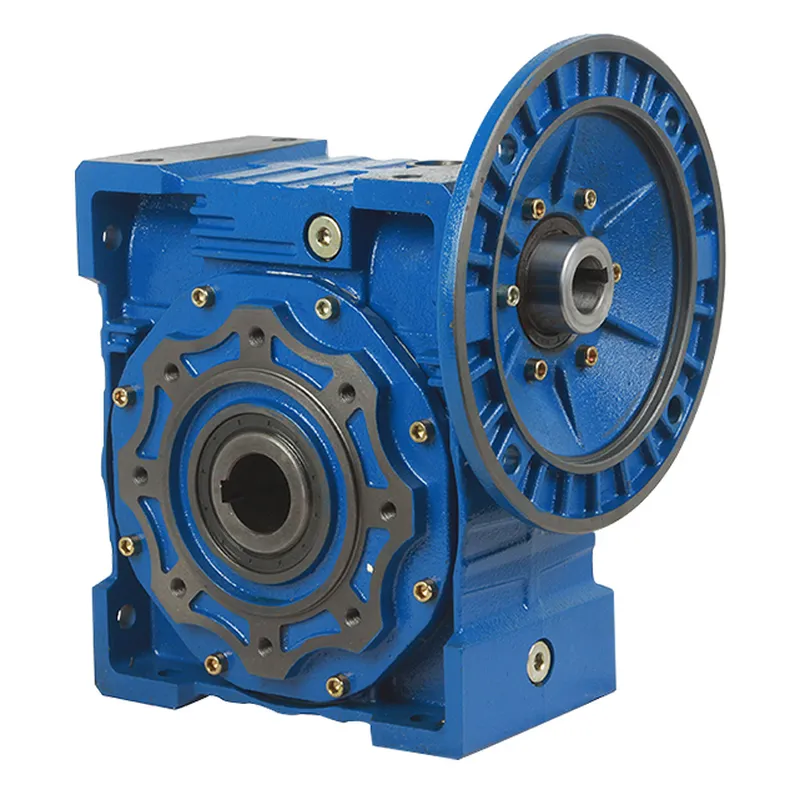
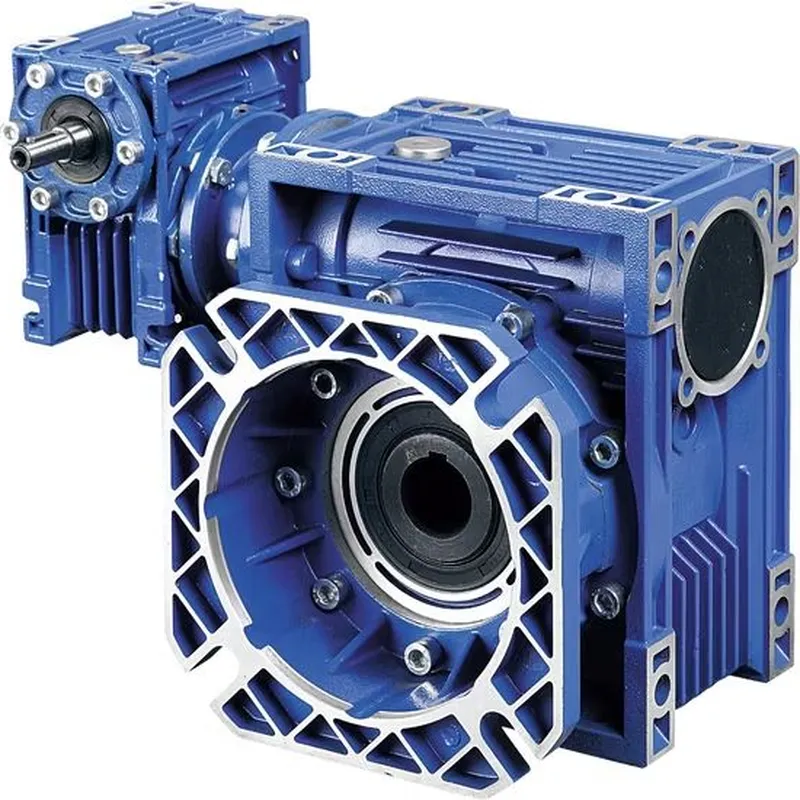
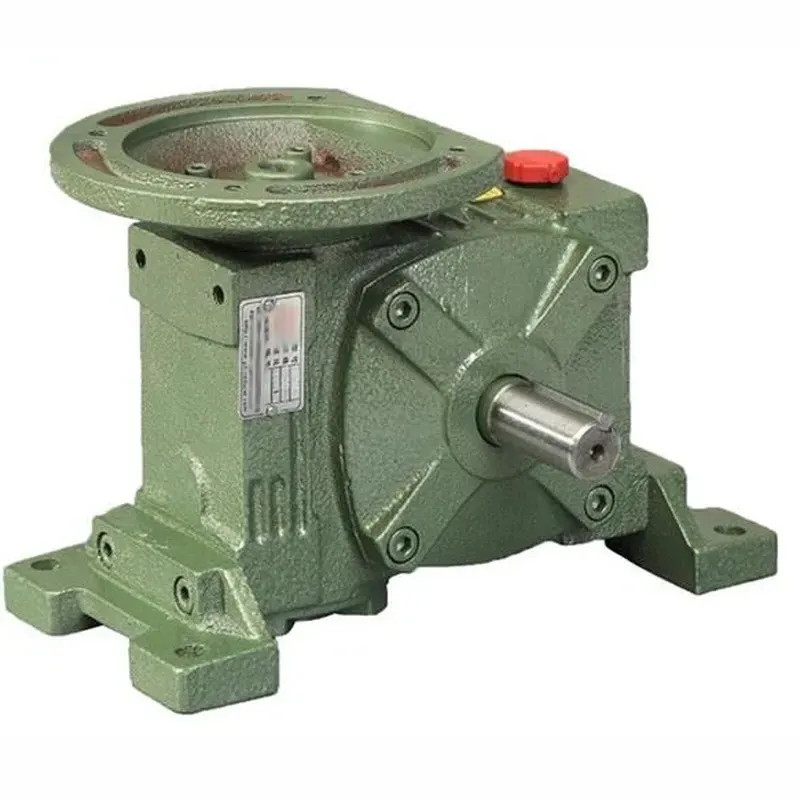
WPWDT Worm Gear Reducers/Worm Gearbox
WPWDT worm gear reducers, commonly referred to as worm gearboxes, are specialized mechanical devices designed to reduce rotational speed while amplifying torque, using a worm gear mechanism. The WPWDT worm gearbox is part of the renowned WP series worm gear speed reducer and features a robust cast iron housing for enhanced durability. It employs a single-stage worm gear system that consists of a worm (a helical input gear) and a worm wheel (a spur-like output gear), arranged at a 90-degree angle for efficient power transmission.
WPWDT worm gear reducers, commonly referred to as worm gearboxes, are specialized mechanical devices designed to reduce rotational speed while amplifying torque, using a worm gear mechanism. The WPWDT worm gearbox is part of the renowned WP series worm gear speed reducer and features a robust cast iron housing for enhanced durability. It employs a single-stage worm gear system that consists of a worm (a helical input gear) and a worm wheel (a spur-like output gear), arranged at a 90-degree angle for efficient power transmission.
These reducers offer flexibility with configurations such as solid or hollow output shafts and horizontal or vertical mounting options, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, including conveyors, material handling, and machinery. With gear ratios ranging from 5:1 to 