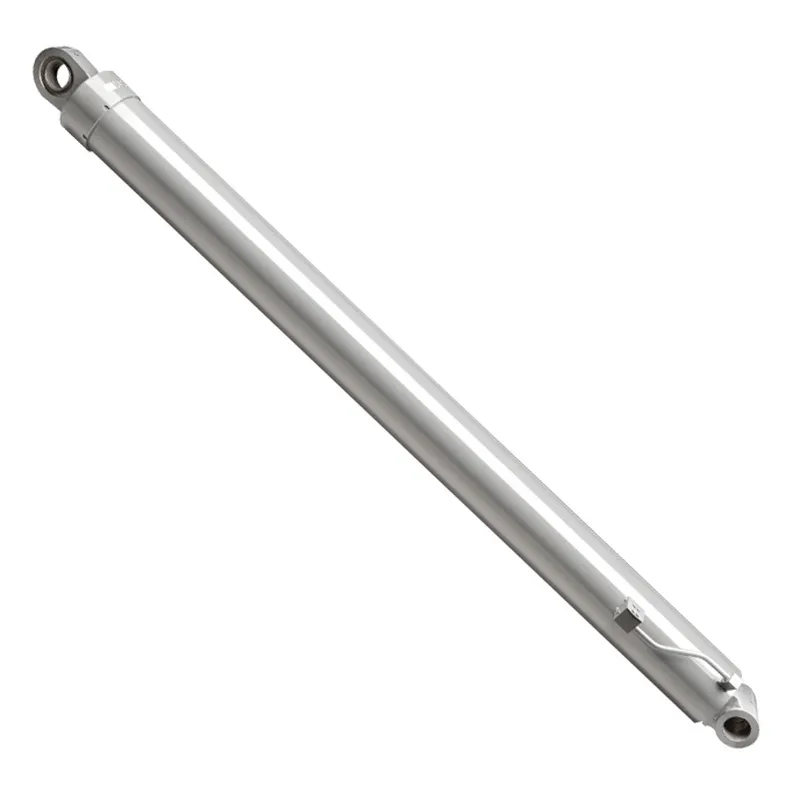
Luffing Hydraulic Cylinder for Truck Crane
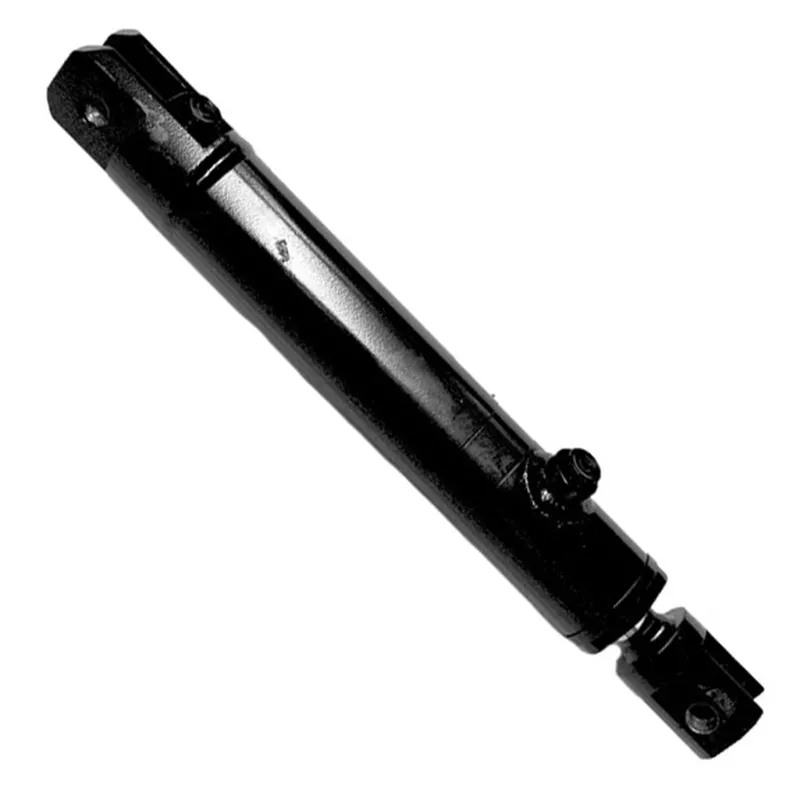
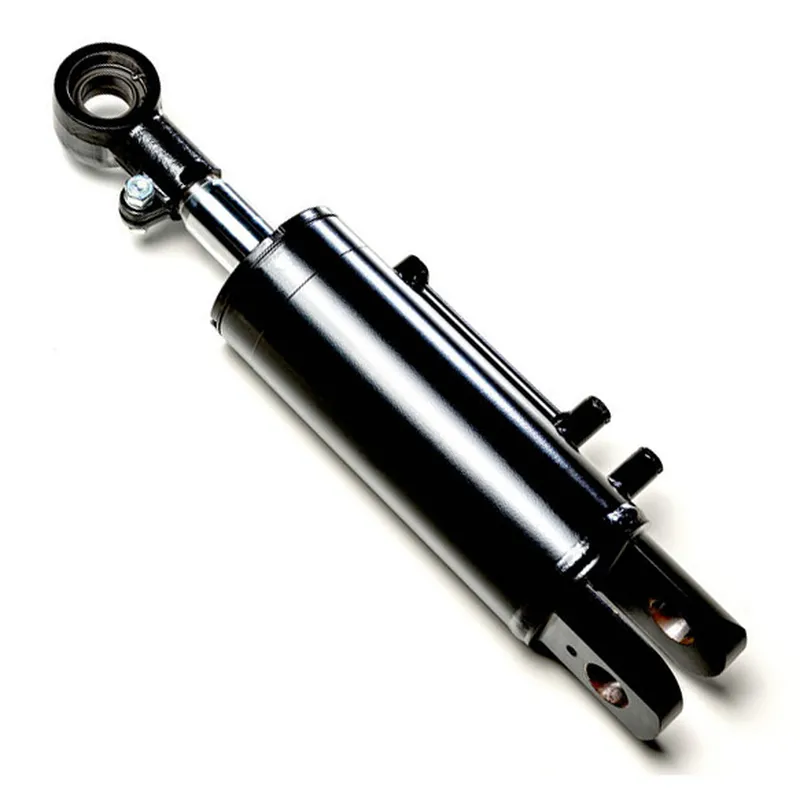
A luffing hydraulic cylinder for a truck crane is a specialized hydraulic component designed to control the vertical movement (luffing) of the crane’s boom or jib, enabling precise lifting and lowering of loads. Mounted between the crane’s main structure and the boom, it uses hydraulic pressure to drive a piston, which extends or retracts to adjust the boom’s tilt angle. This allows the crane to adapt to various lifting heights and navigate confined spaces or obstacles, critical for truck-mounted cranes in construction, shipbuilding, or material handling.
A luffing hydraulic cylinder for a truck crane is a specialized hydraulic component designed to control the vertical movement (luffing) of the crane’s boom or jib, enabling precise lifting and lowering of loads. Mounted between the crane’s main structure and the boom, it uses hydraulic pressure to drive a piston, which extends or retracts to adjust the boom’s tilt angle. This allows the crane to adapt to various lifting heights and navigate confined spaces or obstacles, critical for truck-mounted cranes in construction, shipbuilding, or material handling.
Engineered for high-pressure conditions, these hydraulic luffing cylinders feature robust materials like chrome-plated steel pistons, imported seals, and high-strength alloys to ensure durability and reliability. Advanced designs incorporate special steering structures and precision manufacturing to handle unbalanced loads, ensuring safety and efficiency.

