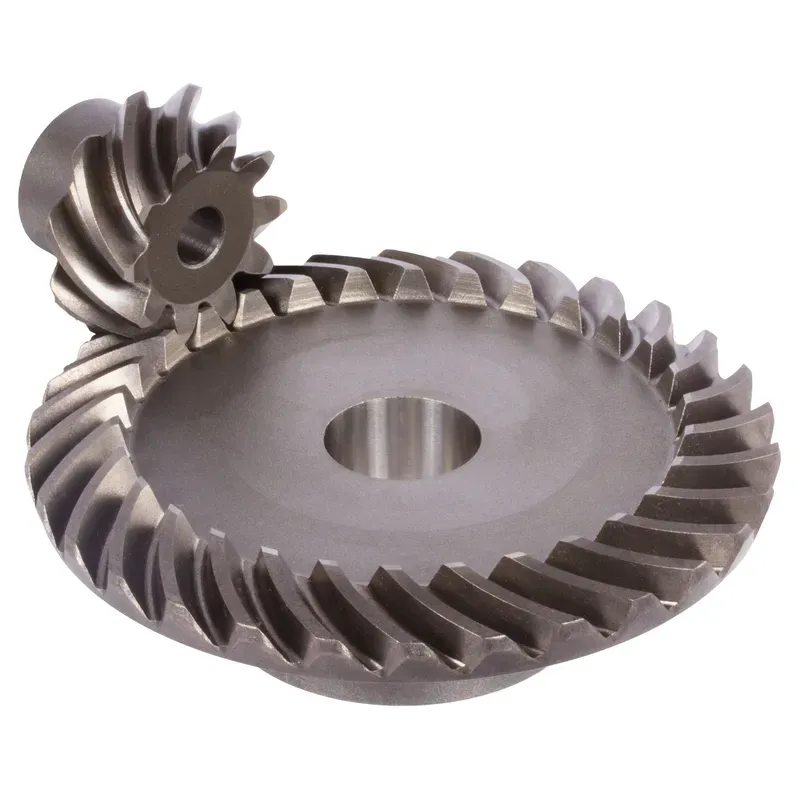
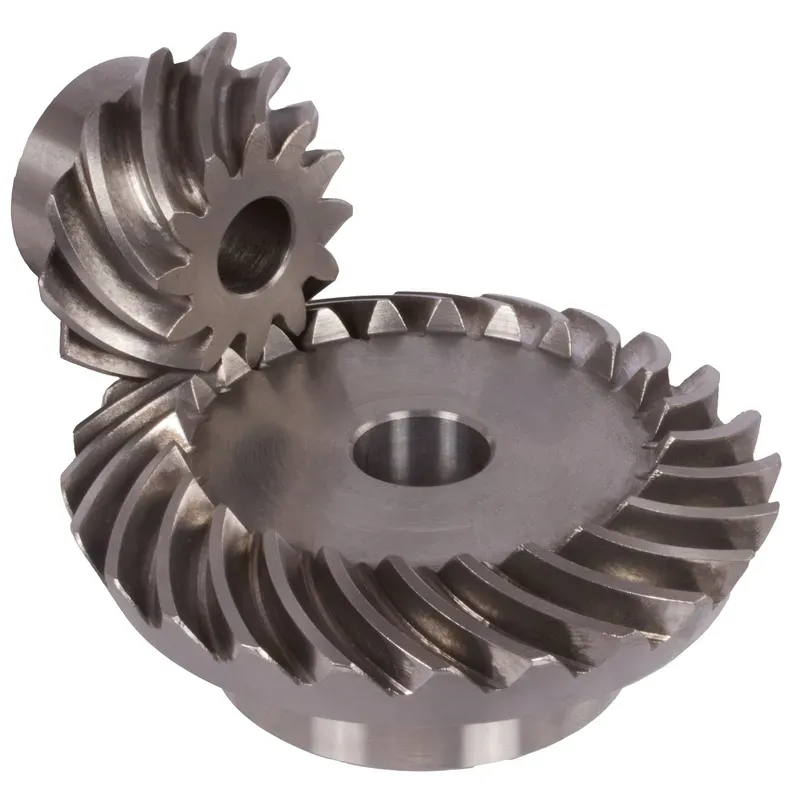
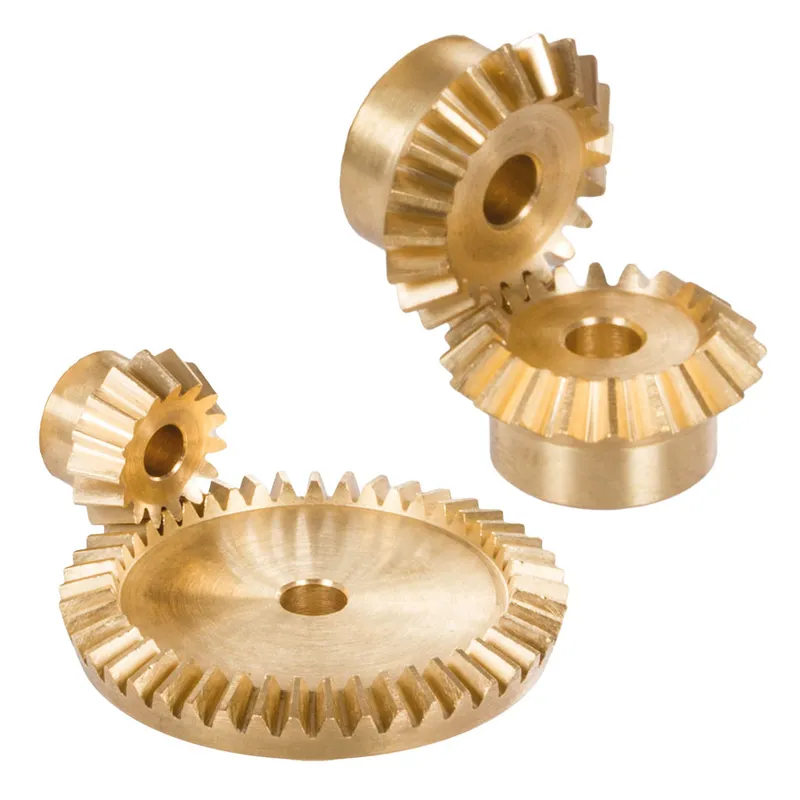
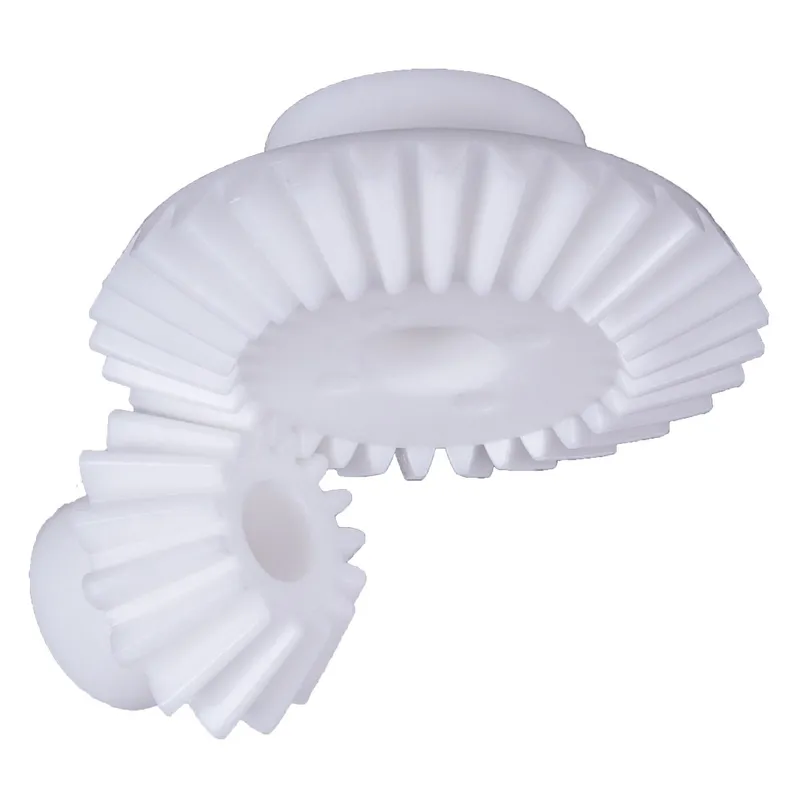
Polyacetal Resin Plastic Bevel Gear Ratio 5:1 Straight Tooth System
A polyacetal resin plastic bevel gear (ratio 5:1, straight tooth system) is a type of mechanical gear designed to transmit motion and power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, in a compact and efficient manner. It is made of polyacetal resin, a thermoplastic known for its high strength, low friction, wear resistance, and excellent dimensional stability. This material makes the gear lightweight, durable, and capable of operating smoothly in high-precision applications.
