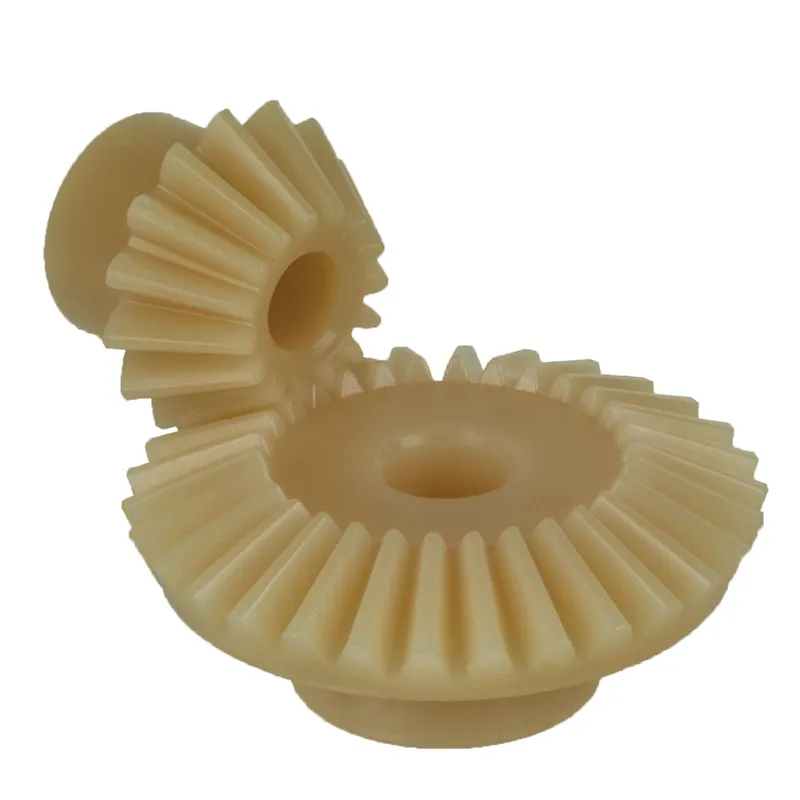
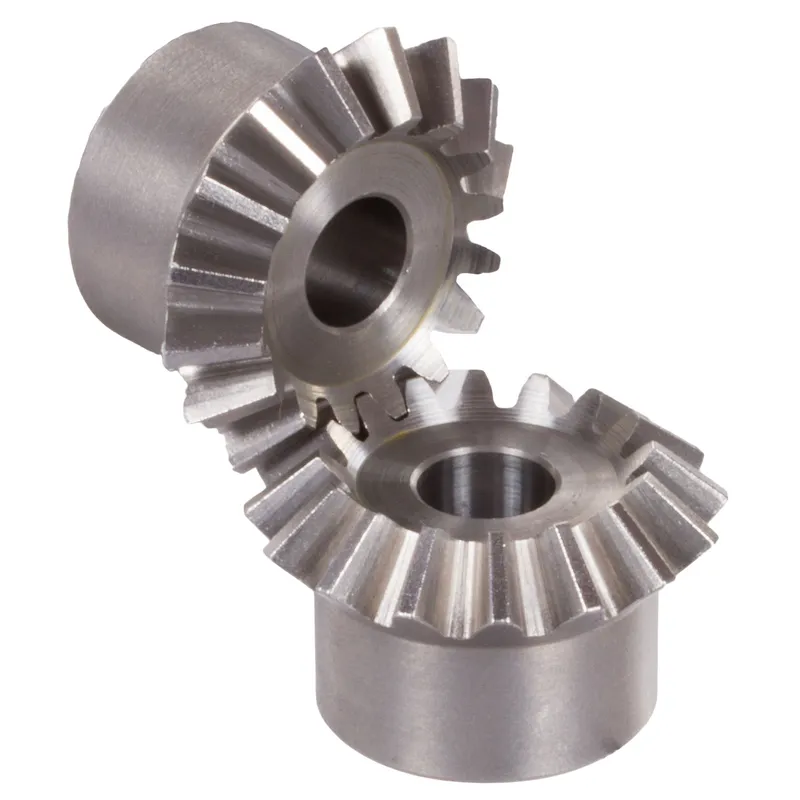
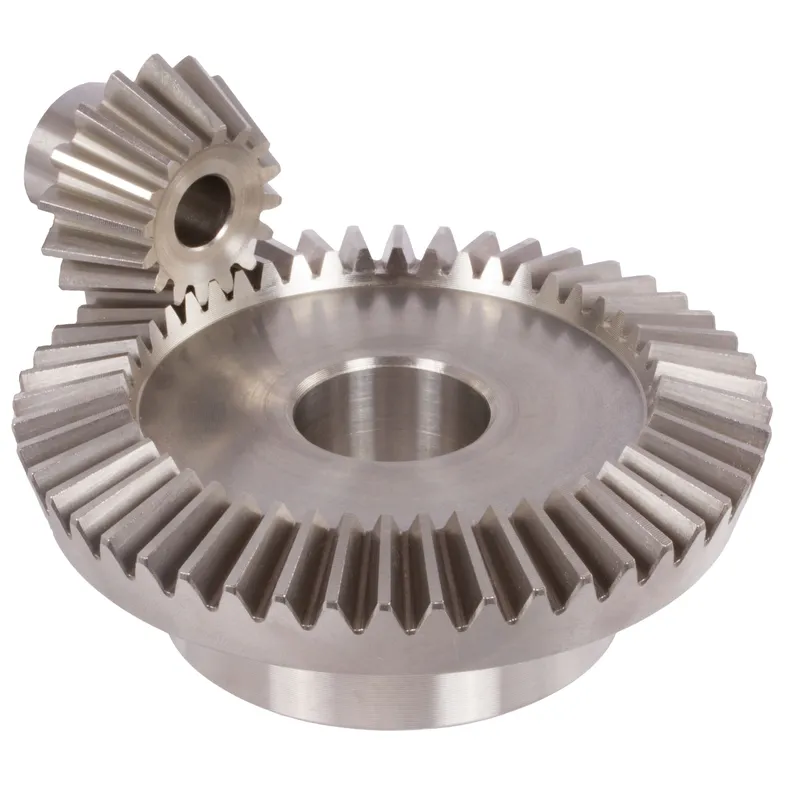
Steel Spiral Bevel Gears Ratio 1.214:1 Spiral Tooth System
A steel spiral bevel gear with a 1.214:1 ratio and spiral tooth system is a specialized type of bevel gear used in mechanical systems to transmit power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. The spiral tooth design features curved, helical teeth (usually at a 12°–20° angle), which provide smoother and quieter operation compared to straight-tooth bevel gears. This is due to the gradual engagement of the teeth, reducing vibration and noise while increasing strength and torque capacity.
A steel spiral bevel gear with a 1.214:1 ratio and spiral tooth system is a specialized type of bevel gear used in mechanical systems to transmit power between intersecting shafts, typically at a 90-degree angle. The spiral tooth design features curved, helical teeth (usually at a 12°–20° angle), which provide smoother and quieter operation compared to straight-tooth bevel gears. This is due to the gradual engagement of the teeth, reducing vibration and noise while increasing strength and torque capacity.
The 1.214:1 ratio indicates that for every 1.214 rotations of the pinion gear, the mating gear completes one rotation, enabling precise speed and torque adjustments. Typically made from high-strength carbon or alloy steels like 42CrMo4 or 16MnCr5, these spiral bevel gears are induction or case-hardened for durability and are used in applications like industrial machinery, automotive systems, and power transmission.