60:1, WPWDT worm reducer gearboxes deliver high torque in a compact, space-efficient design. They are particularly valued for their durability, low noise operation, and self-locking capability at higher ratios (typically 50:1 or more), which prevents back-driving, enhancing safety in applications like hoisting or lifting systems.
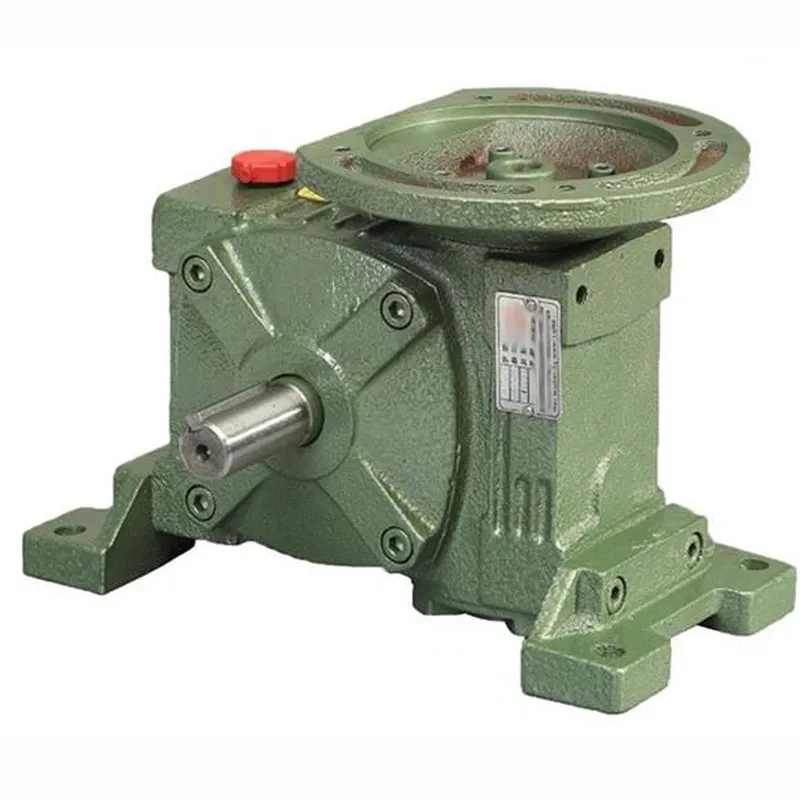

WPWDT Worm Gear Reducer Specifications
| Type: | WPWDT Worm Gearbox/ Worm Gear Speed Reducer |
| Model: | 40,50,60,70,80,100,120,135,155,175,200,250 |
| Ratio: | 10,15,20,25,30,40,50,60 |
| Color: | Blue/Green/Black/Customized |
| Material: | Housing: Die-Cast Iron cast |
| Worm Gear: Copper-9-4# | |
| Worm: 20CrMn Ti with carburizing and quenching, surface hardness is 56-62HRC | |
| Shaft: chromium steel-45# | |
| Packing: | Carton and Wooden Case |
| Bearing: | C&U/SKF/HRB, or on customer request |
| Seal: | NAK/SKF/KSK, or on customer request |
| Warranty: | 12Months |
| Input Power: | 0.12kw~15kw |
| Usages: | Plastics, metallurgy, beverages, mining, lifting and transportation, chemical construction, and so on. |
| IEC Flange: | B5 |
| Lubricant: | Synthetic & Mineral |
WPWDT Worm Gearbox Dimensions
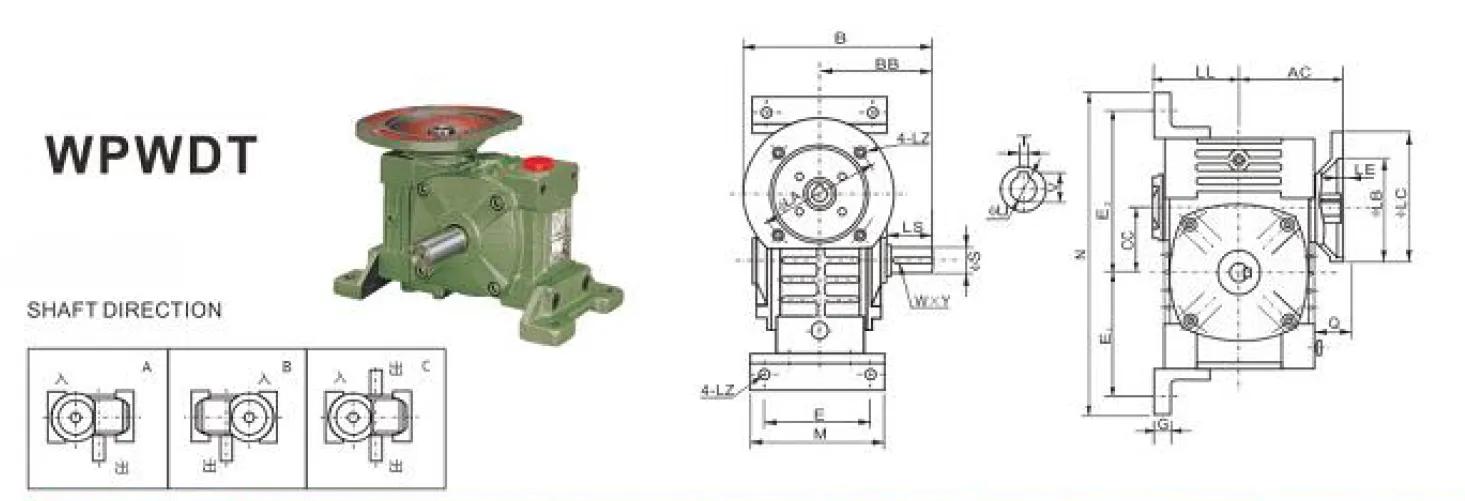
| Model | Input Power (kW) | Ratio | AC | BB | CC | LL | M | N | E | E1 | E2 | G | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0.12 | 1/5 1/10 1/15 1/20 1/25 1/30 1/40 1/50 1/60 | 75 | 79 | 40 | 63 | 90 | 187 | 70 | 72 | 97 | 12 | 10 |
| 50 | 0.18 | 83 | 97 | 50 | 70 | 120 | 226 | 95 | 90 | 110 | 14 | 12 | |