A polyacetal resin plastic bevel gear (ratio 5:1, straight tooth system) is a type of mechanical gear designed to transmit motion and power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle, in a compact and efficient manner. It is made of polyacetal resin, a thermoplastic known for its high strength, low friction, wear resistance, and excellent dimensional stability. This material makes the gear lightweight, durable, and capable of operating smoothly in high-precision applications.
The 5:1 gear ratio indicates that for every five revolutions of the driving gear, the driven gear completes one revolution, allowing for significant torque multiplication. The straight tooth design ensures simplicity in manufacturing and reduces backlash, though it is less efficient than spiral bevel gears in handling higher loads. Common applications include robotics, conveyor systems, and lightweight machinery, where precision, durability, and cost-effectiveness are essential.
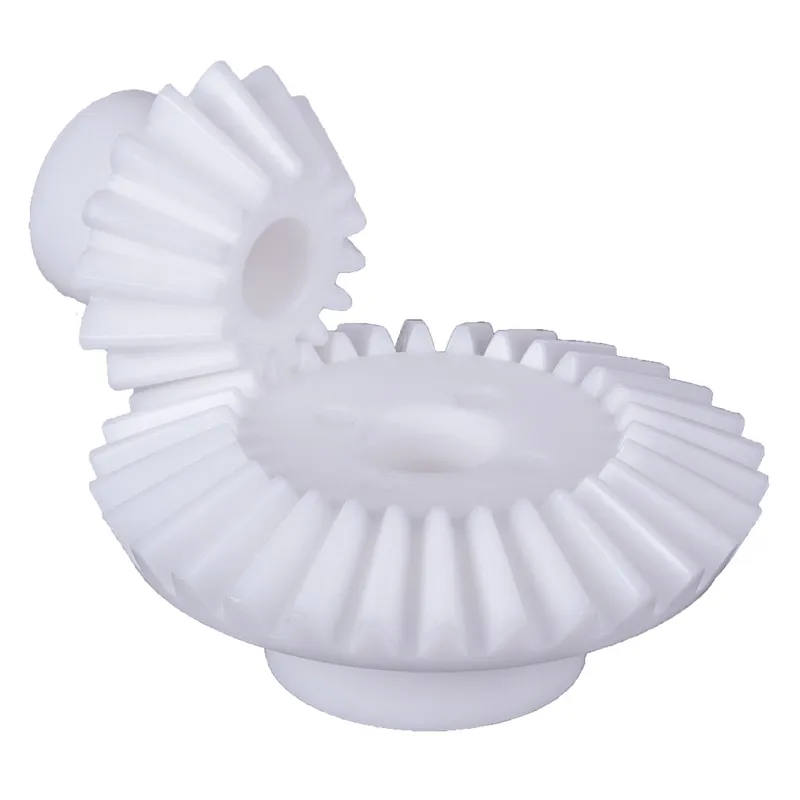

Polyacetal Resin Plastic Bevel Gear Ratio 5:1
 | 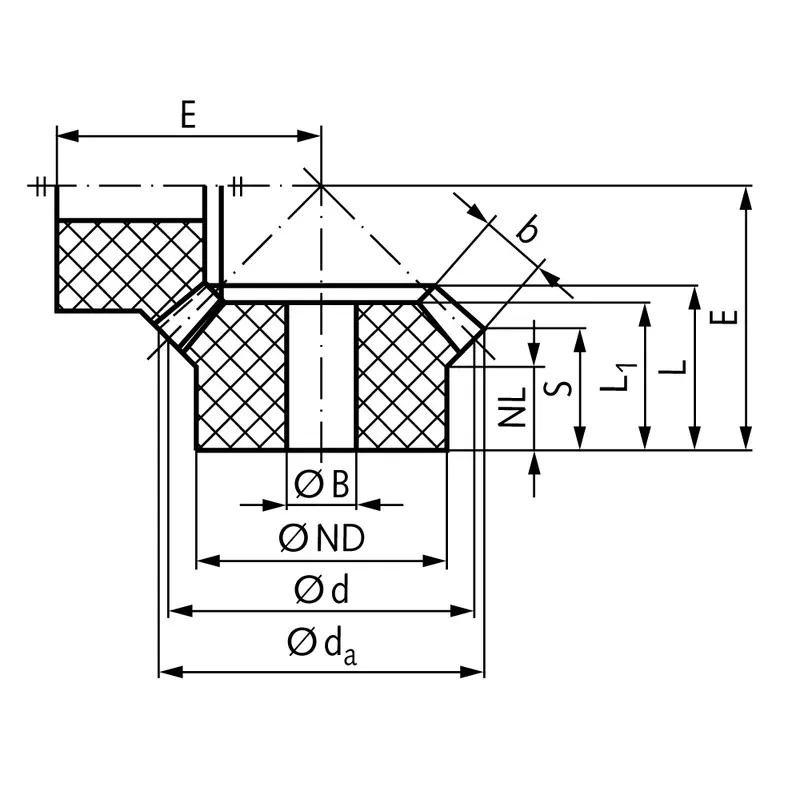 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | B | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1 | 12 | 13,7 | 12 | 9,5 | 10 | 20,3 | 20,3 | 10,5 | 9,5 | 4 | 40,5 | 12 | 1,6 |
| 1 | 60 | 60,4 | 60 | 20,5 | 11 | 15,5 | 17,4 | 15,4 | 9,5 | 10 | 21 | 60 | 20,0 |
Plastic Straight Bevel Gear Design Features
- Material Composition
Plastic straight bevel gears are typically made from engineering-grade plastics such as polyacetal (POM), nylon, or polyethylene. These materials provide excellent wear resistance, low friction, and lightweight properties. They are also corrosion-resistant and operate well in environments where metals may degrade. - Straight Tooth Geometry
The straight teeth are cut along the gear’s face at a specific angle, allowing smooth power transmission between intersecting shafts. This design is simpler and easier to manufacture compared to helical or spiral bevel gears. It is ideal for low to moderate torque applications. - Lightweight Construction
Plastic bevel gears are significantly lighter than their metal counterparts, reducing overall system weight. This feature is especially beneficial in applications like robotics, drones, or small machinery where minimizing weight is critical for performance and efficiency. - Low Noise and Vibration
The use of plastic materials helps to dampen vibrations and reduce operational noise. This makes plastic straight bevel gears an excellent choice for applications requiring quieter operations, such as medical devices, household appliances, and office equipment. - Cost-Effective Production
Manufacturing plastic bevel gears is generally less expensive due to the availability of injection molding processes. The ability to mass-produce with high precision and minimal post-machining reduces costs while maintaining dimensional accuracy and consistent performance. - Self-Lubrication Capabilities
Many plastic materials used in bevel gears have inherent self-lubricating properties, reducing the need for external lubrication. This feature enhances the gear's longevity and makes it suitable for applications requiring minimal maintenance, even under continuous use.