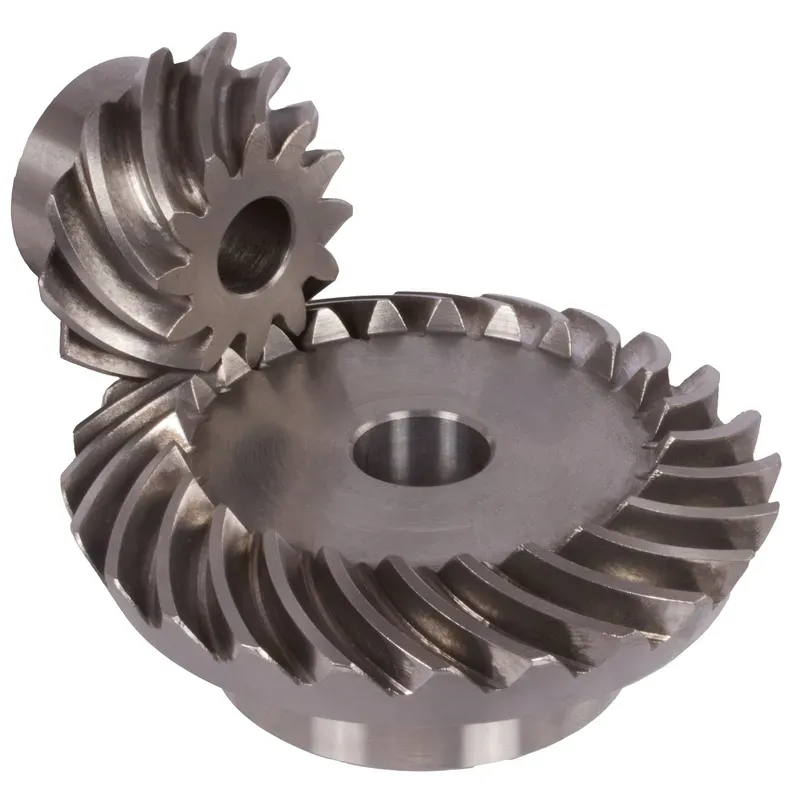

Steel Spiral Bevel Gear Ratio 1.214:1
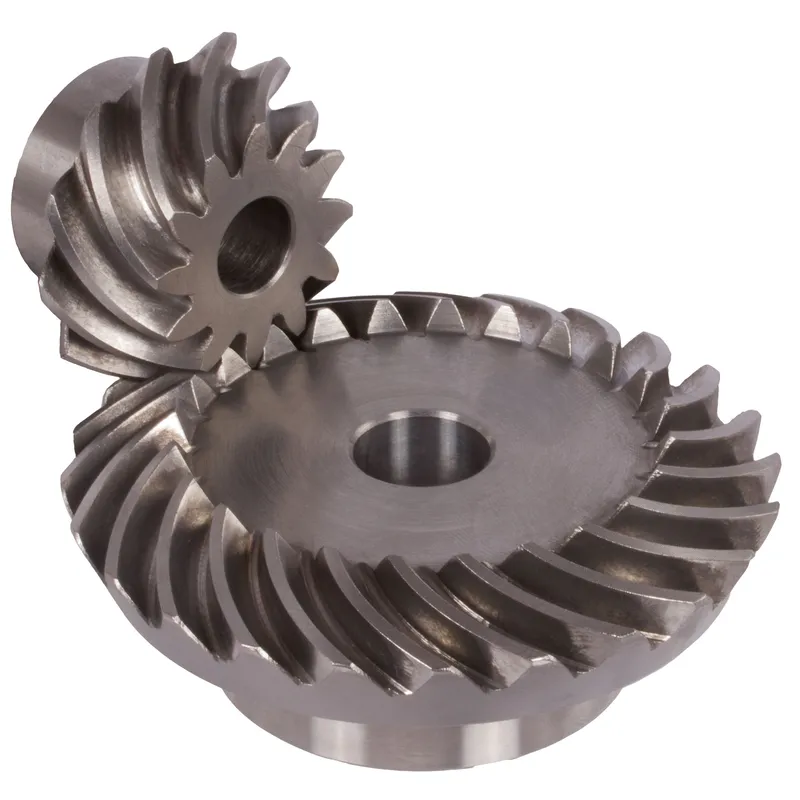 | 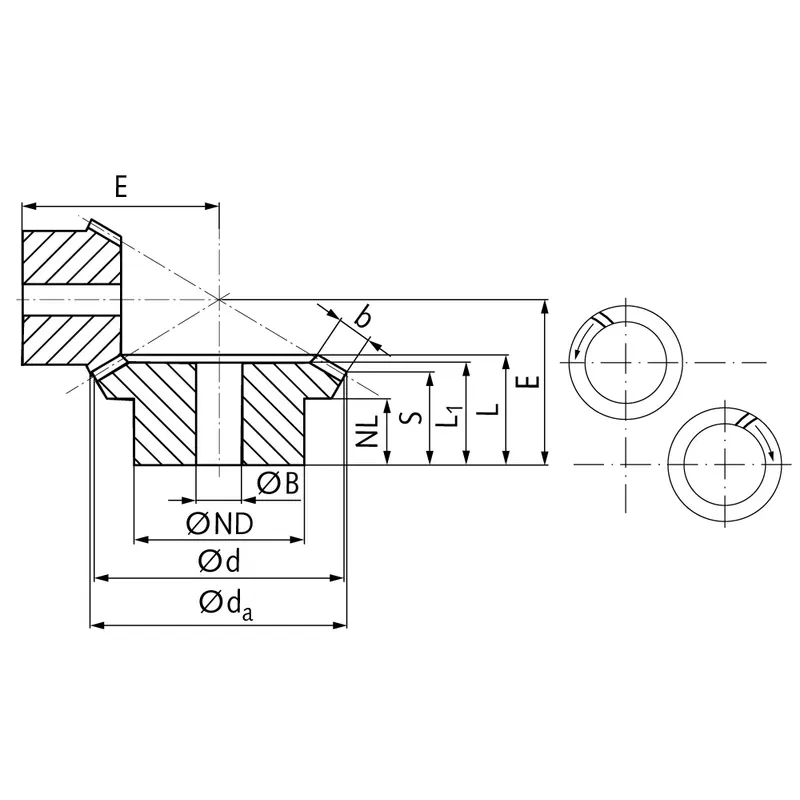 |
| Module | Number of teeth | da | d | ND | NL | L1 | L | S | b | BH7 | E | Torque* | Weight |
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ncm | g | ||
| 1,5 | 14 | 41,0 | 38,7 | 22 | 11 | 21,1 | 24,3 | 15,4 | 11,5 | 12 | 38,0 | 14,1 | 236 |
| 1,5 | 17 | 48,9 | 47,0 | 30 | 11 | 20,9 | 23,9 | 16,6 | 11,5 | 15 | 34,8 | 17,1 | 236 |
Steel Spiral Bevel Gear Benefits
- Smooth and Quiet Operation
The spiral tooth design ensures gradual engagement between teeth, which minimizes vibration and noise during operation. This makes them ideal for applications requiring precision and quiet functionality, such as automotive differentials or high-speed machinery. - Enhanced Torque Transmission
Steel spiral bevel gears are capable of transmitting higher torque due to their robust construction and optimized tooth geometry. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications where high loads and stress are regularly encountered. - Durability and Longevity
Constructed from high-quality steel, these steel bevel gears exhibit excellent wear resistance and durability. They can withstand harsh operating conditions like high temperatures, heavy loads, and continuous usage without significant degradation over time. - Efficient Power Transmission
The curved tooth design provides more surface contact between meshing teeth, which reduces power loss and enhances efficiency. This ensures energy is transmitted effectively with minimal heat generation or wasted movement. - Compact Design for Space-Saving
Steel spiral bevel gears can deliver high performance in a relatively compact form factor. This allows them to be used in machines where space is limited, improving the overall design and functionality of the system. - Versatility Across Applications
These gears are versatile and can be tailored to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Their ability to handle diverse torque and speed requirements makes them a preferred choice for engineers and manufacturers.