| 60 | 0.37 | 91 | 112 | 60 | 80 | 130 | 257 | 105 | 102 | 129 | 15 | 12 | |
| 70 | 0.37 0.75 | 109 111 | 131 | 70 | 95 | 150 | 305 | 115 | 120 | 155 | 20 | 15 | |
| 80 | 0.75 1.5 | 125 | 142 | 80 | 105 | 170 | 350 | 135 | 140 | 180 | 20 | 15 | |
| 100 | 1.5 | 148 | 160 | 100 | 135 | 190 | 410 | 155 | 165 | 215 | 22 | 15 | |
| 120 | 2.2 3.0 | 181 | 190 | 120 | 160 | 230 | 494 | 180 | 195 | 255 | 25 | 18 | |
| 135 | 3.0 4.0 | 202 | 210 | 135 | 185 | 250 | 559 | 200 | 230 | 285 | 30 | 18 | |
| 155 | 5.5 | 247 | 256 | 155 | 220 | 275 | 605 | 220 | 250 | 305 | 35 | 21 | |
| 175 | 5.5 7.5 | 258 | 282 | 175 | 240 | 310 | 675 | 250 | 273 | 348 | 40 | 21 | |
| 200 | 11.0 | 285 | 305 | 200 | 280 | 360 | 749 | 290 | 305 | 390 | 40 | 24 | |
| 250 | 11.0 15.0 | 330 | 360 | 250 | 315 | 460 | 920 | 380 | 375 | 475 | 45 | 28 |
| Flange | Input hole | Output shaft | Weight | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA | LB | LC | LE | LZ | Q | U | T×V | LS | S | W×Y | (kg) |
| 115 | 95 | 140 | 4 | M8 | 31 | 11 | 4×12.8 | 28 | 14 | 5×3 | 5.4 |
| 115 | 95 | 140 | 4 | M8 | 31 | 11 | 4×12.8 | 40 | 17 | 5×3 | 8.5 |
| 130 | 110 | 160 | 4 | M8 | 33 | 14 | 5×16.3 | 50 | 22 | 6×3.5 | 12 |
| 130 | 110 | 160 | 4 | M8 | 40 | 14 | 5×16.3 | 60 | 28 | 8×4 | 17 |
| 165 | 130 | 200 | 4 | M10 | 42 | 19 | 6×21.8 | 60 | 28 | 8×4 | 17 |
| 165 | 130 | 200 | 4.5 | M10 | 48 | 19 | 6×21.8 | 65 | 32 | 10×5 | 26 |
| 165 | 130 | 200 | 4.5 | M10 | 52 | 24 | 8×27.3 | 75 | 38 | 10×5 | 40.5 |