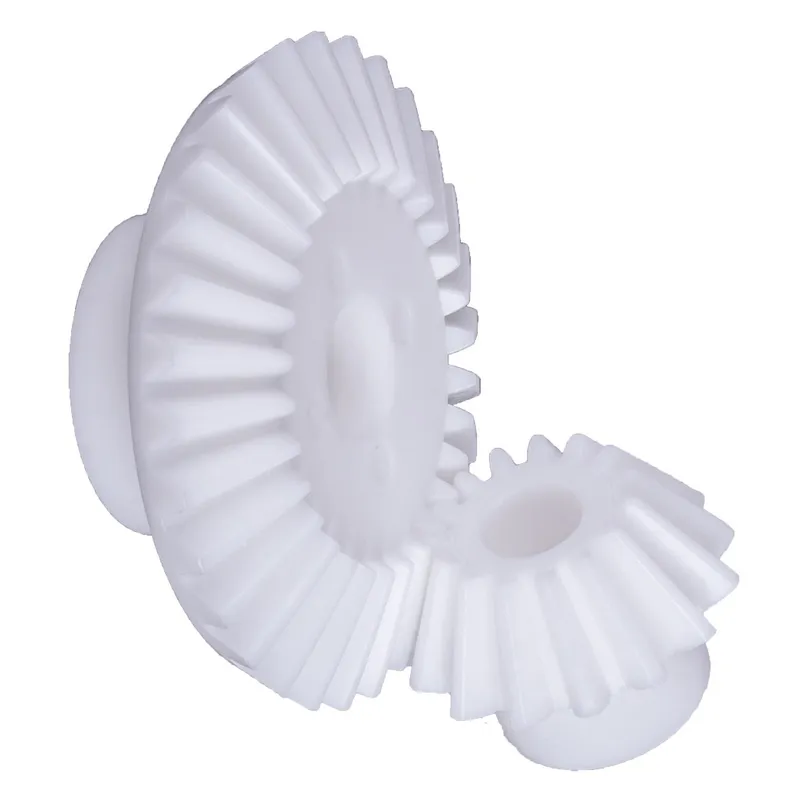

Plastic Bevel Gear Examples and Applications
- Robotics and Automation
Plastic bevel gears are widely used in robotics and automated systems due to their lightweight construction and high precision. They ensure efficient torque transmission in robotic arms, grippers, and motion control systems, providing smooth operation with minimal noise and vibration. - Medical Devices
In medical equipment such as dental tools, surgical instruments, and diagnostic machines, plastic bevel gears are preferred because of their quiet operation and resistance to corrosion. Their lightweight and low-maintenance properties make them ideal for sensitive environments requiring precision and hygiene. - Household Appliances
Common in appliances like blenders, vacuum cleaners, and washing machines, straight bevel gears ensure smooth and quiet performance. Their self-lubrication capabilities and durability make them suitable for prolonged use, reducing wear and tear in everyday consumer products. - Automotive Components
Plastic bevel gears are used in automotive systems such as windshield wipers, seat adjusters, and HVAC systems. Their lightweight nature helps improve fuel efficiency, while their corrosion resistance and low maintenance requirements enhance the longevity of internal vehicle mechanisms. - Office Equipment
In printers, copiers, and shredders, plastic bevel gears enable precise and reliable power transmission. Their ability to reduce noise and vibration makes them well-suited for office environments, where quiet operation is essential for maintaining productivity and comfort. - Aerospace and Drones
Aerospace and drone technologies benefit from plastic bevel gears due to their lightweight construction, which is critical for flight efficiency. They are used in control systems, actuators, and motor drives, ensuring reliable performance under demanding conditions with minimal added weight.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Robotics Industry | Bevel Gear for Marine Industry |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Medical Equipment | Bevel Gear for Aerospace Industry |
Plastic Straight Bevel Gear Troubleshooting
- Excessive Wear and Tear
Excessive wear can occur due to improper alignment of the gears, overloading, or inadequate material selection. To resolve this issue, ensure precise alignment during installation, avoid exceeding the recommended torque limits, and select materials suited for the operating conditions. - Gear Tooth Breakage
Tooth breakage often results from sudden impact loads, high stress, or material fatigue. Troubleshooting involves reducing abrupt torque changes, implementing load distribution measures, and choosing reinforced plastic materials or designs with thicker teeth to withstand higher stress levels. - Noise and Vibration
Increased noise and vibration may stem from poor alignment, insufficient lubrication, or worn-out teeth. To address this, check and correct the alignment, replace damaged gears, and ensure proper lubrication even if the material offers self-lubricating properties. - Heat Build-Up
Overheating in plastic bevel gears can be caused by excessive friction, overloading, or high-speed operation. Troubleshooting includes reducing the load, ensuring adequate airflow for cooling, and using heat-resistant plastic materials designed for high-temperature environments. - Slipping or Loss of Torque Transmission
Slipping occurs when the gear fails to transmit sufficient torque due to improper meshing, wear, or deformation. To fix this, inspect the gear teeth for damage, replace worn parts, and verify that the gears are tightly secured on the shafts. - Deformation or Warping
Plastic gears may deform under prolonged exposure to high temperatures, excessive load, or improper storage. Troubleshooting involves using heat-resistant materials, storing gears in controlled environments, and avoiding prolonged overloading during operation to prevent warping or bending.

Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|