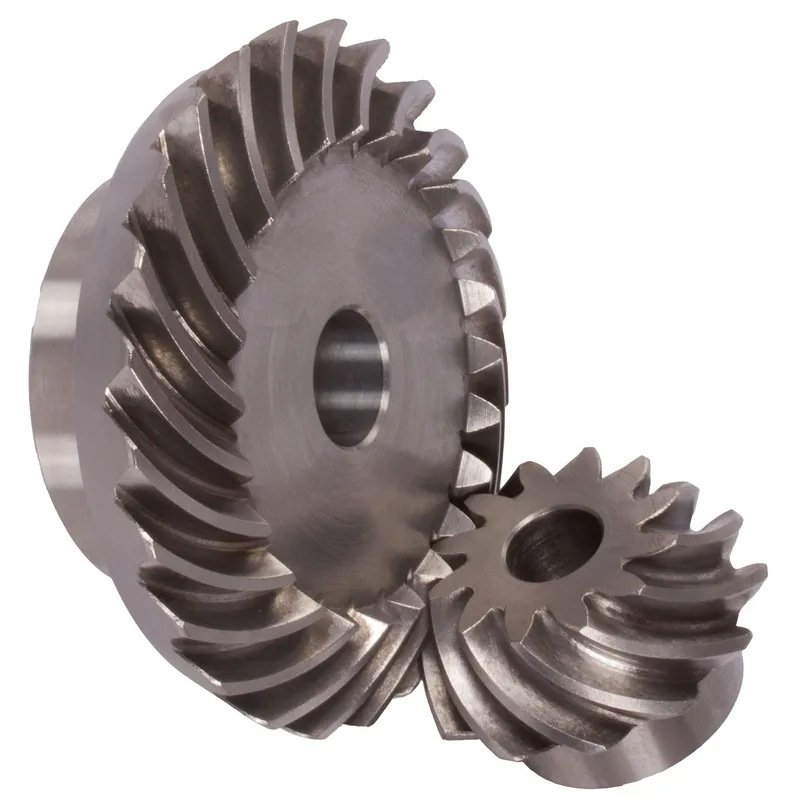 Spiral Bevel Gear vs. Hypoid Gear
Spiral Bevel Gear vs. Hypoid Gear
A spiral bevel gear is a type of bevel gear with teeth that are curved and set at an angle, forming a spiral pattern along the gear’s conical surface. This design allows for smoother and quieter operation, as well as increased tooth contact, resulting in higher load-carrying capacity compared to straight bevel gears. Spiral bevel gears are commonly used in applications that require power transmission between intersecting shafts, such as in automotive differentials, industrial machinery, and aerospace systems.
A hypoid gear is a specialized type of spiral bevel gear with an offset pinion axis. The pinion is positioned below the center of the ring gear, creating a hyperbolic geometry. This unique design enables hypoid gears to handle higher torque and operate more quietly than traditional spiral bevel gears. Hypoid gears are frequently employed in automotive rear axle differentials, where they provide smooth power transmission and allow for greater ground clearance due to the lowered pinion position.
Difference Between Spiral Bevel and Hypoid Gear
Axis Intersection
In spiral bevel gears, the axes of the pinion and gear intersect at a common point, forming an intersection angle typically around 90 degrees.
Conversely, hypoid gears feature axes that do not intersect at a single point. Instead, the pinion axis is offset from the gear axis, resulting in a “hypoid offset” that allows for more flexibility in positioning the gears.
Shape
Spiral bevel gears have teeth that are curved and oblique, forming a spiral or helical pattern around the cone-shaped gear blank. This spiral tooth geometry provides smooth, gradual engagement between the mating gears.
Hypoid gears have teeth that are curved and oblique but also skewed, meaning they are not symmetrical about the gear axis. This skewed tooth geometry is a result of the hypoid offset and allows for a larger contact area between the mating gears.

Tooth Geometry
Spiral bevel gears have teeth with a constant spiral angle and uniform depth along the face width. This geometry results in a line contact between the mating teeth, which helps distribute the load evenly.
Hypoid gears have teeth with a variable spiral angle and non-uniform depth along the face width. This complex tooth geometry creates a combination of sliding and rolling contact between the mating teeth, which increases the contact ratio and load-carrying capacity.