| 215 | 180 | 250 | 5 | M12 | 63 | 28 | 8×31.3 | 85 | 45 | 14×5.5 | 59 |
| 215 | 180 | 250 | 5 | M12 | 63 | 28 | 8×31.3 | 95 | 55 | 16×6 | 89 |
| 215 | 180 | 250 | 5 | M12 | 63 | 28 | 8×31.3 | 110 | 60 | 18×7 | 138 |
| 265 | 230 | 300 | 5 | M12 | 83 | 38 | 10×41.3 | 110 | 65 | 18×7 | 172 |
| 265 | 230 | 300 | 5 | M12 | 83 | 38 | 10×41.3 | 125 | 70 | 20×7.5 | 246 |
| 300 | 250 | 350 | 6 | M16 | 114 | 42 | 12×45.3 | 155 | 90 | 25×9 | 410 |
WPWDT Worm Reducer Gearbox Part Structure
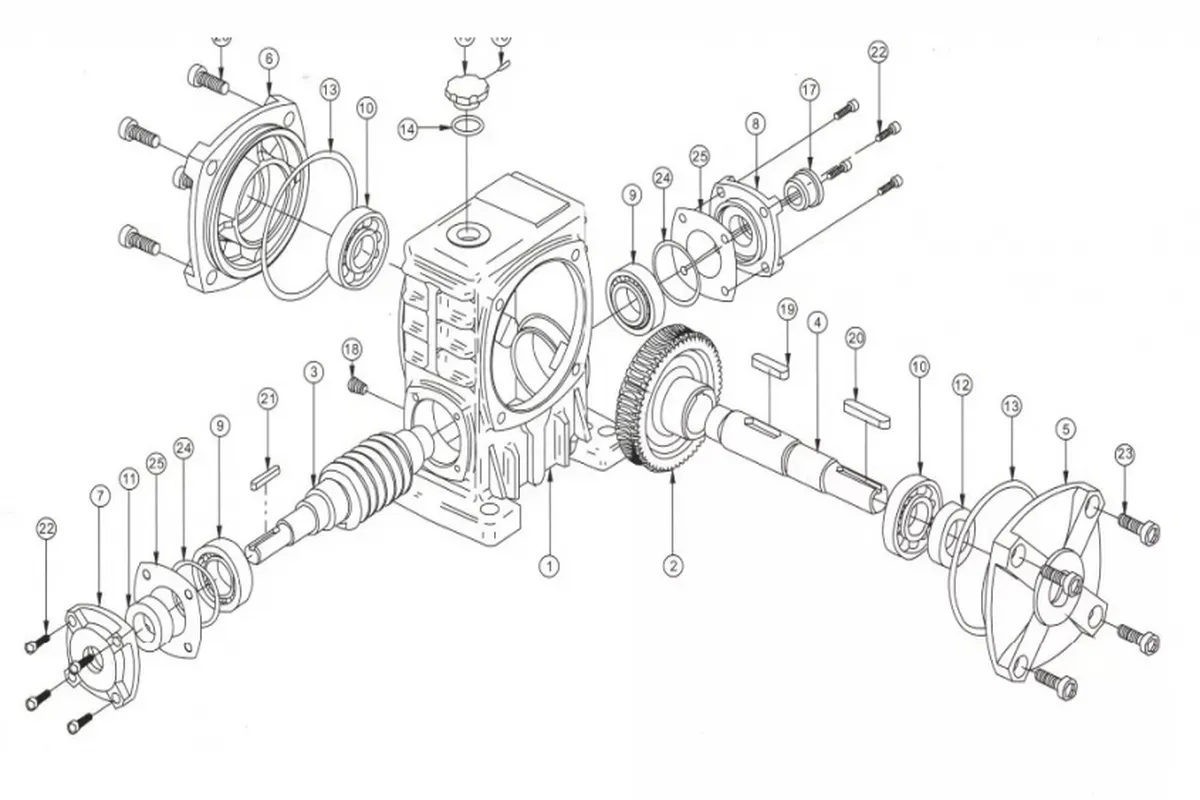
| 1 | Frame | 13 | O Ring |
| 2 | Worm Wheel | 14 | O Ring |
| 3 | Worm Shaft | 15 | Oil Hole Cover |
| 4 | Output Shaft | 16 | Pin |
| 5 | Output Shaft Cover | 17 | Oil Guage |
| 6 | Output Shaft Cover | 18 | Oil Plug |
| 7 | Input Shaft Cover | 19 | Key |
| 8 | Input Shaft Cover | 20 | Key |
| 9 | Bearing | 21 | Key |
| 10 | Bearing | 22 | Intl.hex Screw |
| 11 | Oil Seal | 23 | Intl.hex Screw |
| 12 | Oil Seal | 24 | Shim |
WPWDT Worm Gear Speed Reducer Benefits

WPWDT Worm and Wheel Gearbox Applications
- Conveyor Systems in Manufacturing
WPWDT worm and wheel gearboxes are widely used in conveyor systems to control speed and provide high torque for moving heavy loads. Their compact design and ability to handle continuous operation make them ideal for manufacturing lines, packaging systems, and material transport applications. - Lifting and Hoisting Equipment