Luffing Hydraulic Cylinder Dimensions
 |
|
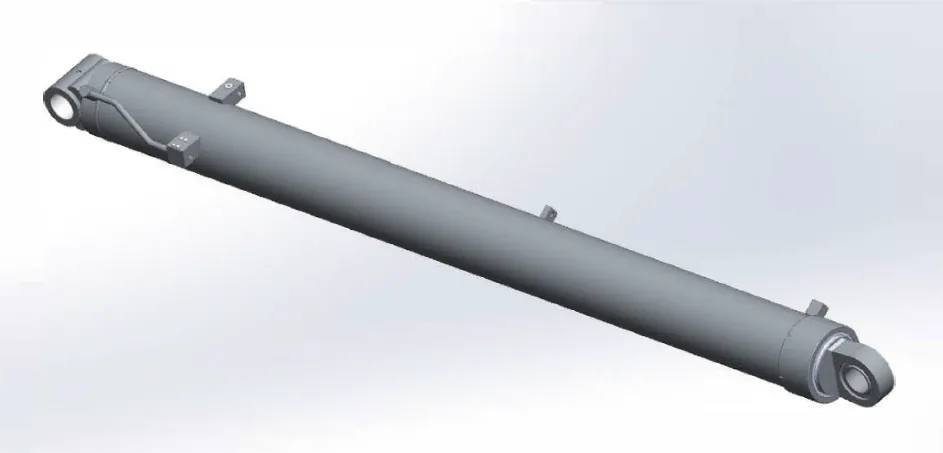 |
 |
| Hydraulic Luffing Cylinder | ||||||
| Cylinder model | Specifications | Working pressure | Maximum withstand pressure | Trip | Installation distance | Weight |
| CMNYY11112021 | Φ280xΦ250x3507 | 31.5MPa | 39MPa | 3507 | 4218 | 1155kg |
| Product Name: | Luffing Hydraulic Cylinder |
| Function: | Control the movement of the main arm. |
| Cylinder diameter: | 180mm-220mm |
| Rod diameter: | 110mm-180mm |
| Travel: | 1000mm-200mm |
| Maximum pressure: | 25MPa |
| Maximum thrust: | 950KN |
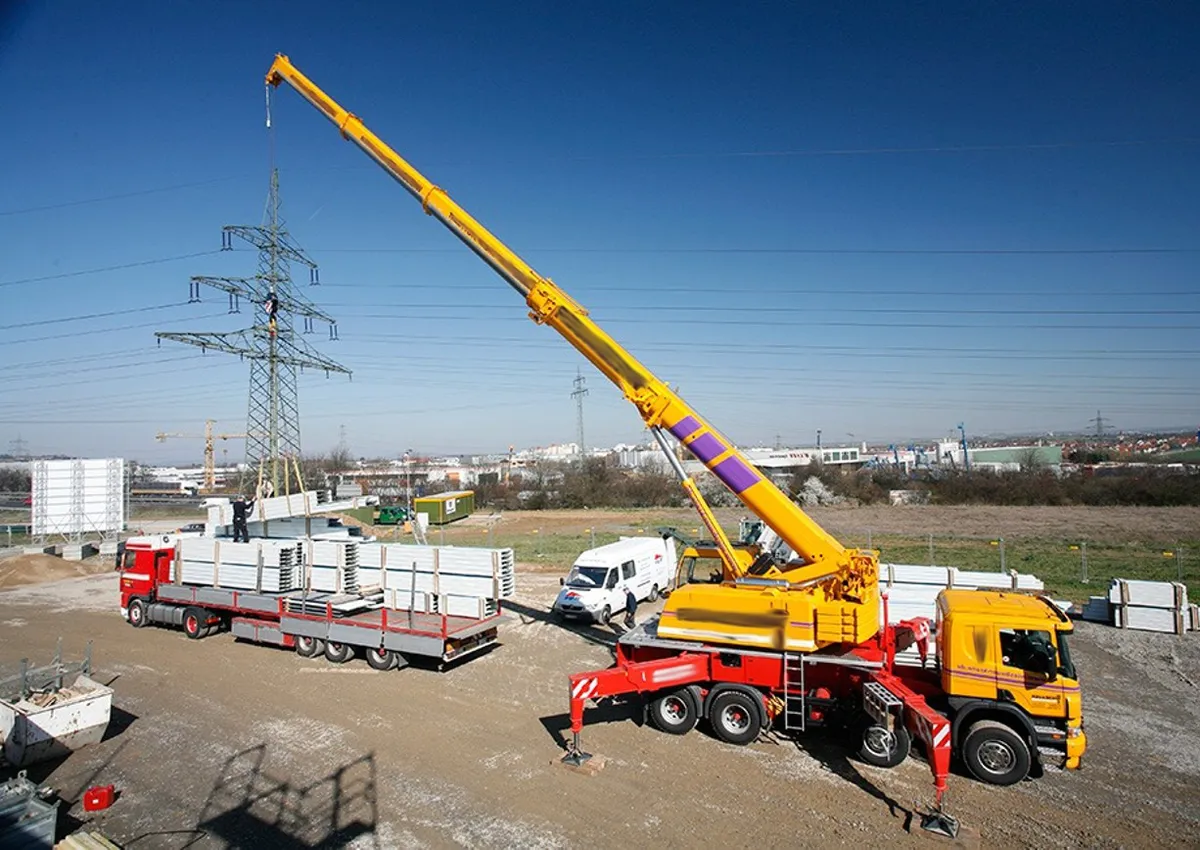
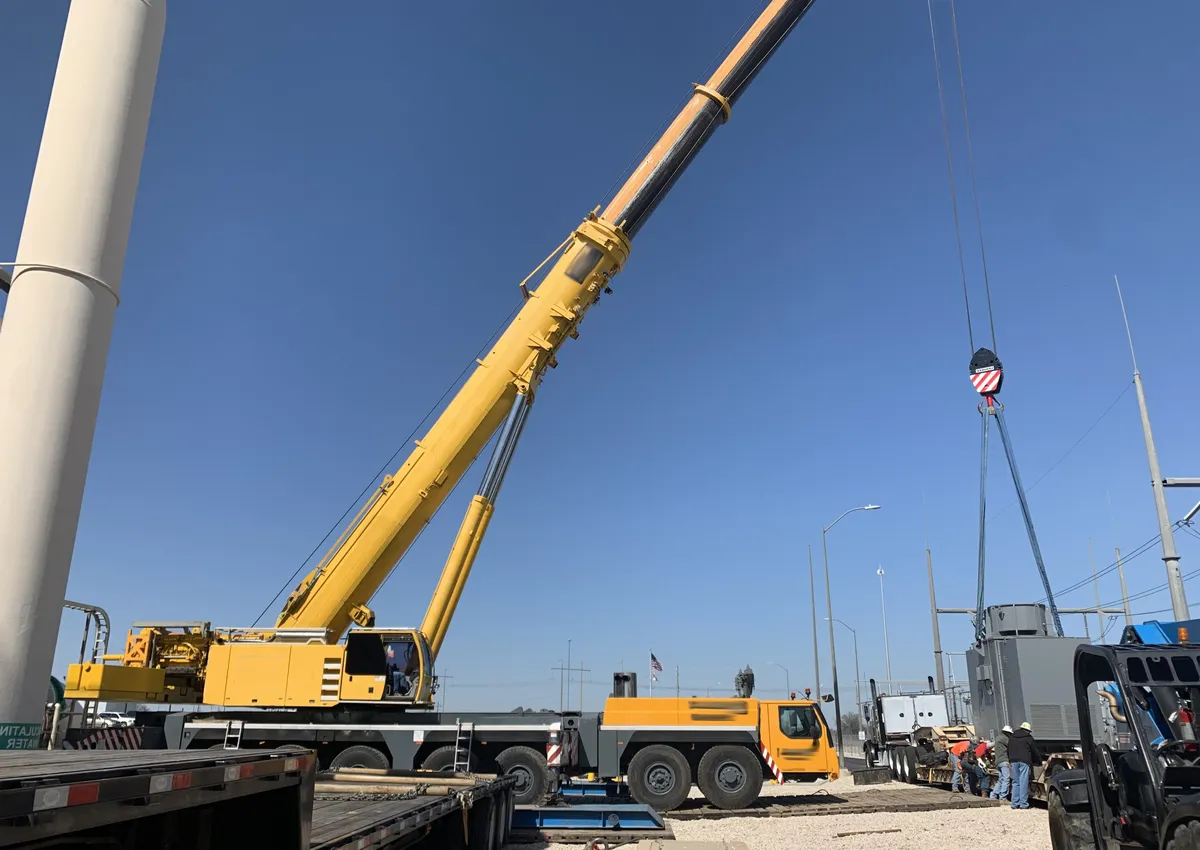
Truck Crane Hydraulic Cylinder Types
- Hydraulic Counterweight Cylinders
These cylinders are used to adjust and stabilize the counterweight system of the truck crane. They precisely position the counterweight to balance the crane during heavy lifting operations. By altering the counterweight location, they enhance overall stability and prevent tipping. Built to handle significant forces, these cylinders ensure safe and efficient crane operation, especially when lifting heavy or uneven loads. - Hydraulic Luffing Cylinders
Hydraulic luffing cylinders control the angular movement of the crane’s boom, allowing it to move up or down. This adjustment is essential for positioning the load accurately and adapting to different working scenarios. These cylinders are designed to provide smooth and controlled motion, ensuring stability during lifting. Their robust structure allows them to withstand the pressure and stress of frequent operation under heavy loads. - Hydraulic Horizontal Cylinders
These cylinders are responsible for extending or retracting components of the crane horizontally, such as sections of a telescopic boom. They enable the crane to reach specific locations with precision and efficiency. By providing controlled horizontal movement, they improve the crane’s versatility in confined or complex environments. Their durability ensures consistent performance during operations that require frequent adjustments. - Hydraulic Support Leg Cylinders