Pinion Size and Contact Area
In spiral bevel gears, the pinion and gear are typically of similar size, resulting in a relatively small contact area between the mating teeth.
Hypoid gears often feature a smaller pinion with a larger number of teeth compared to the gear. This design, combined with the skewed tooth geometry, allows for a larger contact area between the mating teeth, which improves load distribution and reduces contact stresses.
Torque Capacity
Due to their larger contact area and improved load distribution, hypoid gears generally have a higher torque capacity compared to spiral bevel gears of similar size. The sliding and rolling contact between the hypoid gear teeth also contributes to their ability to handle higher torque loads without excessive wear or fatigue.
Spiral bevel gears, while still capable of transmitting significant torque, may be more limited in their capacity due to the smaller contact area and purely rolling contact between the teeth.
Efficiency
Spiral bevel gears typically have higher efficiency than hypoid gears due to their rolling contact and lower sliding velocities between the mating teeth. This reduced sliding friction results in less heat generation and power loss.
Hypoid gears, with their sliding and rolling contact, tend to have lower efficiency due to increased friction and heat generation.
Noise
Spiral bevel gears generally produce less noise than hypoid gears due to their uniform tooth contact and purely rolling motion. The gradual engagement of the spiral bevel gear teeth helps reduce vibration and noise.
Hypoid gears, with their sliding and rolling contact, can generate more noise, especially at high speeds or under heavy loads. The increased sliding velocities between the hypoid gear teeth can lead to greater vibration and noise.
Offset
The offset between the pinion and gear axes is a defining characteristic of hypoid gears. This offset, known as the hypoid offset, allows for greater flexibility in positioning the gears and can provide several benefits. This offset also allows for a larger pinion with more teeth, which increases the contact ratio and load-carrying capacity. Additionally, the hypoid offset can be used to optimize the tooth contact pattern and reduce the risk of edge loading or uneven wear.
Spiral bevel gears, in contrast, do not have this offset, as their axes intersect at a common point.
Applications
Spiral bevel gears are commonly used in applications where high efficiency, low noise, and moderate torque capacity are prioritized. They are often found in industrial machinery, power transmission systems, and aerospace applications.
Hypoid gears, with their higher torque capacity, compact design, and offset flexibility, are widely used in automotive and heavy-duty applications. Rear axle drives in vehicles, industrial gearboxes, and marine propulsion systems often employ hypoid gears to transmit power between nonparallel shafts while accommodating space constraints and high torque demands.

Steel Spiral Bevel Gear Purpose
1. Automotive Industry
In the realm of automobiles, spiral bevel gears are pivotal in the differential system, ensuring drive wheels can rotate at different speeds during turns. Their smooth meshing attributes make them ideal for quieter operations. Additionally, they're incorporated in specific transmission setups and are fundamental in 4WD vehicles, facilitating balanced power distribution to both front and rear axles.
2. Industrial Equipment
Industrial machinery, especially those requiring power to be transferred at right angles, heavily relies on spiral bevel gears. They're a common sight in power tools like drills, where direction change is essential, and in conveyor systems, ensuring materials move smoothly across different levels.
3. Marine Industry
Marine vessels utilize spiral bevel gears in their propulsion mechanisms, transferring power efficiently from engines to propellers. Their precision also finds use in advanced navigation systems, allowing for accurate steering and movement in the vast marine environment.
4. Robotics and Automation
In robotics and automated systems, spiral bevel gears are used for precise motion control and efficient power transmission. Their smooth, quiet operation and ability to work in compact spaces make them ideal for advanced robotic arms and automated production systems.
5. Aerospace Engineering
In aerospace systems, these gears are used in applications such as helicopter rotor transmissions and aircraft engines. Their precision, lightweight design, and ability to operate under extreme conditions ensure reliability and safety in demanding environments with strict performance requirements.
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Automotive Industry | Bevel Gear for Industrial Equipments |
 |  |
| Bevel Gear for Marine Industry | Bevel Gear for Robotics |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|