The self-locking capability of worm reducer gearboxes at higher gear ratios ensures safety and stability in lifting and hoisting systems. They are commonly found in cranes, elevators, and winches, where preventing back-driving is essential to avoid accidents and ensure precise load control during operations. - Automated Machinery in Industrial Processes
WPWDT worm drive gearboxes are integral to automated machinery, where precise speed reduction and torque control are critical. They are used in robotics, CNC machines, and assembly lines to deliver smooth, efficient power transmission, enabling accurate and reliable operation in repetitive and high-precision tasks. - Material Handling Equipment
In material handling applications like forklifts, pallet jacks, and automated guided vehicles, worm gear gearboxes provide the necessary torque to move heavy loads efficiently. Their durability and ability to operate in confined spaces make them a reliable choice for such demanding environments. - Mixers and Processing Equipment
In industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals, WPWDT worm gear reducers are used in mixers, crushers, and other processing equipment. Their ability to provide precise speed control and high torque ensures consistent and efficient operation, even under heavy or variable loads. Textile Machinery: WPWDT worm gear speed reducers are used in textile equipment, such as spinning and weaving machines. Their smooth operation and wide range of gear ratios enable precise control of rotational speeds, ensuring consistent fabric production while minimizing noise and vibration in manufacturing facilities.