Hydraulic support leg cylinders stabilize the crane by extending and retracting its outriggers or support legs. They create a stable base by distributing the crane’s load evenly across the ground. These cylinders are critical during lifting operations to prevent tipping and ensure safety. Built with high-strength materials, they provide reliable performance on various terrains and under varying load conditions.

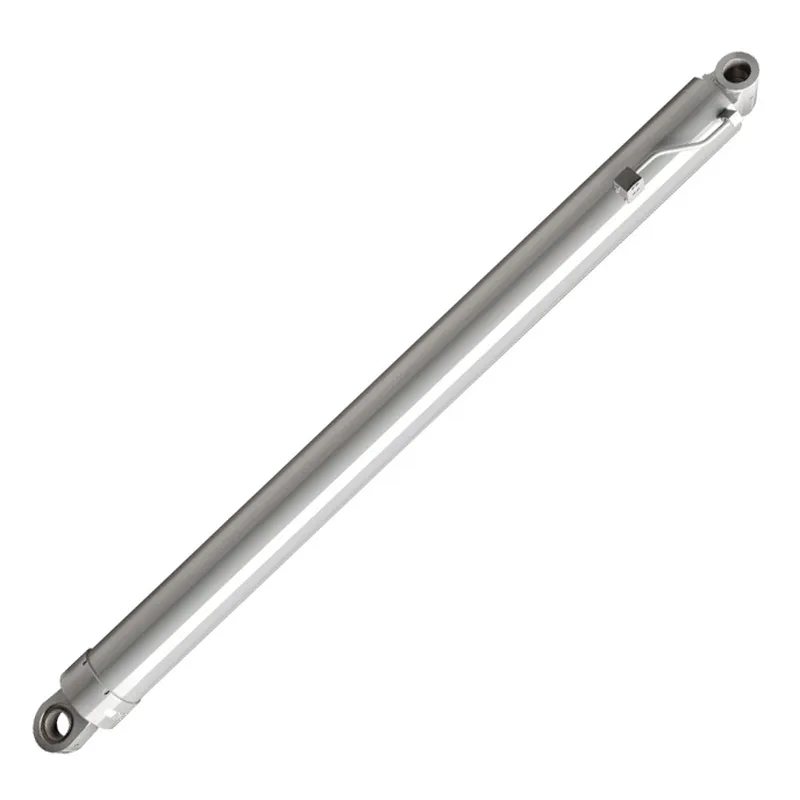
Truck Crane Luffing Hydraulic Cylinder Parts
- Cylinder Barrel
The hydraulic cylinder barrel is the main body of the luffing hydraulic cylinder, housing the piston and hydraulic fluid. It is constructed from high-strength materials like steel to withstand immense pressure and prolonged stress. Its interior is precision-machined to ensure smooth piston movement and prevent fluid leaks, which are critical for maintaining consistent performance and durability during heavy lifting tasks. - Piston
The hydraulic cylinder piston is a key internal component that moves within the cylinder barrel to create the force required for luffing. It separates the hydraulic fluid chambers and converts hydraulic pressure into mechanical motion. The piston is engineered with tight tolerances and is often coated with wear-resistant materials to ensure longevity and efficient operation under demanding conditions. - Piston Rod
The hydraulic cylinder piston rod connects the piston to the external parts of the crane, transmitting the force generated by hydraulic pressure to move the boom. It is typically made from hardened steel to resist bending, corrosion, and wear. The rod is also polished to reduce friction, ensuring smooth and consistent movement even under high loads and frequent use. - Seals and Gaskets
Hydraulic cylinder seals and gaskets are critical for preventing hydraulic fluid leakage and maintaining pressure within the cylinder. They are placed around the piston, rod, and barrel joints to ensure a tight seal. Made from durable and heat-resistant materials, these components protect the cylinder from contamination and ensure reliable performance in various weather and operational conditions. - End Caps
Hydraulic cylinder end caps enclose the hydraulic cylinder and provide structural integrity to the assembly. They are located at both ends of the cylinder barrel and serve as mounting points for the cylinder within the crane system. These caps are engineered to handle the immense pressure generated during operation, ensuring stability and preventing deformation under heavy loads. - Hydraulic Ports
Hydraulic cylinder ports are openings in the cylinder where hydraulic fluid enters and exits to generate the necessary pressure for movement. These ports are designed to accommodate high-pressure hoses and ensure a secure connection. Properly machined and reinforced, they allow for efficient fluid flow, helping the cylinder deliver precise and responsive performance during luffing operations.

Choose the Right Hydraulic Luffing Cylinder for Truck Crane
- Bore Diameter:
The bore diameter directly affects the hydraulic cylinder's lifting capacity and force. A larger bore diameter allows the cylinder to generate more force by accommodating a greater volume of hydraulic fluid. When choosing a luffing cylinder, ensure the bore diameter matches the load requirements of the truck crane. Improper sizing may lead to insufficient lifting power or excessive strain on the cylinder during operation. - Rod Diameter:
The rod diameter determines the cylinder's ability to withstand bending and buckling under heavy loads. A thicker rod provides greater structural strength, making it suitable for demanding applications. Selecting a rod diameter that matches the crane’s operational requirements ensures durability and prevents premature wear or damage. This is especially important for cranes operating in rugged or high-load environments. - Working Pressure:
The working pressure of the hydraulic cylinder must align with the hydraulic system of the truck crane. It measures the maximum pressure the cylinder can handle during operation without failure. Choosing a cylinder with a compatible working pressure ensures efficient performance and prevents system overloads. Always consider safety margins to account for pressure spikes during heavy lifting tasks. - Installation Distance:
Installation distance refers to the mounting length of the cylinder when fully retracted. Ensuring the correct installation distance is important for proper fitting and alignment with the crane’s structure. If the cylinder is too short or too long, it may hinder the movement of the boom, reduce operational efficiency, or cause mechanical interference during use. Accurate measurements are critical for seamless integration. - Stroke Length:
The stroke length defines the range of movement the hydraulic cylinder can achieve. It determines how far the crane’s boom can move up or down during luffing operations. Selecting the appropriate stroke length ensures the cylinder can meet the crane’s operational requirements without overextending or limiting its functionality. A mismatch in stroke length can lead to restricted movement or mechanical failure. - Thrust Force:
The thrust force is the amount of force the cylinder can generate to lift or move the boom. It is determined by the bore diameter, working pressure, and hydraulic fluid capacity. Choosing a cylinder with sufficient thrust force is essential for handling the crane’s maximum load capacity. Insufficient thrust force can result in inefficient lifting, reduced performance, and potential safety hazards.
 |
 |
Additional information
| Edited by | Yjx |
|---|