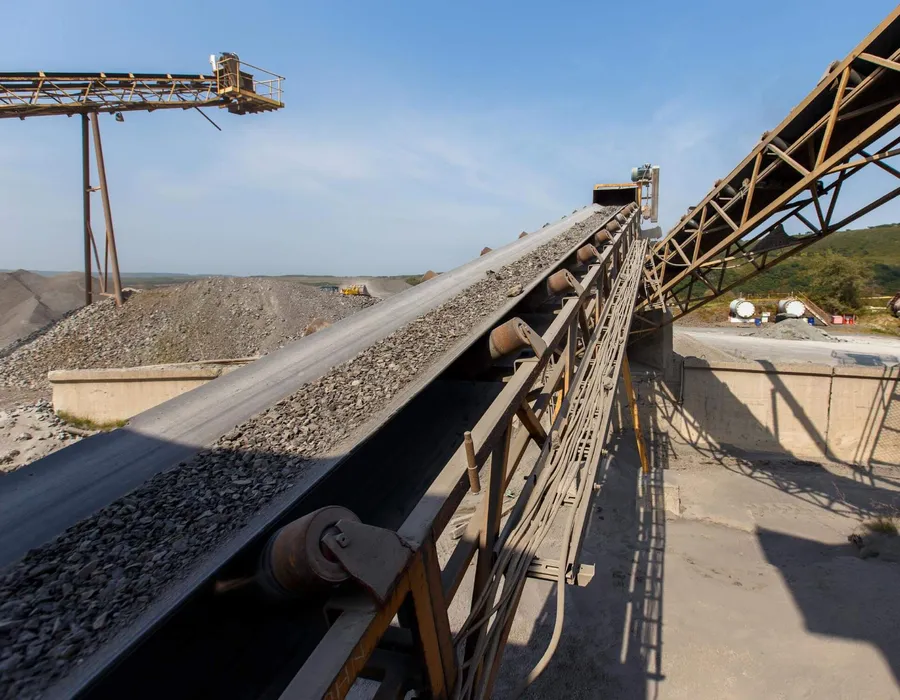 |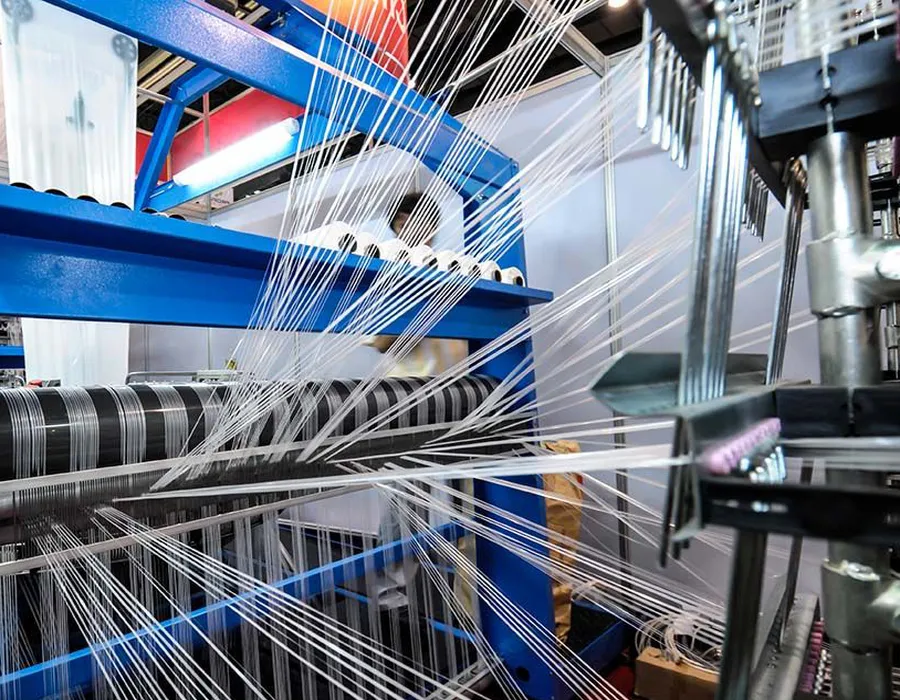  |
| Worm Gearbox for Conveyor Equipment | Worm Gearbox for Textile Industry |
 |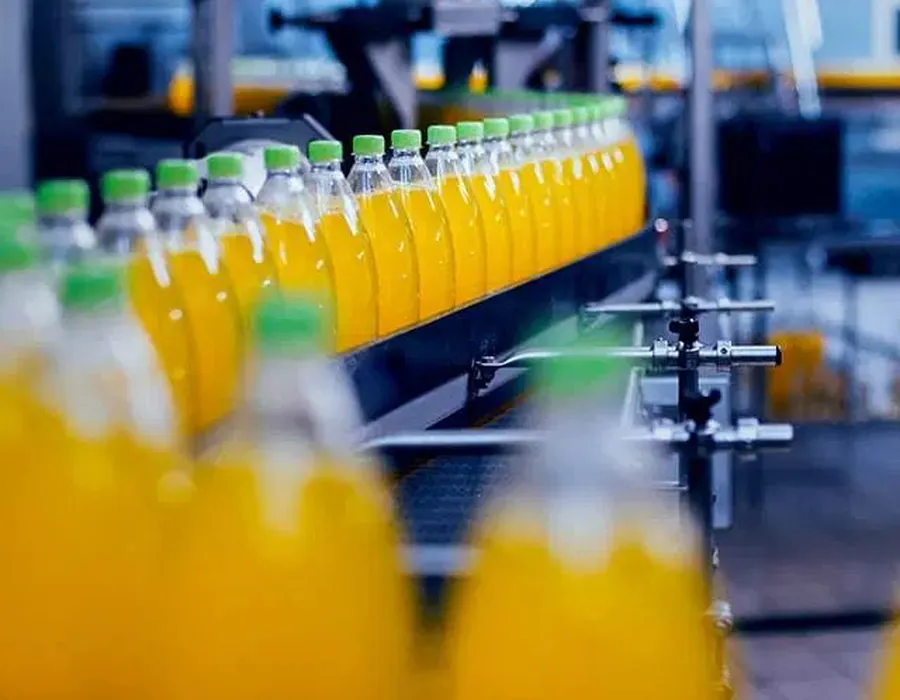  |
| Worm Gearbox for Construction Industry | Worm Gearbox for Food and Beverage Industry |
Difference Between Worm Gearbox and Helical Gearbox
What Is Helical Gearbox
A helical gearbox uses gears with teeth that are cut at an angle to the axis of the gear. The angled teeth allow the gears to mesh gradually, resulting in smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears. Helical gearboxes are widely used in applications that require high power transmission efficiency and low noise levels.
The angled teeth of helical gears create thrust loads that act parallel to the gear shaft. To accommodate these thrust loads, helical gearboxes typically incorporate thrust bearings or other means of axial load support. The helix angle of the gear teeth can vary, with higher angles providing greater load capacity but also increased axial thrust.
What Is Worm Gearbox
A worm gearbox consists of a worm (similar to a screw) that drives a worm wheel (a specialized gear). The worm is mounted on a shaft that is perpendicular to the worm wheel’s shaft. As the worm rotates, its threads engage with the teeth of the worm wheel, causing it to rotate as well.
Worm gearboxes are known for their high reduction ratios in a single stage, often ranging from 5:1 to 100:1 or more. They are also compact and can transmit high torque loads. The sliding action between the worm and worm wheel results in quiet operation but also lower efficiency compared to other gear types.
The Difference Between Helical Gearbox and Worm Gearbox
Gear Type
Helical gearboxes use helical gears with teeth cut at an angle, while worm gearboxes use a worm gear with a screw-like design to drive a worm wheel.
Shaft Orientation
In helical gearboxes, the input and output shafts are typically parallel to each other. The angled teeth of the helical gears allow for power transmission between parallel shafts.
Worm gearboxes have perpendicular input and output shafts, with the worm mounted on one shaft and the worm wheel on the other.
Reduction Ratio
Worm gearboxes can achieve higher reduction ratios in a single stage compared to helical gearboxes. Worm gears typically provide ratios from 5:1 to 100:1, while helical gears offer ratios up to 10:1 per stage.
Efficiency
Helical gearboxes have higher efficiency, often exceeding 90%, due to the gradual engagement of the helical teeth. Worm gearboxes have lower efficiency, typically ranging from 40% to 85%, because of the sliding contact between the worm and worm wheel.
Load Capacity
Helical gearboxes can handle higher loads compared to worm gearboxes of similar size. The overlapping tooth contact in helical gears distributes the load more effectively.
Noise Level
Helical gearboxes operate with lower noise levels due to the gradual engagement of the helical teeth. Worm gearboxes tend to be quieter than spur gears but may produce more noise than helical gears.
Self-Locking
Worm gearboxes have an inherent self-locking capability. The sliding action between the worm and worm wheel creates friction that prevents the gearbox from being back-driven by the load.
Helical gearboxes do not have inherent self-locking properties.
Axial Thrust
Helical gears generate axial thrust loads due to the angled teeth. These thrust loads act parallel to the gear shaft and must be accommodated by thrust bearings or other means of axial load support.
Worm gearboxes do not generate significant axial thrust loads because the worm and worm wheel are perpendicular to each other.
Backdriving
Helical gearboxes can be back-driven, meaning the output shaft can drive the input shaft if an external force is applied.
Worm gearboxes, due to their self-locking nature, cannot be easily back-driven. The high friction between the worm and worm wheel prevents reverse motion under normal operating conditions.
Cost
The manufacturing cost of helical gears is generally lower compared to worm gears of similar quality. Worm gears require more complex machining and heat treatment processes, resulting in higher production costs.
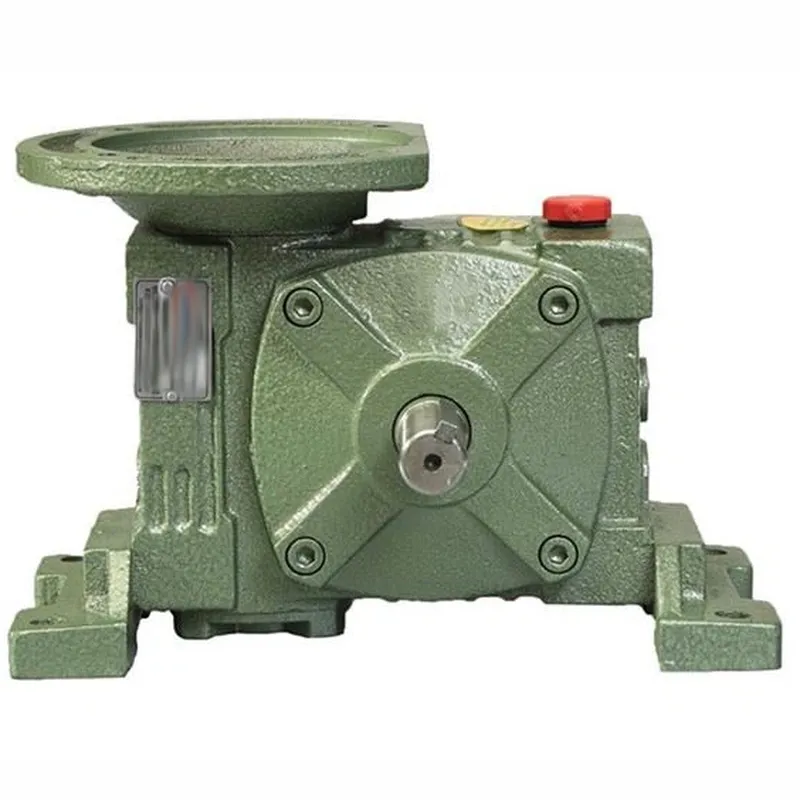 |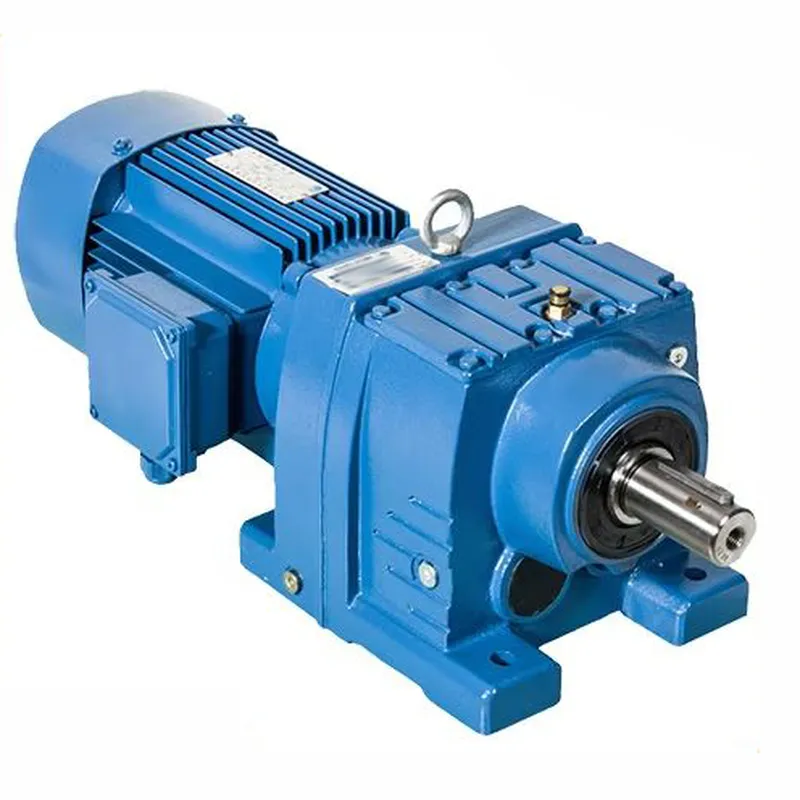  |
| Worm Gearbox | Helical Gearbox |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|





